Summary

1. Your Eyes Need Vitamin A
Vitamin A plays a key and well-known role in helping your eyes see, especially at night.

2. Age Related Vision Loss
However, when it comes to age-related vision loss, the science is less clear on the benefits of Vitamin A supplements.

3. Antioxidants
Clinical trials have shown that antioxidants such as zinc and lutein from vegetables may actually matter more.
The Science
Key Facts
Functions
Key Facts
- TypeFat soluble
- SourceDiet
- Other NamesRetinol, retinyl ester
Appearance

Key Sources

Carrots

Sweet Potatoes

Spinach

Vision
Vitamin A plays a key role in our black and white and night vision.

Immunity
Vitamin A helps your immune system fight off disease.

Cell Growth
Vitamin A helps your cells grow and develop properly, particularly in young children.

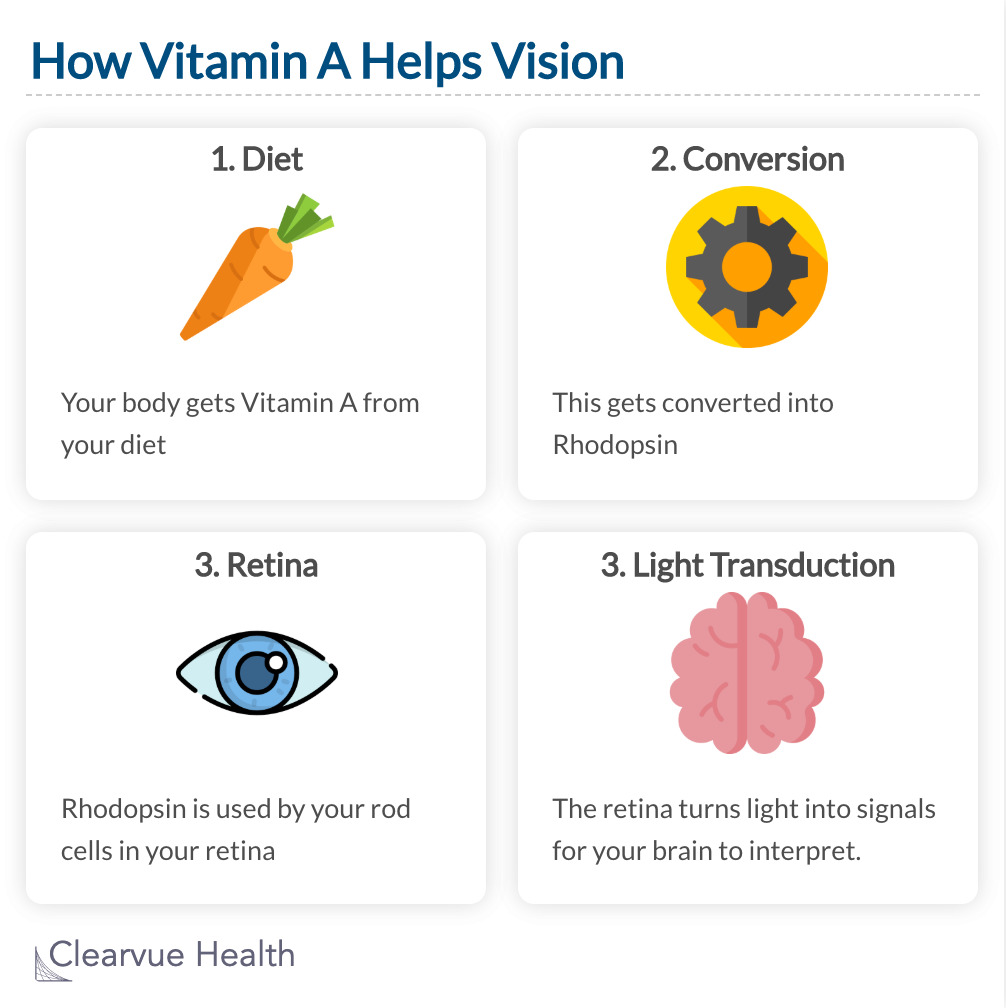
Your body gets Vitamin A from your diet. Vitamin a gets converted into rhodopsin. Rhodopsin is used by your rod cells in your retina. The retina turns light into signals for your brain to interpret.
Study 1

A clinical trial found that a combination of Vitamin C, Vitamin E, beta-carotene, zinc, and copper significantly reduces the risk of moderate visual acuity loss. OR, 0.73; 99% CI, 0.54–0.99

What this means
Researchers found that Vitamin A, in combination with Zinc and other antioxidants, could reduce your risk of vision loss over time.
Data Source
"Those with extensive intermediate size drusen, at least 1 large druse, noncentral geographic atrophy in 1 or both eyes, or advanced AMD or vision loss due to AMD in 1 eye, and without contraindications such as smoking, should consider taking a supplement of antioxidants plus zinc such as that used in this study."
Study 2
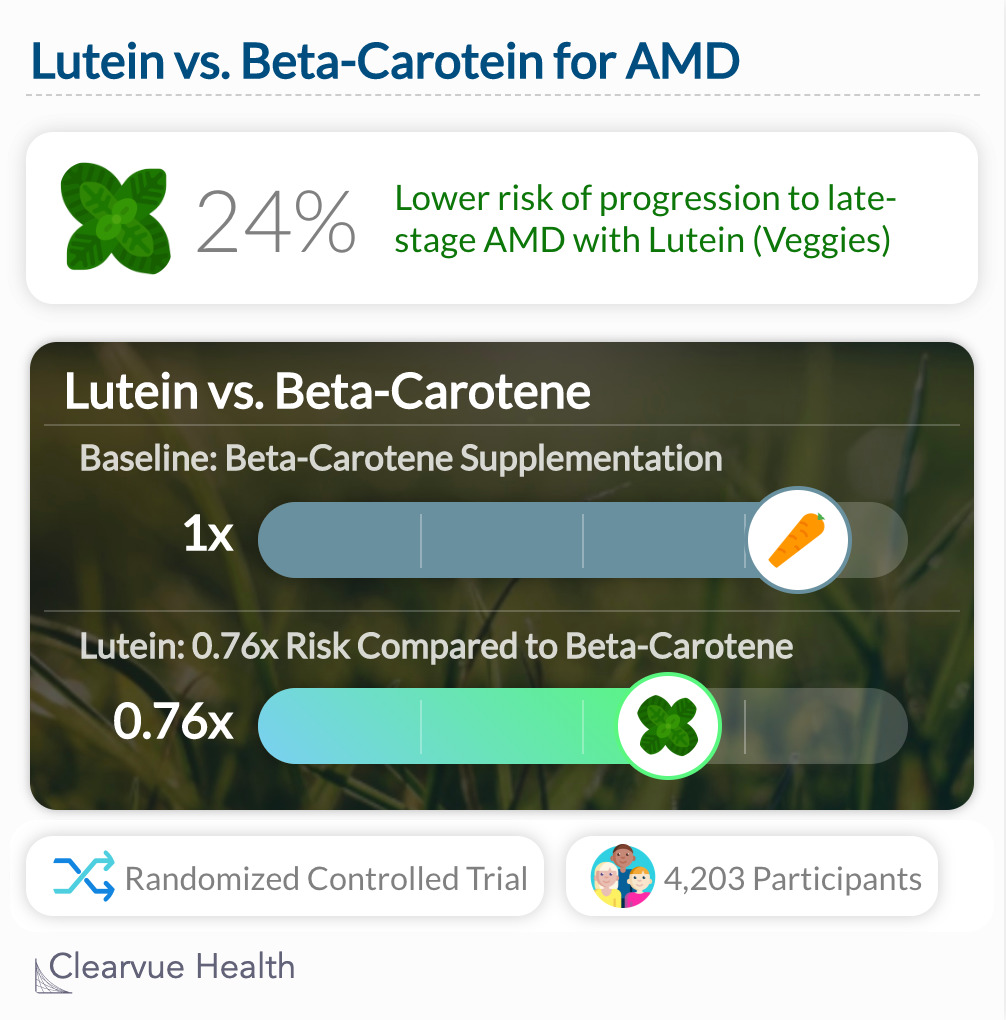
Researchers found that lutein showed significantly more protection against age-related macular degeneration than beta-carotene. (HR 0.76, 95% CI, 0.61-0.96; P = .02) This suggests that leafy green veggies may in fact be the way to go for eye and vision health.

What this means
While we need vitamin A for your vision, lutein may actually be the better supplement for preventing vision loss. Those who received lutein had a significantly lower risk of age-related macular degeneration. Eating your veggies will always be a good thing!
More Info



More Info

#nutrition
Scroll for more ->





#vision
Scroll for more ->
#vitamina
Scroll for more ->




#new
Scroll for more ->