Key Points

Why you need vitamin c
Your body needs to obtain all of its daily Vitamin C from your diet. Unlike Vitamin D, you cannot make it on your own.

What's it used for?
Your body uses Vitamin C to grow and repair itself, particularly when it comes to wound healing. Vitamin C also plays a role in fighting off immunity.

Where can you get vitamin C?
Fruits and vegetables tend to be great sources of your daily Vitamin C requirements. We list some of the best examples below.
Adults
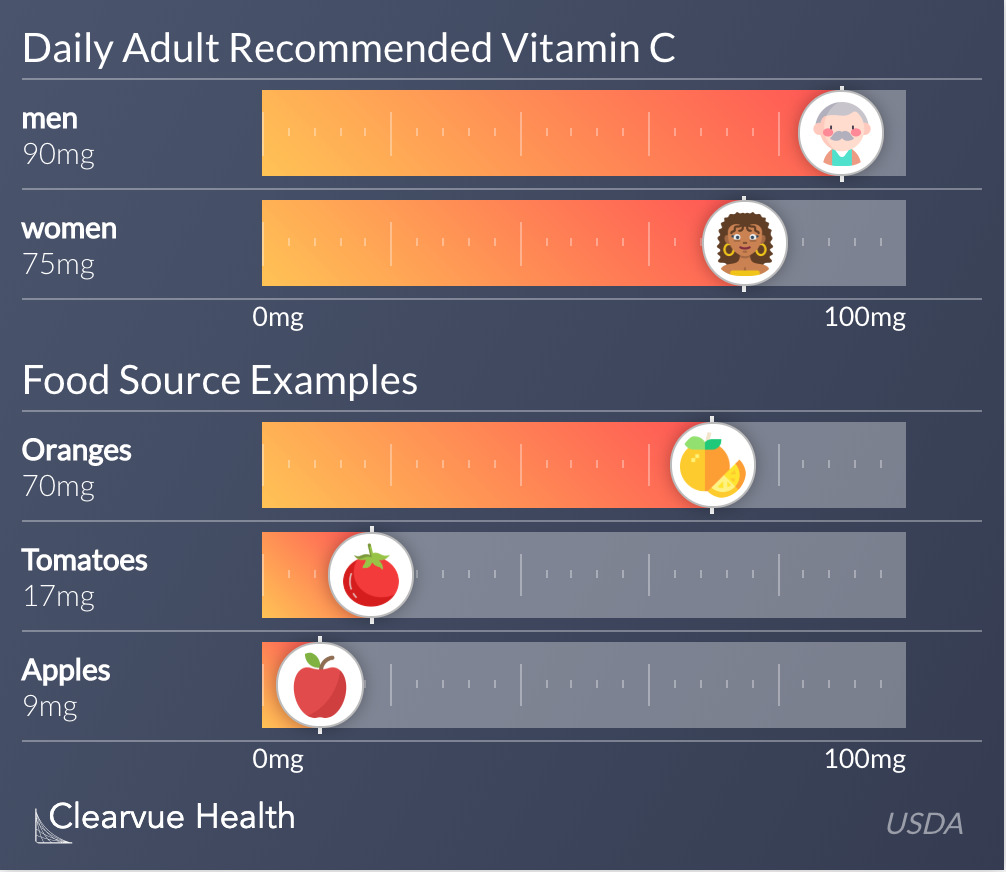
The chart above compares the amount of Vitamin C needed by adult men and women. Men need 90 milligrams of Vitamin C each day. Women need 75 mg of Vitamin C. We compare this amount to the amount of Vitamin C found in common fruits. An orange has nearly all the Vitamin C an adult needs in a day. This information was sourced from the Office of Dietary Supplements within the NIH.
Children
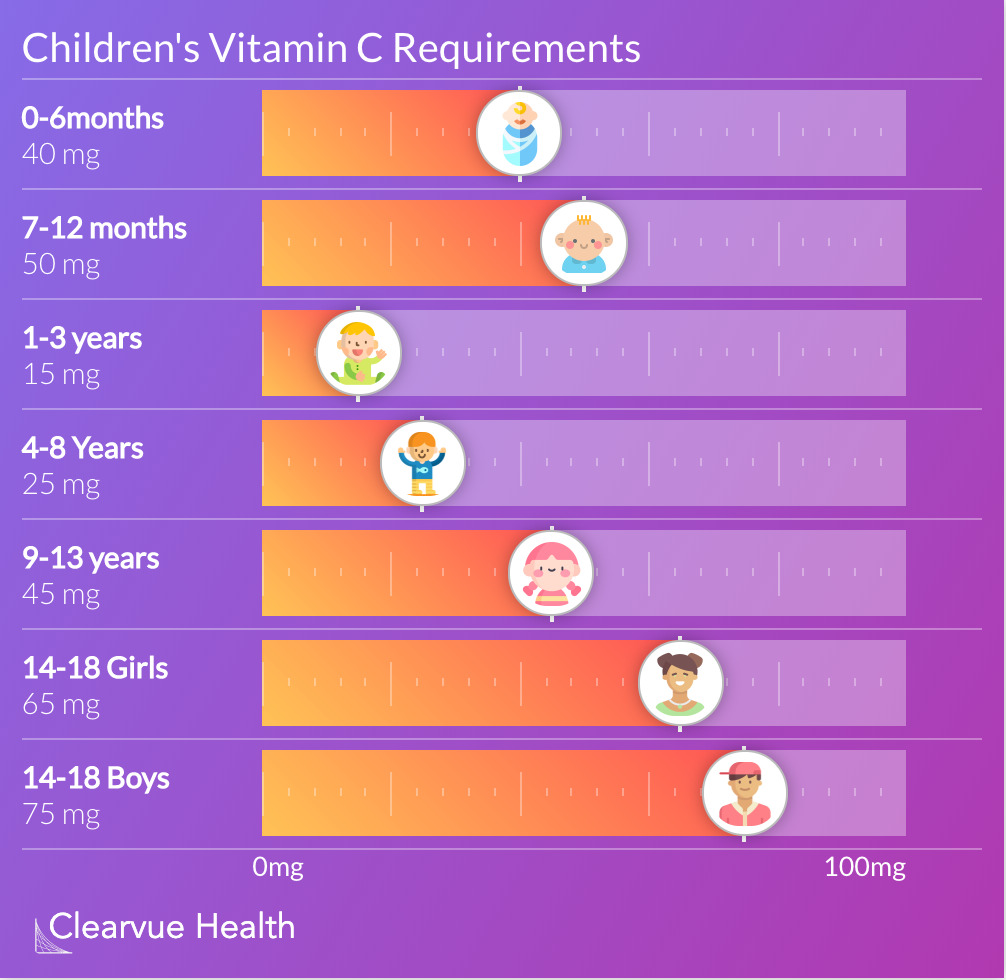
The chart above shows the relative amounts of Vitamin C needed by children as they grow up. At age 1, children only need 15mg of Vitamin C. This increases with age until adulthood when they need 90mg for men and 75mg for women.
Background

The Importance of Vitamin C
Vitamin C is one of the most well-known, and important, vitamins. Fortunately, it's pretty easy to get as long as you eat a healthy diet. We outline all of the key functions and benefits of Vitamin C below.
Key Facts
Key Functions
Key Facts
- TypeEssential, Water soluble
- Other Namesascorbic acid
- Daily AllowanceWomen: 75mg, Men:90mg
Appearance

Key Sources

Fruits

Vegetables

Peas

Collagen
Your body needs Vitamin C to create collagen, a critical component of joints and connective tissue.
Wound Healing
Vitamin C helps your body heal wounds
Immunity
Vitamin C helps your body fight off infection

Top Benefits
Benefit #1
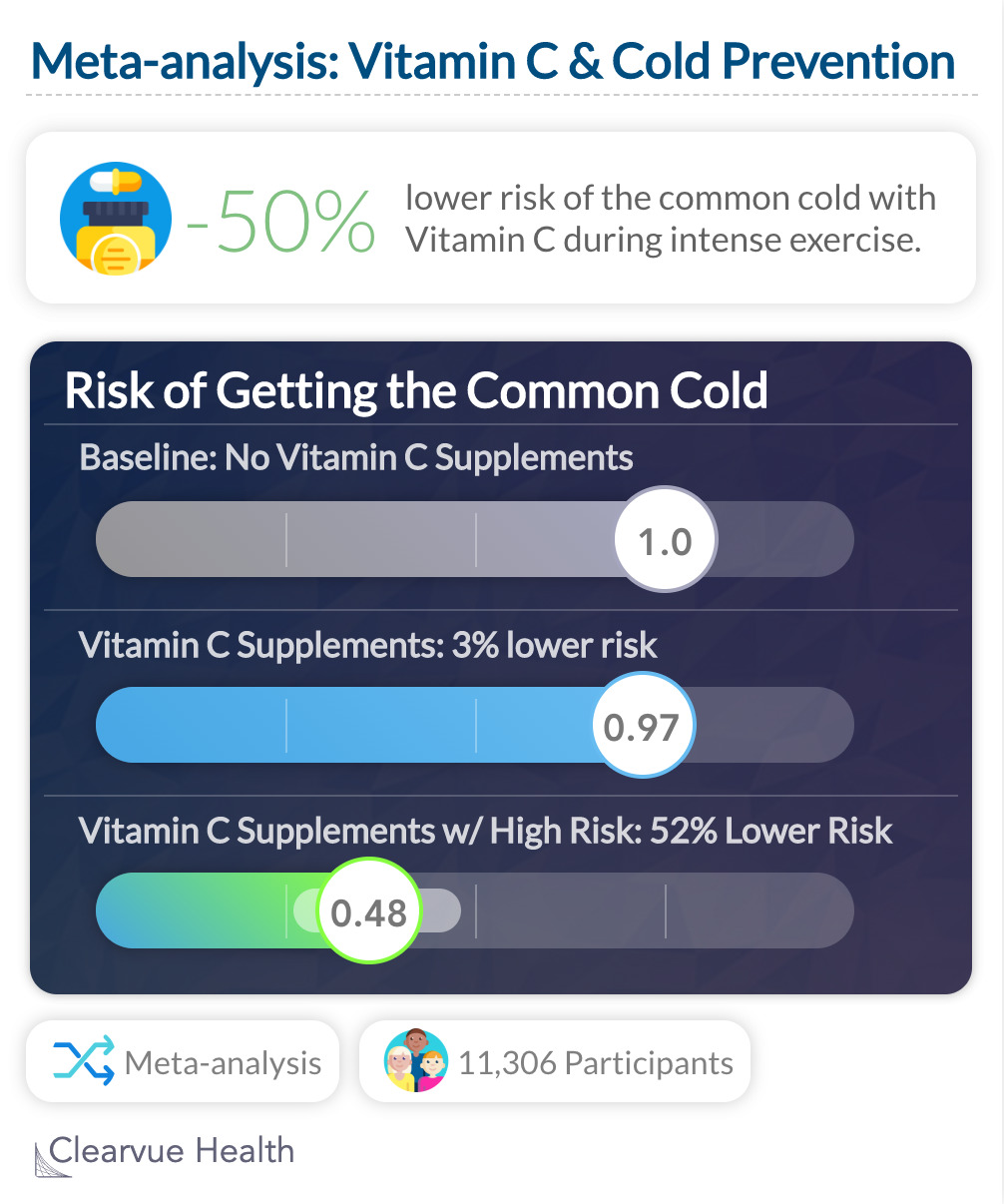
A meta-analysis of 29 trials found that taking vitamin C can slightly lower your risk of getting the cold. RR 0.97 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.94 to 1.00). Among skiers, marathon runners, and soldiers in subarctic exercises, this was much more effective, with a approx. 50% risk reduction: 0.48 (95% CI 0.35 to 0.64)
Vitamin C Benefit #2

Vitamin C Benefit #3
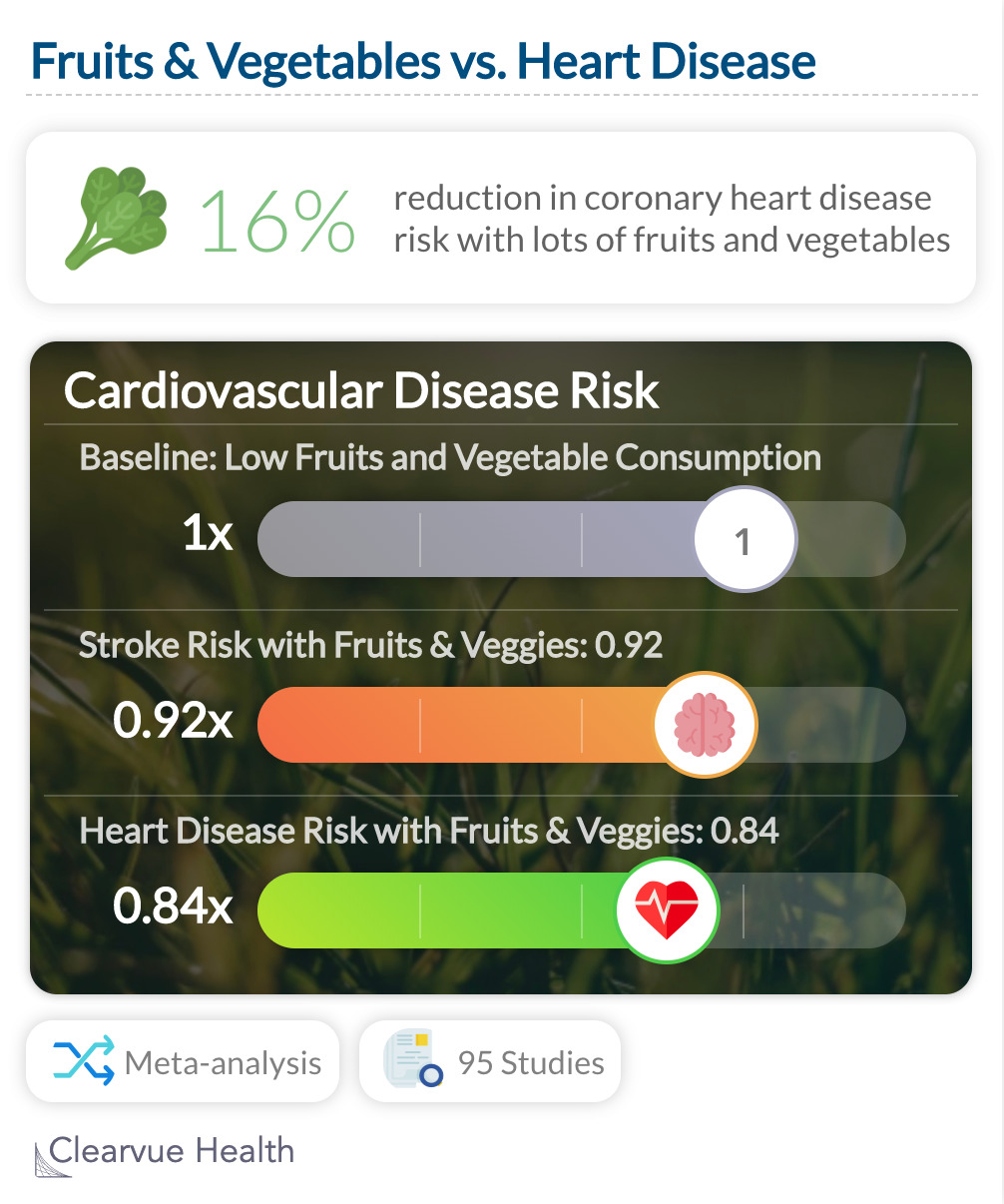
A meta-analysis of 95 studies showed that generally, high fruit and vegetable consumption is correlated with a lower risk of heart disease 0.84 (95% CI: 0.76–0.92) and a lower risk of stroke: 0.92 (95% CI: 0.90–0.95)

#nutrition
Scroll for more ->





#vitaminc
Scroll for more ->





#new
Scroll for more ->