caffeine and job performance: Effectiveness of caffeine and naps on night worker performance
Let's be honest, we all enjoy a nice nap every now and then. Whether it be between classes or on a rainy Sunday, naps help us feel refreshed from a long week. If there is no time for a nap, a cup of joe is the go-to pick me up. Our tiredness has kept a coffee shop open on every street corner. As refreshing as caffeine and rest can be, they are essential for some people working oddly-scheduled jobs.
Working the night shift
Night shift workers keep our communities running. From the emergency department nurses taking the midnight shift to the workers restocking our grocery stores, night shift workers are essential for a smooth and coherent society. To help these important workers function at their best, researchers wanted to determine the most effective way to promote alertness in the late hours.
To evaluate the effects of napping, caffeine, and napping plus caffeine on performance and alertness in both laboratory and field settings.
Source: Laboratory and Field Studies of Naps and Caffeine as Practical Countermeasures For Sleep-Wake Problems Associated With Night Work
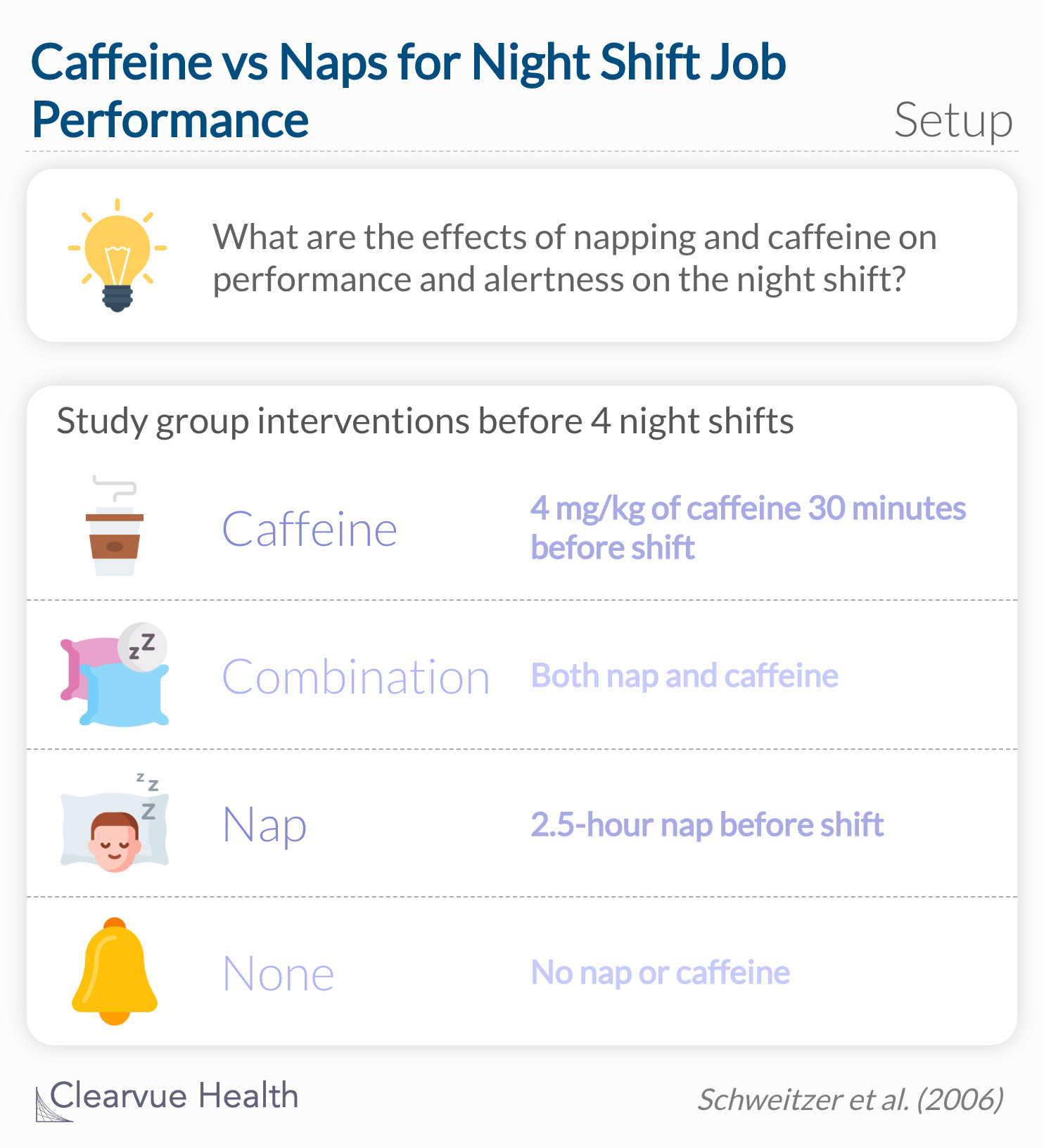
Four groups of night shift workers were assigned to different interventions: caffeine, nap, combination, and none. Each group followed the intervention for 4-night shifts and recorded their sleepiness throughout the night. They were also given vigilance tests that measured job performance.
Group differences were present on night 1 only,
with CAF (mean KSS = 5.4 [SD 1.9]) and NAP+CAF (mean KSS
= 4.8 [SD 1.7]) reporting less sleepiness than PBO (mean KSS =
6.8 [SD 1.6]); P = .029 and P = .001, respectively) with a trend for NAP (mean KSS = 5.7 [SD 1.8]) to be less sleepy than PBO
(P = .07).
Participants who had a combination of napping and caffeine reported the lowest sleepiness scores, meaning they were the least sleepy. There were overlaps when comparing each night, but naps and caffeine were overall an effective strategy in reducing sleepiness. Job performance was also improved by a combination of napping and caffeine based on the vigilance test. Obviously there are many factors that can influence someone's tiredness during a night shift, but this study supports the use of caffeine and naps to battle the heavy eyelids.
Driving on the job
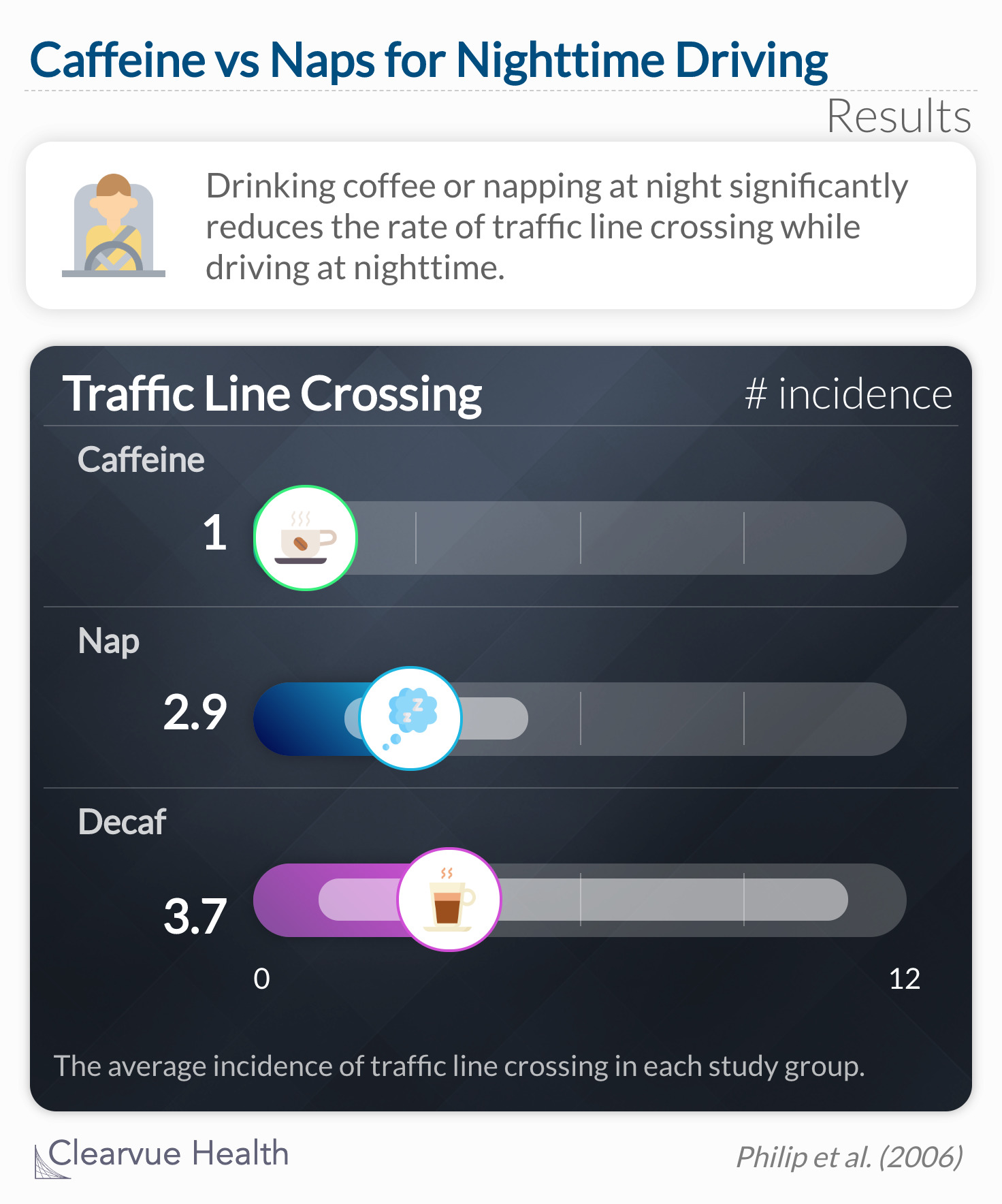
To test the effects of 125 mL of coffee (half a cup) containing 200 mg of caffeine, placebo (decaffeinated coffee containing 15 mg of caffeine), or a 30-minute nap (at 1:00 a.m.) in a car on nighttime driving performance.
Source: The effects of coffee and napping on nighttime highway driving: a randomized trial
Truck driving is another job that requires alertness at odd times. The wakefulness of truck drivers is imperative for the safety of not only themselves by anyone else on the road. A sample of truck drivers was split into three groups: caffeine, nap, and decaf coffee. They measured driving effectiveness by how often the driver veered across traffic lines while driving 125 miles between 2:00 am and 3:30 am. Both caffeine and naps significantly reduced the rate of traffic line crossing compared to decaf coffee consumption.
Drinking coffee or napping at night statistically significantly reduces driving impairment without altering subsequent
sleep.
Free caffeine for essential workers?
These studies, along with others, support the consumption of caffeine for improving alertness and job performance among night shift workers. The productivity and safety of nightshift workers should be a major concern for company leaders and oversight organizations. If something as simple as a cup of coffee can promote the success of these workers, that seems to be a small price to pay for the prosperity of companies and society as a whole.