Training of Working Memory in Children With ADHD
Torkel Klingberg , Hans Forssberg, Helena Westerberg
Objectives
ADHD can affect more than just hyperactivity and attention. It can also affect our cognition and the way we think. One of the most significant ways it affects us is in our working memory.
Working memory refers to the small amount of memory we use when performing a task.
This study wanted to see whether practice and training could improve working memory in children with ADHD.
Working memory (WM) capacity is the ability to retain and manipulate information during a short period of time. This ability underlies complex reasoning and has generally been regarded as a fixed trait of the individual. Children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) repre...
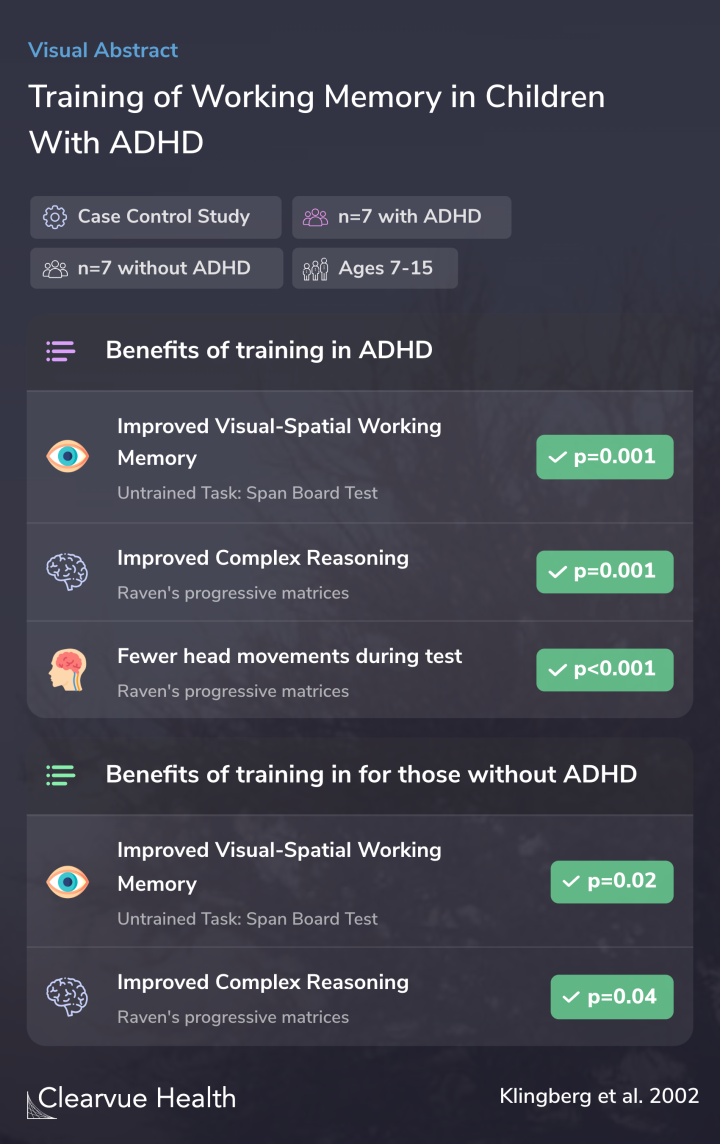
Methods
Researchers had children practice with working memory tasks to see whether this would lead to improvements in their cognitive test results. They tracked their performance over time and tested them on other working memory tests to see whether improvements in working memory carried over to working memory in general.
In the present study, we used a new training paradigm with intensive and adaptive training of WM tasks and evaluated the effect of training with a double blind, placebo controlled design.
Results
Researchers found that working memory training improved performance on working memory tests, including tests that the children were not trained on. This suggests that training can help with working memory in general.
Children without ADHD who were trained also performed better on complex reasoning tests, and they had fewer head movements during the test.
There was also evidence that children without ADHD benefited from training, suggesting that practice with cognitive tasks may help healthy individuals.
Training significantly enhanced performance on the trained WM tasks. More importantly, the training significantly improved performance on a nontrained visuo-spatial WM task and on Raven's Progressive Matrices, which is a nonverbal complex reasoning task. In addition, motor activity--as m...
Conclusions
Studies have shown that working memory deficits are quite common among those with ADHD:
Based on these results, researchers concluded that working memory training could potentially improve some of the cognitive deficits in ADHD.
Subsequent studies have found similar benefits of brain training in working memory:
These results demonstrate that performance on WM tasks can be significantly improved by training, and that the training effect also generalizes to nontrained tasks requiring WM. Training improved performance on tasks related to prefrontal functioning and had also a significant effect on ...