music and surgery recovery: Evidence supporting the use of music in pain and stress relief
There is an array of complementary treatments meant to help patients recover from surgery. For example, most hospitals have a chapel or meditation room accessible for all patients to pray or find peace in their own way. While religion and spirituality are not considered pillars of Western medicine, there are plenty of studies that have observed the measurable impact of prayer on physical and mental healing. Music is another means of healing that is actually supported by evidence.
The Lancet, a well-respected medical journal, published a meta-analysis discussing music as an aid for postoperative recovery in adults. A meta-analysis is a study that systematically pools data from a number of existing studies. The researchers pooled the results of 73 randomized, controlled trials. Along with measuring efficacy, they examined the differences between music played before, during, and after surgery.
Source: Music as an aid for postoperative recovery in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
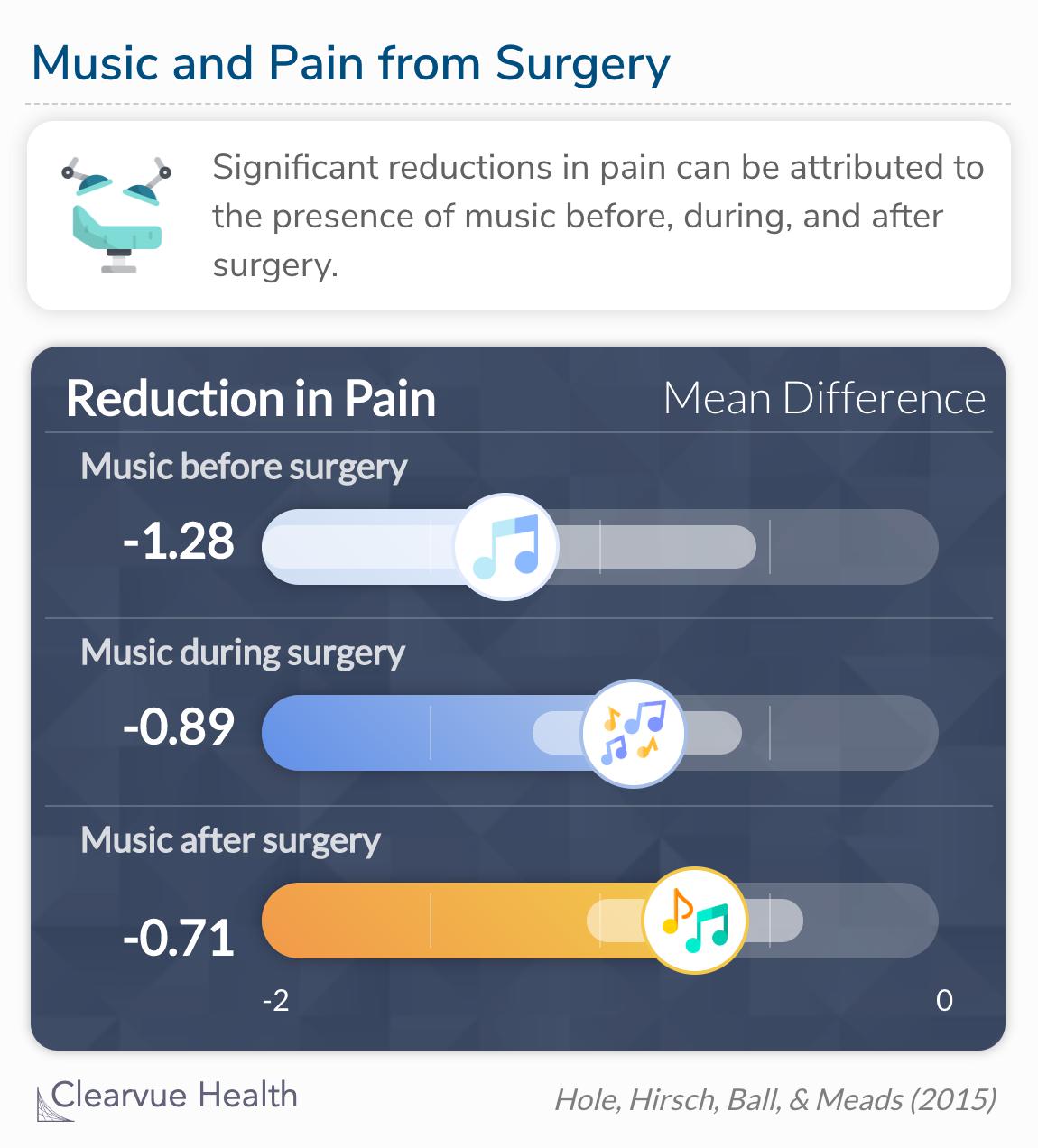
Music reduced postoperative pain
The pain seemed to be reduced most when music was
played preoperatively (SMD –1·28 [–2·03 to –0·54]),
then intraoperatively (–0·89 [–1·20 to –0·57]), and then postoperatively (–0·71 [–1·03 to –0·39]).
Pain is subjective, meaning that everyone perceives and tolerates pain differently. The best way to measure pain is with a standardized scale that tries to reduce these subjective differences. In this case, patients filled out a scale while in the healing process. The study found that patients exposed to music before, during, and after surgery reported significant reductions in their pain compared to patients with no music exposure. Particularly, music before surgery was most effective in pain reduction. However, pain reduction is not where the benefits of music cease.
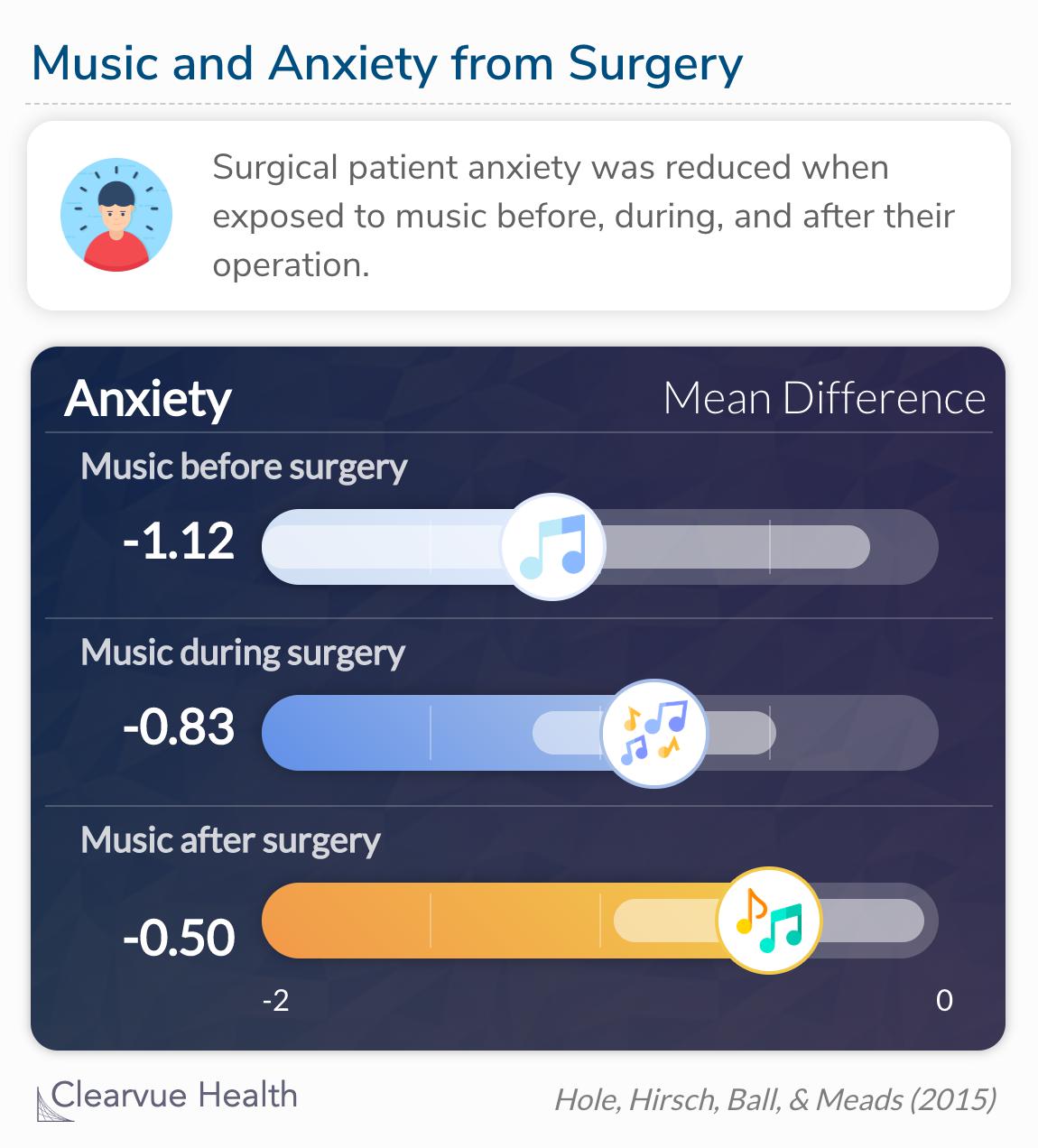
Music reduced postoperative anxiety
Anxiety was
likewise reduced when music was used preoperatively
(–1·12 [–2·05 to –0·19]), compared with intraoperatively
(–0·83 [–1·19 to –0·47]), and postoperatively (–0·50
[–0·96 to –0·04]).
Similar to pain, anxiety is a subjective feeling that is expressed and perceived differently from person to person. Anxiety is also measured with a standardized questionnaire rooted in psychological research. The study found that patients exposed to music before, during, and after surgery reported significant reductions in their anxiety compared to patients with no music exposure. Again, music before surgery was most effective in anxiety reduction. This is immeasurability important for the success of the operation and patient well-being. Patients expressing anxiety may find it difficult to deal with hospital procedures and see delays in recovery.
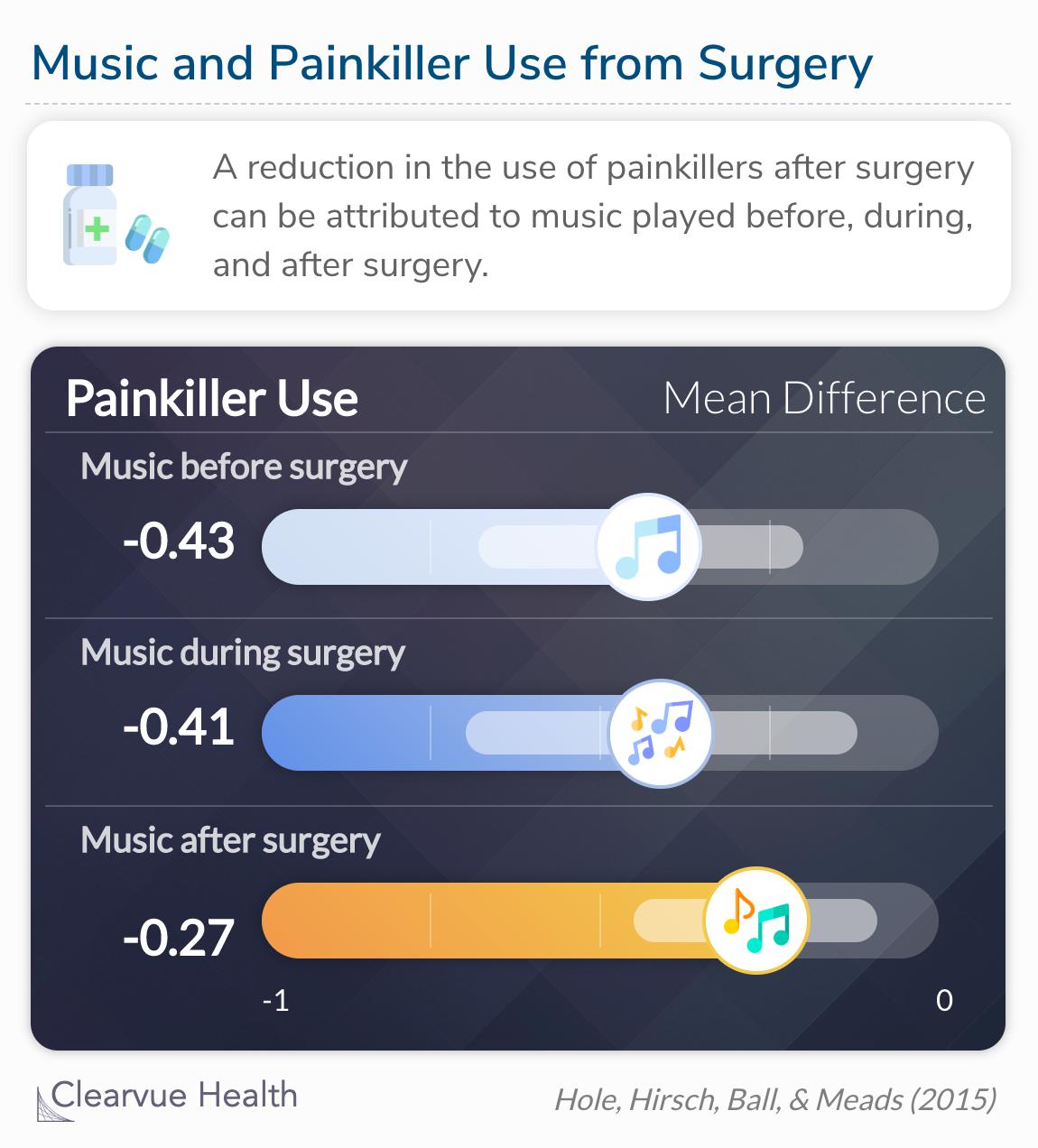
Music reduced the use of painkillers
Analgesia use was reduced when music was played
preoperatively (–0·43 [–0·67 to –0·20]), compared with
intraoperatively (–0·41 [–0·70 to –0·12]), and
postoperatively (–0·27 [–0·45 to –0·09]).
Lastly, a quantitative analysis suggested that patients exposed to music before, during, and after surgery were less likely to take painkillers. This statistic goes hand in hand with the reduction in pain and anxiety. Obviously, patients feeling less pain do not need stronger medications. A reduction in anxiety can also balance a patient's need for pain medications. For example, a patient anxious about the possibility of pain may take painkillers preemptively. Also, a less anxious person may be more inclined to overcome the pain without drugs. However, this is all very dependent on the individual patient.
Final thoughts
While music can not cure medical conditions, it can play a vital role in the healing process. Pain and anxiety management are particularly important after going under the knife. A patient's perception of their experience in the hospital and satisfaction with the process can greatly impact the body's response to trauma. The mind must heal along with the body, as a person overcomes the stress and life associated with their medical condition.