Key Facts

1. Vitamin C & Cold Prevention
Vitamin C can potentially help protect you from a cold if you are at high risk of catching one.

2. Vitamin C Can Shorten a Cold
Taking Vitamin C can potentially help you recover faster, particularly for children.

3. Take the Recommended Amount
However, taking a super-high dose of Vitamin C may not be beneficial and it can carry some risks. Always take the recommended amount and talk to your doctor.
Background
Key Facts
Key Functions
Key Facts
- TypeEssential, Water soluble
- Other Namesascorbic acid
- Daily AllowanceWomen: 75mg, Men:90mg
Appearance

Key Sources

Fruits

Vegetables

Peas

Collagen
Your body needs Vitamin C to create collagen, a critical component of joints and connective tissue.
Wound Healing
Vitamin C helps your body heal wounds
Immunity
Vitamin C helps your body fight off infection

Vitamin C
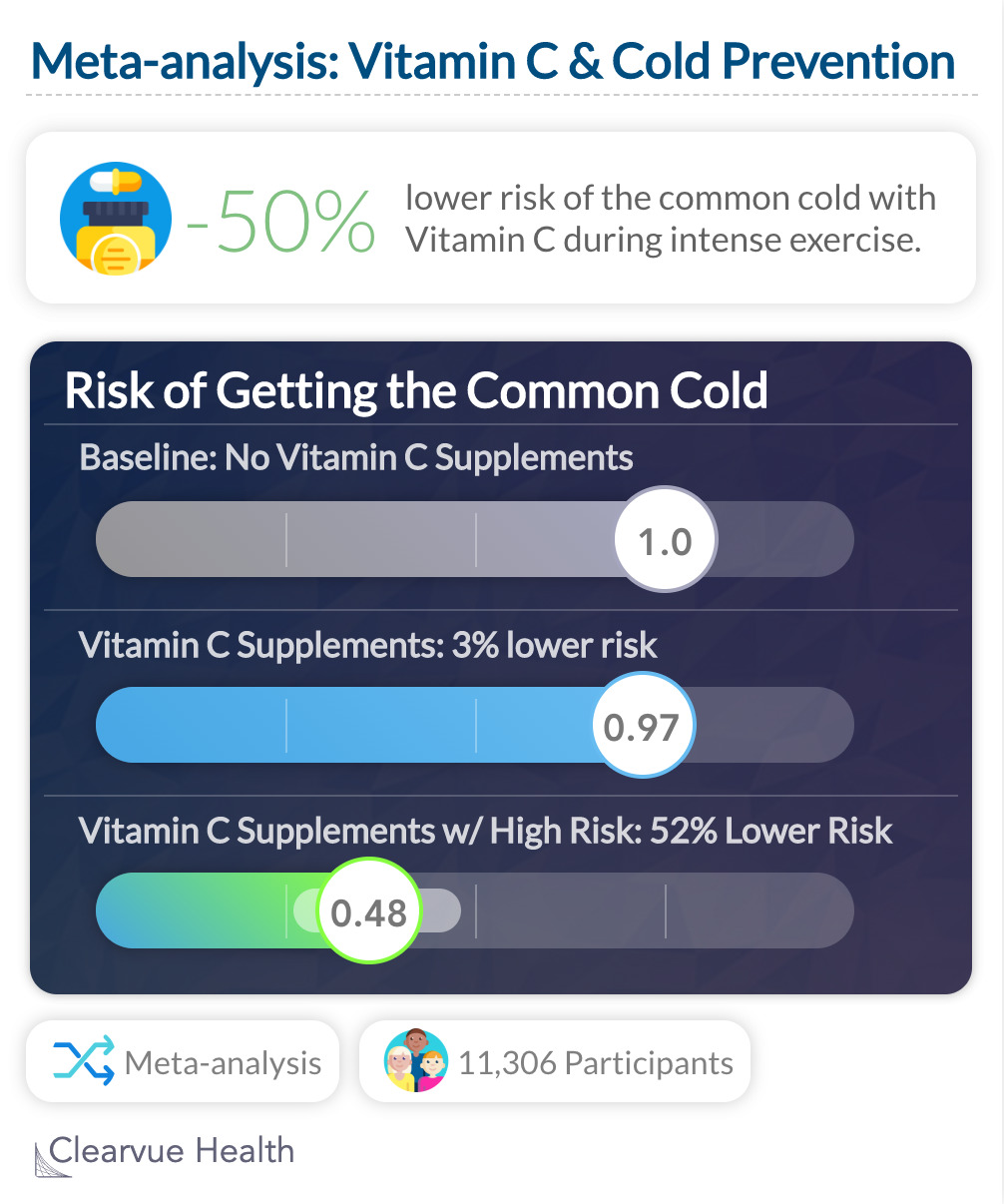
A meta-analysis of 29 trials found that taking vitamin C can slightly lower your risk of getting the cold. RR 0.97 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.94 to 1.00). Among skiers, marathon runners, and soldiers in subarctic exercises, this was much more effective, with a approx. 50% risk reduction: 0.48 (95% CI 0.35 to 0.64)
Data Source
"The failure of vitamin C supplementation to reduce the incidence of colds in the general population indicates that routine vitamin C supplementation is not justified, yet vitamin C may be useful for people exposed to brief periods of severe physical exercise."
Vitamin C & Cold Duration
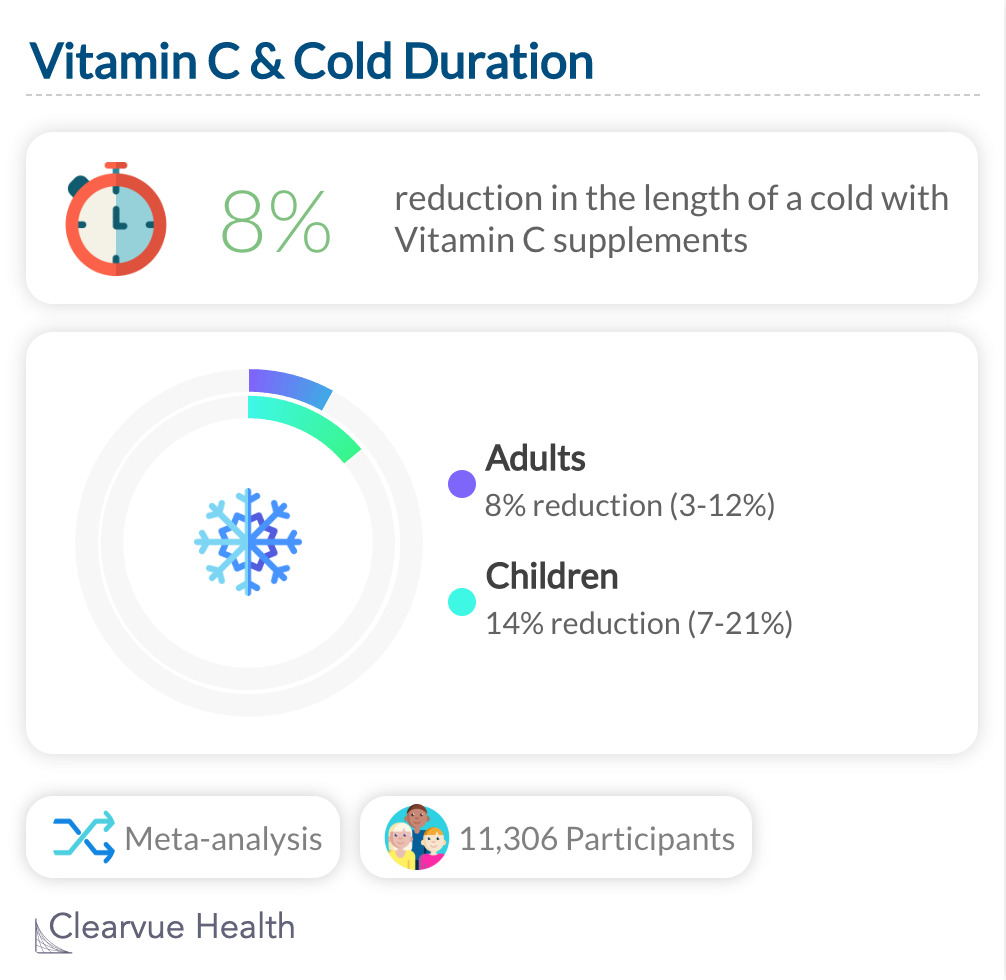
A meta-analysis found that taking Vitamin C can potentially reduce the length of your cold by 8% for adults and 14% for children.
Data Source
"Duration of cold episodes that occurred during prophylaxis was significantly reduced in both children and adults. For children this represented an average reduction of 14% in symptom days, while in adults the reduction was 8%."

Key Takeaways
While limited, studies do show that taking Vitamin C can potentially protect you from the cold, and may help you recover faster.

More Info

#vitaminc
Scroll for more ->





#nutrition
Scroll for more ->





#new
Scroll for more ->