Vitamin D & Depression
TL;DR: Vitamin D vs. Depression


Background
Unlike most vitamins, your body can actually make some of its own Vitamin D with the help of the sun.
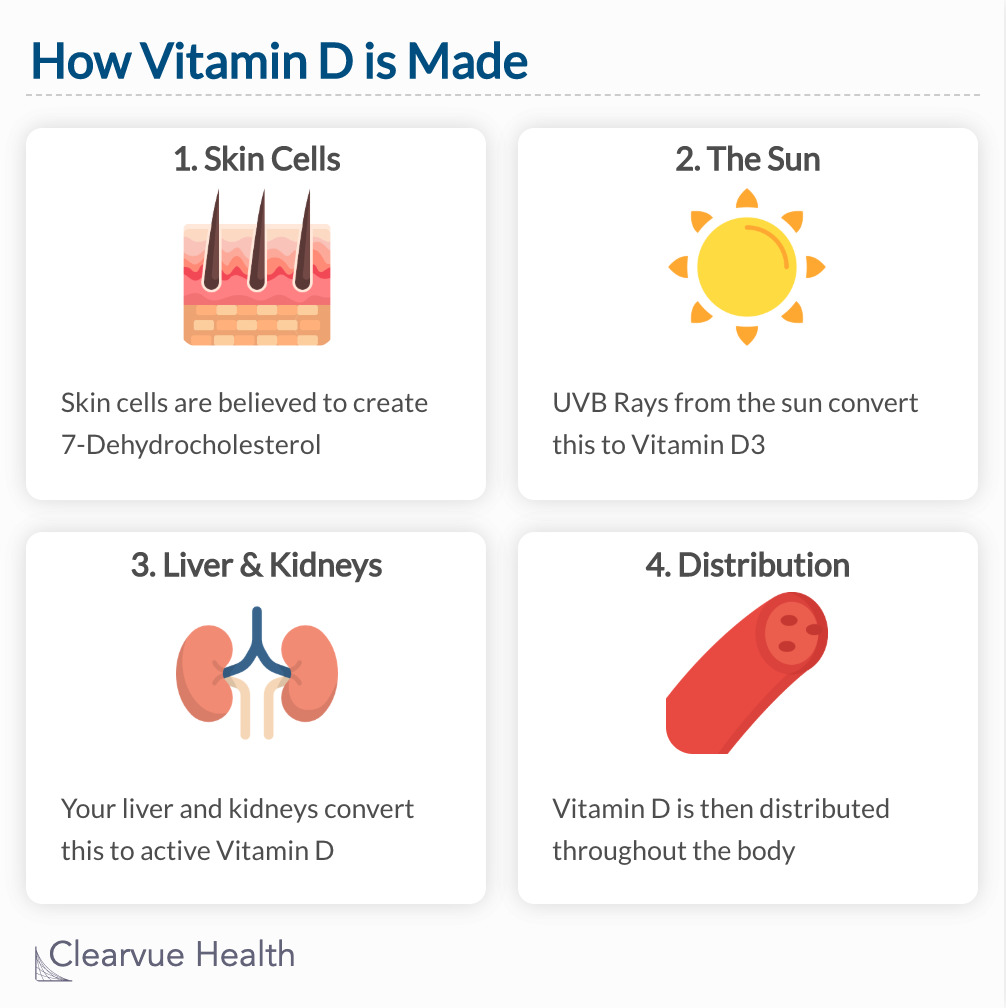
Not getting enough sun can lead to Vitamin D deficiency. Together with Vitamin D that you consume, your daily Vitamin D plays important role in absorbing nutrients, keeping your bones strong, and supporting your immune system.
Vitamin D and Depression
Vitamin D has also been suspected to play a role in mental health.




"Our analyses are consistent with the hypothesis that low vitamin D concentration is associated with depression"
Clinical Trials: Vitamin D & Depression
Clinical trials of Vitamin D have so far been unable to confirm this link. One trial of nearly 20,000 volunteers gave Vitamin D to some and a placebo to others. Those that received Vitamin D were slightly less likely to get depression. However, the results were not significant.





Among adults aged 50 years or older without clinically relevant depressive symptoms at baseline, treatment with vitamin D3 compared with placebo did not result in a statistically significant difference in the incidence and recurrence of depression or clinically relevant depressive symptoms or for change in mood scores over a median follow-up of 5.3 years.

#vitamind
Scroll for more ->





#nutrition
Scroll for more ->





#new
Scroll for more ->