the science
Key Facts
Functions
Key Facts
- TypeFat soluble
- SourceDiet
- Other NamesRetinol, retinyl ester
Appearance

Key Sources

Carrots

Sweet Potatoes

Spinach

Vision
Vitamin A plays a key role in our black and white and night vision.

Immunity
Vitamin A helps your immune system fight off disease.

Cell Growth
Vitamin A helps your cells grow and develop properly, particularly in young children.

Key Findings

1. Vitamin A might help
Having more Vitamin A in your body correlates with a lower risk of breast cancer. This finding has been replicated in multiple studies.

2. Dietary Vitamin A is good for you
Eating a diet that is high in Vitamin A has also been associated with a lower risk of breast cancer.

3. Supplements might not help
However, Vitamin A in the form of supplements has not been shown to help. In fact, they've been shown to have negative effects in some studies.
Study 1

More vitamin A = Lower risk
Scientists around the world have found that a higher level of Vitamin A in your bloodstream correlates with a significantly lower risk of breast cancer.
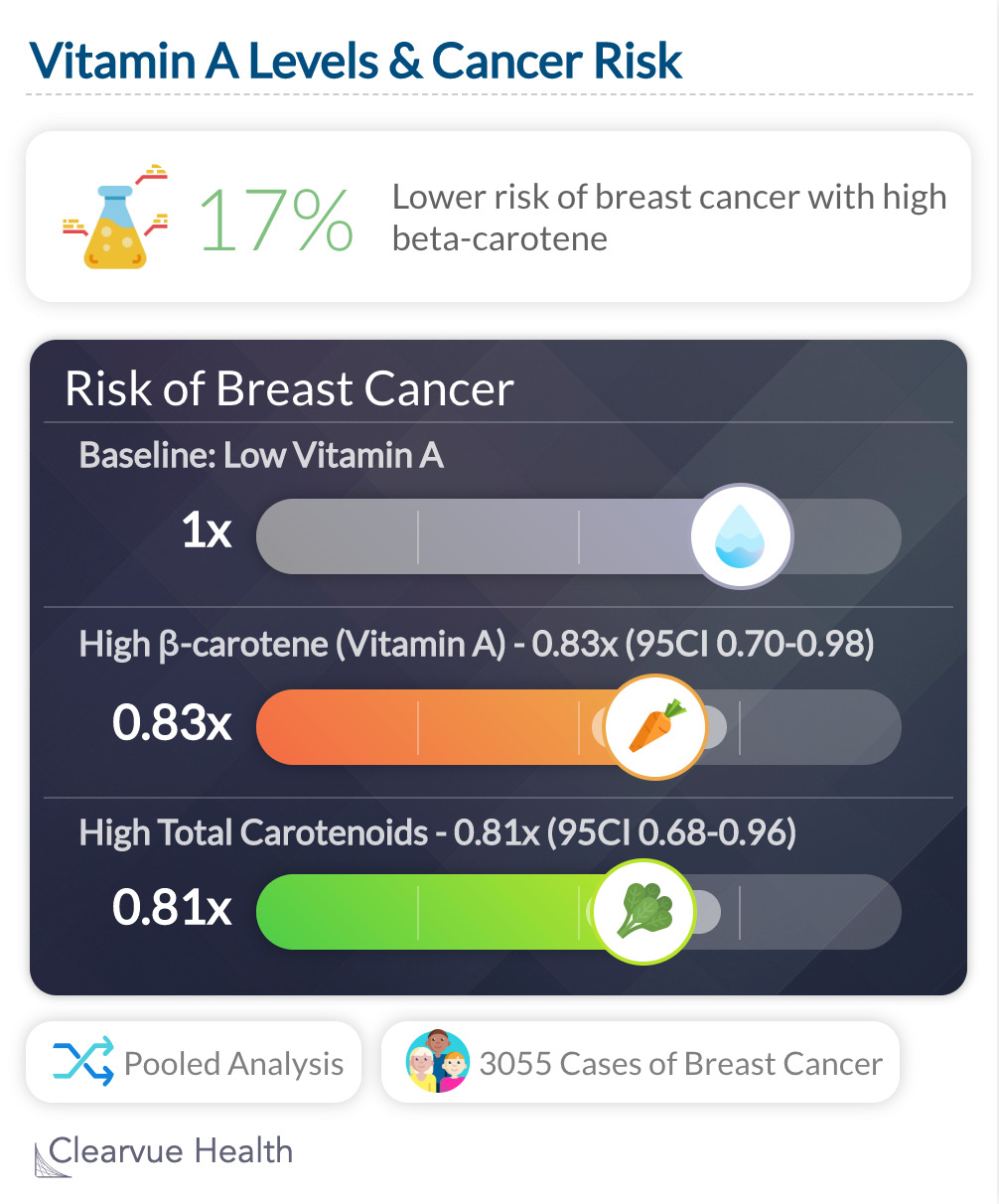
A pooled analysis of eight cohort studies found that Vitamin A levels in your blood correlate with your risk of breast cancer. Having a lot of vitamin A in the form of β-carotene correlates with a 17% lower risk of breast cancer. Having a lot of total carotenoids, which includes the pigments found in vegetables, correlates with a 19% lower risk of breast cancer.
Data Source
" This comprehensive prospective analysis suggests women with higher circulating levels of α-carotene, β-carotene, lutein+zeaxanthin, lycopene, and total carotenoids may be at reduced risk of breast cancer."
Study 2

Carrots might help
When scientists asked participants to keep food diaries, they found that those who eat lots of carrots and other foods rich in Vitamin A had a slightly lower risk of developing breast cancer.
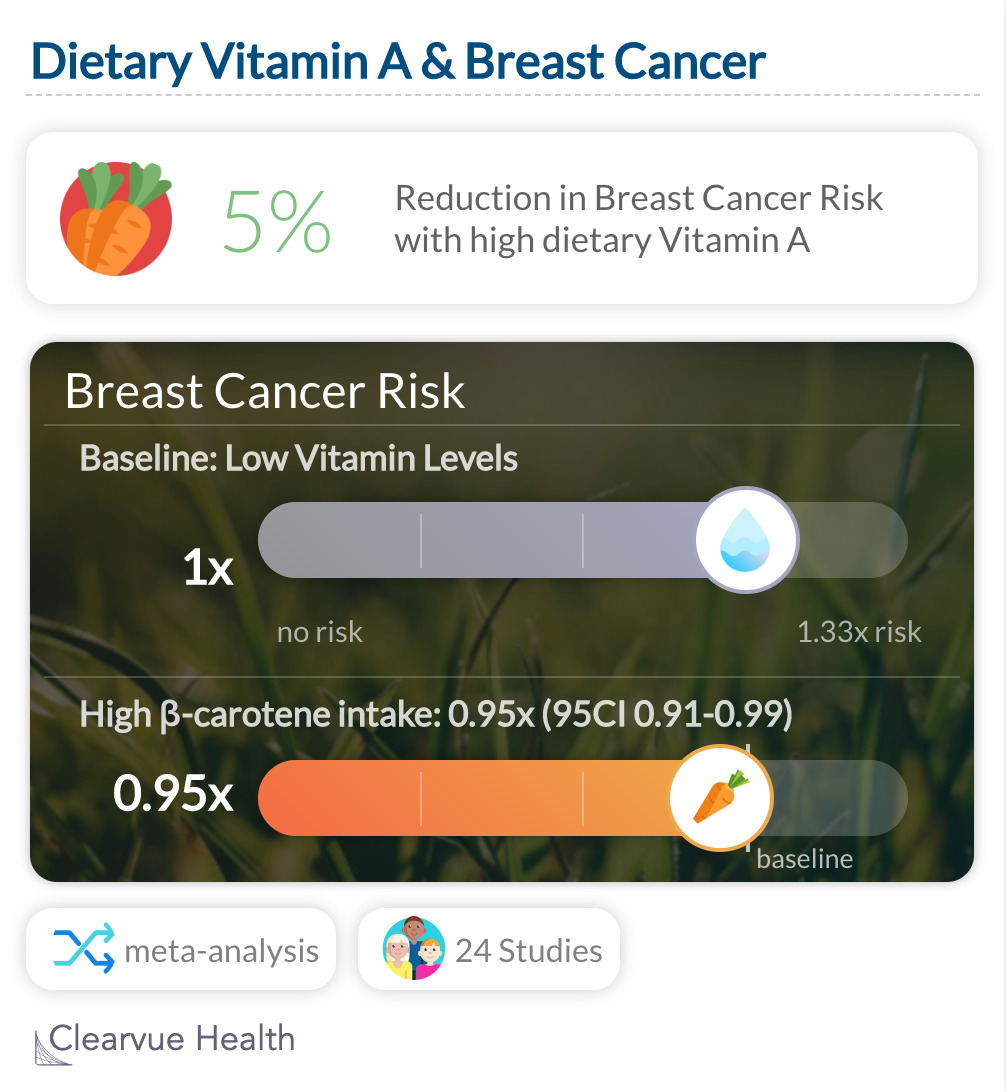
Dietary Vitamin A has only a weak association with reduced breast cancer risk. Those who report eating a lot of β-carotene, found in carrots, had a small but still significant reduction in breast cancer risk.
Data Source
"In this meta-analysis, no association was found between dietary intake of carotenoids and breast cancer risk, except for a weak reduction in risk with dietary β-carotene."
Study 3

3. Supplements may not help
However, when it comes to supplements, the picture is less clear. In the study below, scientists found that Vitamin A supplements given over 12 years had no effect in preventing cancer or deaths from cancers in over 22,000 men. This may be a specific finding for men, or it may show that vitamin A diets are more helpful than vitamin A supplements.
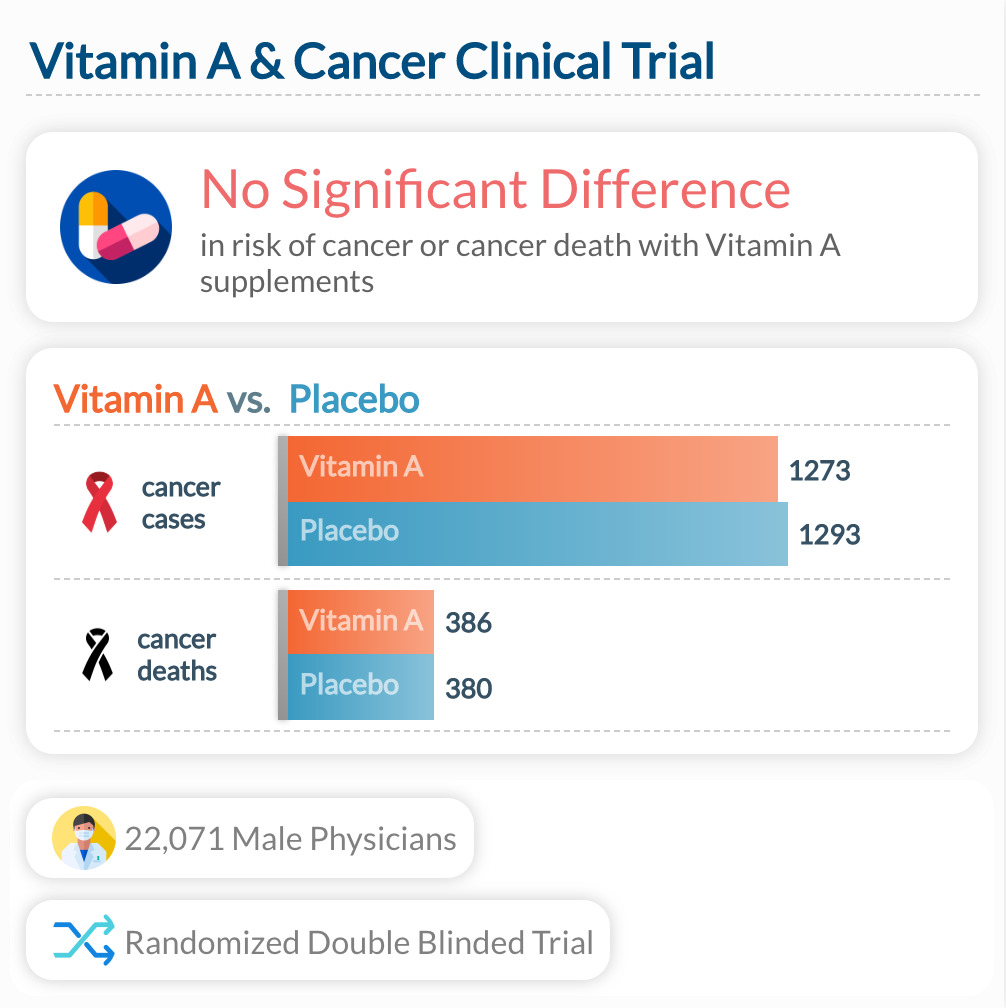
A clinical trial found that Vitamin A supplements in the form of β-carotene did not reduce cancer risk or cancer deaths in a clinical trial. 22,071 Male Physicians were given supplements over 12 years to see whether it would reduce their risk of cancer in a randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled clinical trial. Results showed no significant differences.
Data Source
"In this trial among healthy men, 12 years of supplementation with beta carotene produced neither benefit nor harm in terms of the incidence of malignant neoplasms, cardiovascular disease, or death from all causes. "
The bottom line

Vitamin A & Cancer
Eat lots of carrots and vegetables. Research has consistently shown that those who eat lots of vitamin A and other carotenoids from vegetables have a lower risk of cancer. However, there isn't enough evidence yet to support taking Vitamin A supplements. As with many things in nutrition, you can't replace the benefits of healthy food with a pill yet.

#vitamina
Scroll for more ->




#cancer
Scroll for more ->




#new
Scroll for more ->