Impulsive behavior in adults with attention deficit/ hyperactivity disorder: characterization of attentional, motor and cognitive impulsiveness
Understanding Impulsivity in Adult ADHD
Malloy-Diniz L, Fuentes D, Leite WB, Correa H, Bechara A
Objectives
The study focused on understanding a specific aspect of ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder), particularly the persistent impulsivity in adults with this condition. The authors aimed to delve into three particular types of impulsivity - attentional, non-planning, and motor - and how these relate to the brain's ability to control impulses.
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is characterized by inattention and/or hyperactivity/impulsivity. Impulsivity persists in adults with ADHD and might be the basis of much of the impairment observed in the daily lives of such individuals. The objective of this study was to ...
Methods
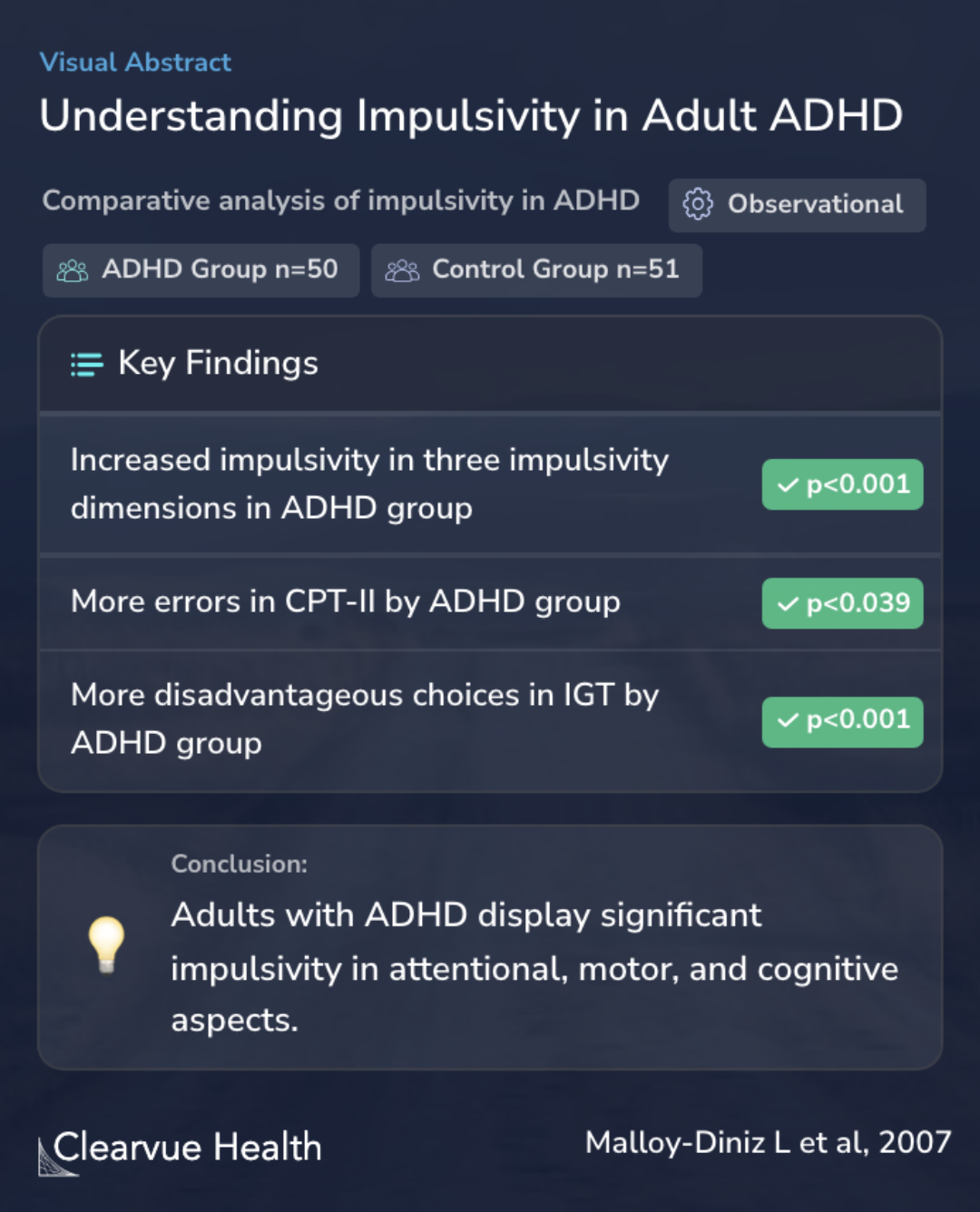
In their research, the authors compared 50 adults diagnosed with ADHD to 51 healthy individuals without ADHD. They used tools like the Barratt Impulsivity Scale Version 11 (BIS), Continuous Performance Task (CPT-II), and the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT) to measure different aspects of impulsivity. This approach provided a comprehensive view of how impulsivity manifests in individuals with ADHD.
We studied a sample of 50 adults with ADHD and 51 healthy comparison controls using the Barratt Impulsivity Scale Version 11 (BIS), and neuropsychological tasks, namely the Continuous Performance Task (CPT-II) and the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT).
Results
In their study, the researchers found that the group of adults with ADHD showed higher levels of impulsivity in three key areas when compared to those without ADHD. These areas were measured using the Barratt Impulsivity Scale (BIS), a tool that helps to understand how impulsive a person is. Not only were they more impulsive, but they also made more mistakes in a task called the Continuous Performance Task (CPT-II). This task tests how well someone can focus and pay attention.
Additionally, they tended to make riskier choices in the Iowa Gambling Task, a task that measures decision-making skills. These results were not just random findings; they were backed up by strong statistical evidence, indicating that these differences were significant and consistent.
The ADHD group showed more signs of impulsivity on the three dimensions of BIS, committed more errors of omission and commission on the CPT-II, and made more disadvantageous choices on the IGT.
Conclusions
These results support the existence of deficits related to three components of impulsivity: motor, cognitive, and attentional among adults with ADHD. Most importantly, this study also highlights the complementary nature of self-report questionnaires and neuropsychological tasks in the as...
Key Takeaways
Context
Impulsivity can be difficult to cope with for those with ADHD. It has been linked with other challenges, including addiction and reckless behavior.
In ADHD, impulsivity can make it difficult to follow social norms others take for granted, for example to wait their turn and to wait in line.