internet gaming disorder: when does internet gaming become a psychological disorder?
Gamers often face misconceptions about the role of games in their life. The conspiratory noise of false stereotypes actually detracts from what may be a serious consequence of the rise of gaming. Psychologists are now becoming increasingly aware of a negative mental phenomenon that can indeed occur from excessive gaming, especially socially on the internet, called Internet Gaming Disorder.
“
Internet gaming disorder: persistent and recurrent use of the Internet to engage in games, often with other players, leading to impairment or clinically significant distress
American Psychiatric Association
Clinically Significant Distress
While impairment and distress are rather general qualifiers, the American Psychiatric Association has a very precise diagnostic definition with nine possible symptoms. If a patient demonstrates any five of these criteria simultaneously for at least 12 months, they can be diagnosed with internet gaming disorder.
Gamers must fulfill at least five symptoms for at least a 12-month period to receive an internet gaming diagnosis.
It is important to note that internet gaming disorder specifically refers to internet gaming, denoting a social aspect of gaming, as opposed to offline or independent gaming. Psychologists have determined the effects of obsession with games for their social component are distinctly habit-forming. Due to the novelty of the condition, there is still much confusion about which of the prior criteria are the most important and most common, and who is most likely to develop an unhealthy relationship to online gaming.
Internet Gaming Disorder in Society
To shed light on these issues, scientists conducted surveys with gamer groups and general population cohorts to determine rates of internet gaming disorder among gamers, tease the relationships between criteria, and try to unearth new risk factors.
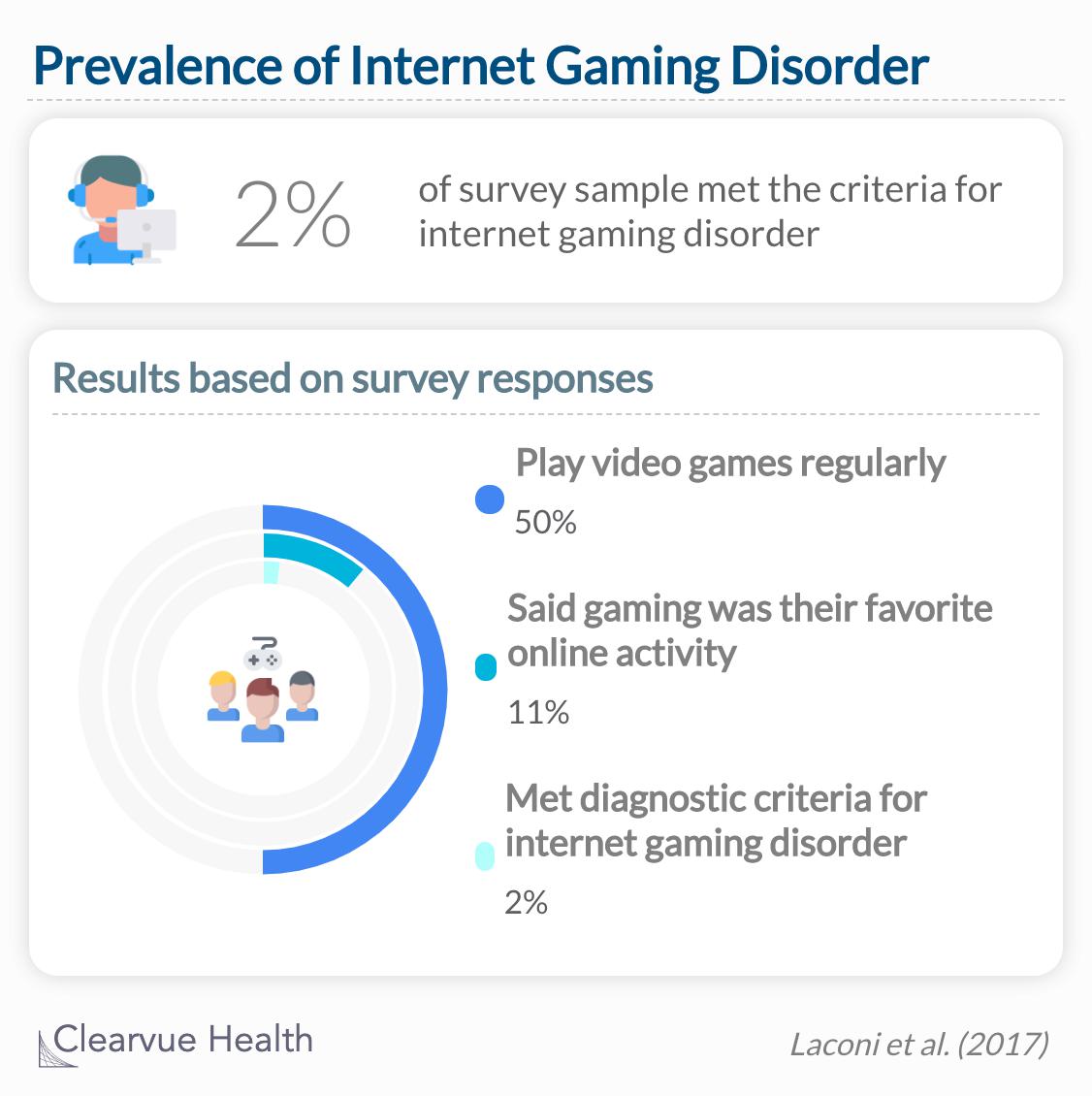
The prevalence of Internet gaming disorder was nearly 2% (n = 8)
Source: Internet gaming disorder, motives, game genres and psychopathology
Surveys found that more than 50% of the population regularly plays games online. Of these, 68% reported not a single criterion of internet gaming disorder. However, roughly 2% of gamers checked off the minimum 5 boxes for diagnosis over their gaming lifetime. Of these, less than 1% of all gamers were experiencing gaming disorder during the survey period.
While this indicates that gaming is largely a harmless hobby for the vast majority of people, it can lead to deep dependency. It is critical to note, however, that when scientists compared these rates to gambling addiction among regular gamblers, internet gaming disorder rates were significantly lower. Thus, online gaming should not be seen as equally dangerous or habit-forming as gambling.
Who becomes dependent on internet gaming?
First off, playing for long hours was not a significant risk factor for internet gaming disorder symptoms, regardless of what your parents say. Rather, people that reported symptoms of depression overlapped strongly with those reporting internet gaming disorder symptoms. Whether these people were already depressed before their gaming habits is unclear.
The most common predictors of internet gaming disorder are depressive symptoms, a need to escape, coping with stress, competition, and a need for social interaction.
Source: Internet Gaming Disorder: Investigating the Clinical Relevance of a New Phenomenon
Many gamers with internet gaming disorder reported the need to mentally escape from an unpleasant reality. Interestingly, using games as a coping mechanism was significantly more common among men. Meanwhile, women reported especially high levels of social competition as drivers for their unhealthy gaming habits. In regards to genre, it is important to note that first-person shooters, long thought to cause negative psychological responses and violence, and casual games, long thought to be innocuous, had equal weight in predicting disorder symptoms.
Final thoughts
For the vast majority of people, gaming, even for long hours, is not a risky activity. That being said, parents, clinicians, and friends alike must realize that with the wrong mental state or approach, their loved ones could be heading into an unhealthy relationship with internet games. Checking in and addressing the underlying concerns may be the best way to avoid mental health crises.