Time perception differences in children with and without ADHD
Comparing Time Perception in Children With and Without ADHD
Julie B Meaux, John J Chelonis
Objectives
The study aimed to compare how children with and without attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) perceive time. Specifically, it investigated their ability to estimate time using a time reproduction task. This task was designed to assess how accurately the children could judge and reproduce time intervals.
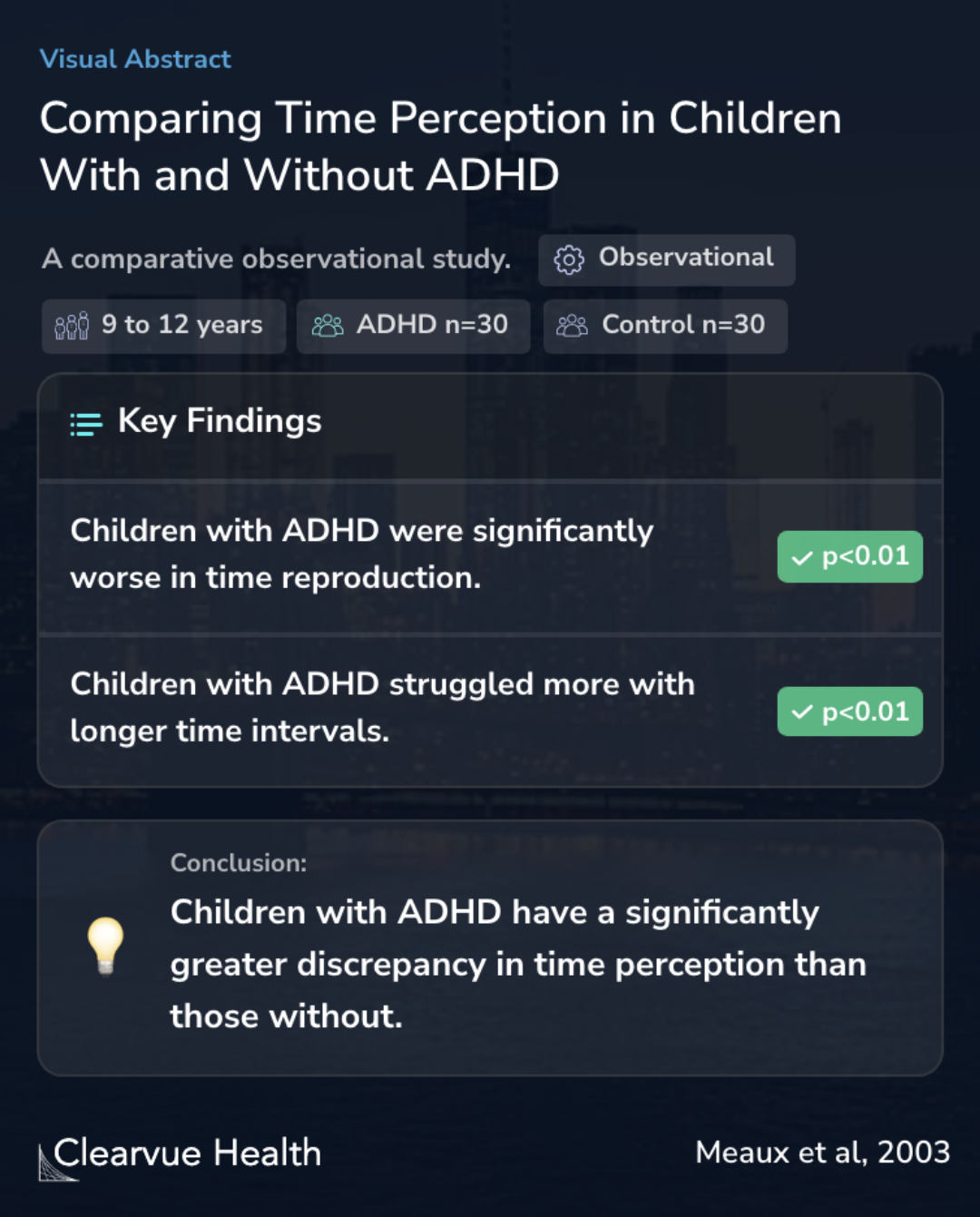
The purpose of this study was to compare time perception in children with and without attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) with use of a time reproduction task.
Methods
The research involved a sample of 60 children, half diagnosed with ADHD and the other half without this condition. The children's ages ranged from 9 to 12 years. The methodology employed a unique approach: children observed a light, guessed the duration it was on, and then held a lever down for what they thought was the same amount of time. This process was repeated across 16 trials with varying time lengths of 3, 6, 12, or 24 seconds, totaling 64 trials.
The sample consisted of 60 children (30 with ADHD and 30 without ADHD) ranging in age from 9 to 12 years. Children were asked to watch a light, verbally estimate how long the light was illuminated, and hold a lever in a depressed position for the same amount of time they thought the ligh...
Results
Children with ADHD displayed a significant discrepancy in their time reproduction task, with notably greater errors compared to the control group. This discrepancy became more pronounced over longer time intervals. These results highlight a distinct challenge faced by children with ADHD in accurately perceiving time.
Children with ADHD had significantly greater absolute discrepancy scores on the time reproduction task (F(1,58) = 10.878; P <.01) than did children in the control group. In addition, children with ADHD had greater increases in absolute discrepancy scores across time intervals (F(3,174...
Conclusions
The study concluded that children with ADHD have a significantly impaired perception of time compared to those without ADHD. This adds to our understanding of the challenges faced by children with ADHD. It underscores the importance of considering time perception difficulties in the overall management and support strategies for children with ADHD.
The findings of this study indicate that children with ADHD have impaired time perception compared with children who do not have ADHD.
Context
This paper contributes to our understanding of ADHD in children, especially in time perception. It resonates with other research findings, such as a study by Toplak et al., 2005, which found that adolescents with ADHD faced higher thresholds in visual duration discrimination tasks.
Furthermore, Smith et al., 2002, supported this by showing that children with ADHD particularly struggle with perceiving shorter time spans. This aligns with the current study's findings, highlighting a consistent trend across research that ADHD may fundamentally affect how time is perceived and processed.