Time Perception Deficits in Children and Adolescents with ADHD: A Meta-analysis
Understanding Time Perception in ADHD
Que Zheng, Xinyue Wang, Ka Yu Chiu, Kathy Kar-Man Shum
Objectives
The study aims to explore inconsistencies in previous research regarding time perception impairments in children and adolescents with ADHD. These past studies have shown varied results, and the current research seeks to provide a clearer understanding of this aspect of ADHD.
Prior studies have reported time perception impairment in children and adolescents with ADHD but the results were inconsistent.
Methods
The method adopted for this investigation was a meta-analysis of 27 empirical studies. This analysis focuses on comparing time perception abilities between children and adolescents diagnosed with ADHD and those without.
The current meta-analysis reviews 27 empirical studies published in English after year 2000 that compared time perception competence among children and adolescents with and without ADHD.
Results
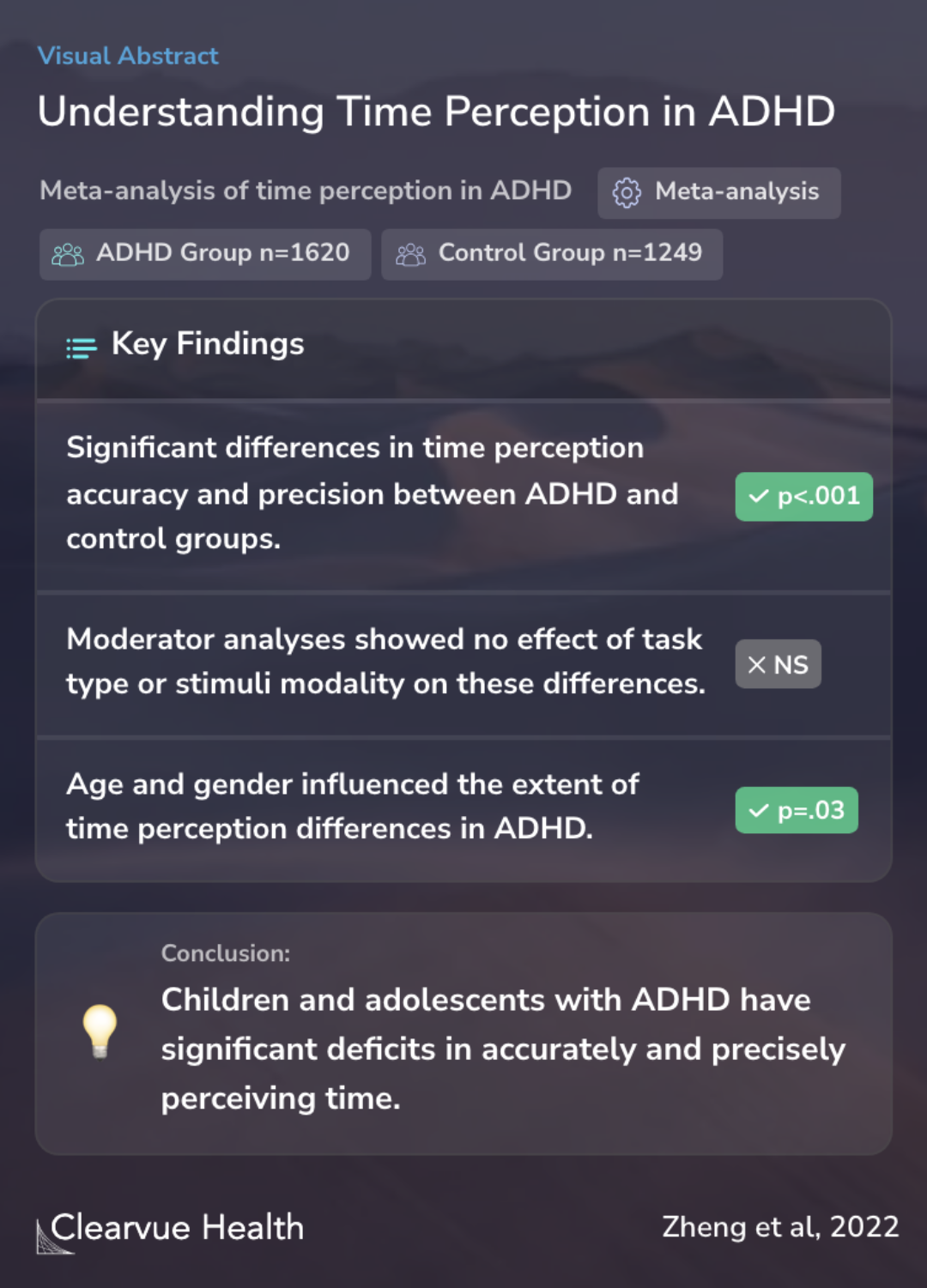
The results of this meta-analysis, involving 1620 participants with ADHD and 1249 healthy controls, revealed significant time perception deficits in those with ADHD. Children and adolescents with this condition were found to have less accuracy and precision in perceiving time, often overestimating it compared to their healthy peers. The study also noted that these differences were not influenced by the type of timing tasks or the stimuli modality used in the tasks. However, age and gender played a role in the extent of these time perception differences.
Results from 1620 participants with ADHD and 1249 healthy controls showed significant timing deficits in ADHD. Children/adolescents with ADHD perceived time less accurately (Hedges' g > 0.40), less precisely (Hedges' g = 0.66) and had higher tendency to overestimate time than their healt...
Conclusions
The findings of this study contribute to the existing knowledge about neuropsychological deficits in ADHD. They highlight significant challenges faced by children and adolescents with ADHD in accurately and precisely perceiving time. This insight is crucial for future research, clinical assessments, and treatment approaches for ADHD.
These findings may update current understanding of the underlying neuropsychological deficits in ADHD and provide insight for future research in clinical assessments and treatments for ADHD.
Context
This meta-analysis underscores the difficulty individuals with ADHD face in perceiving and measuring time, integrating data from various studies on the topic. It adds to the growing body of research indicating that time perception is among the numerous cognitive effects of ADHD.
Moreover, beyond cognitive impacts, ADHD is also associated with challenges in working memory and verbal learning. This suggests that ADHD's influence extends beyond cognition to other aspects of mental processing.
The current study's findings align with these broader research trends, highlighting the multifaceted nature of ADHD and its extensive impact on various cognitive and emotional aspects of individuals affected by it.