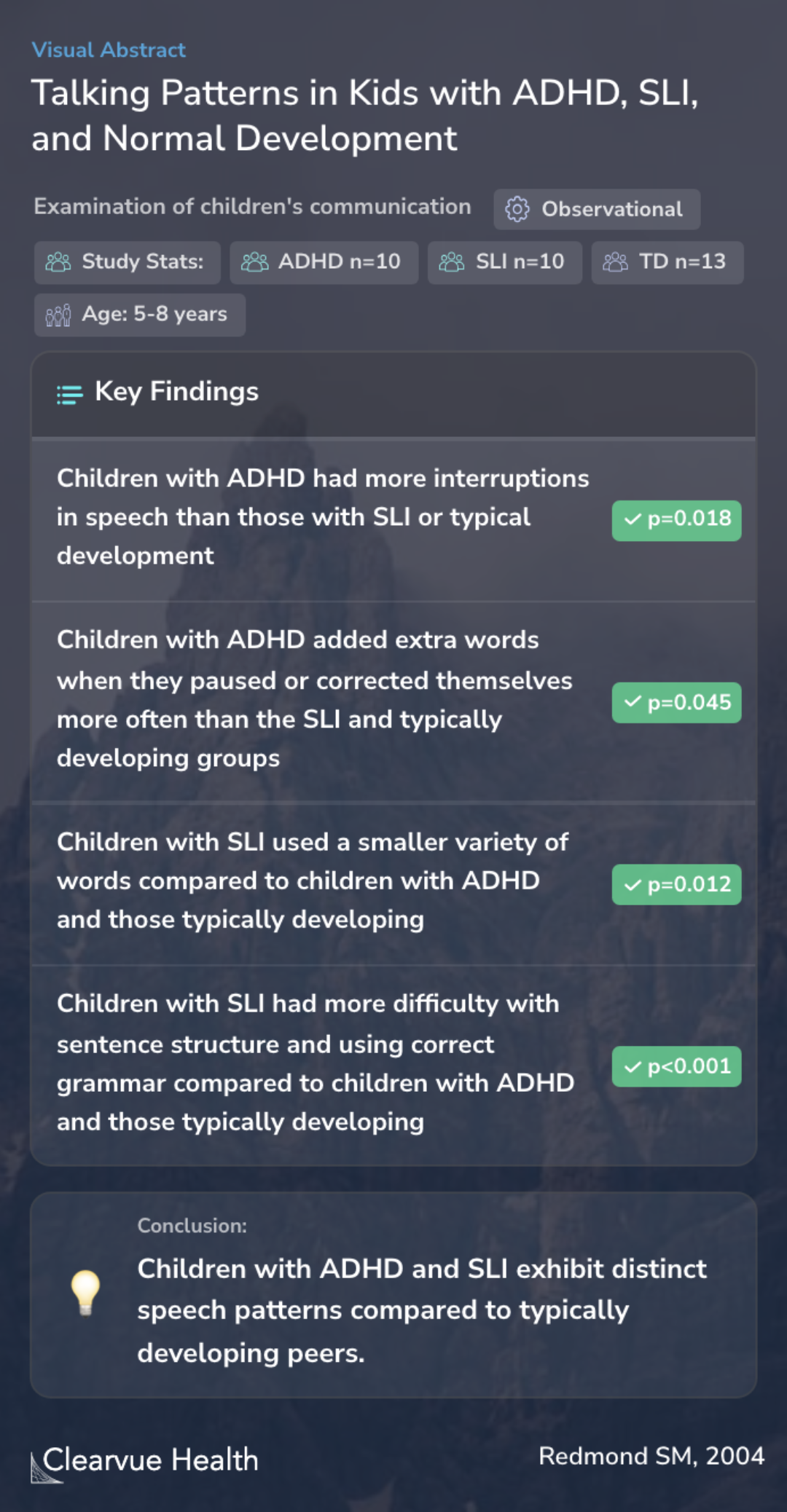
Conversational profiles of children with ADHD, SLI and typical development
Talking Patterns in Kids with ADHD, SLI, and Normal Development
Redmond SM
Objectives
The study aimed to explore how children with ADHD, children with SLI, and children with typical development differ and resemble each other in terms of conversational abilities. By focusing on specific language impairment indicators during conversations, the researchers sought to understand the unique and shared characteristics of language use among these groups.
Conversational indices of language impairment were used to investigate similarities and differences among children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), children with Specific Language Impairment (SLI) and children with typical development (TD).
Methods
In this study, the examination centered around observing and analyzing children's communication skills. The research included children from three distinct groups: those with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), those with Specific Language Impairment (SLI), and those with typical development (TD). The age range of the participants was between 5 to 8 years. The methods employed aimed to differentiate between these groups based on their utterance formulation and language complexity.
Utterance formulation measures (per cent words mazed and average number of words per maze) differentiated the ADHD group from the SLI and TD groups (ADHD>TD=SLI). In contrast, measures of lexical diversity, average sentence length and morphosyntactic development (number of different word...
Results
The findings of the study revealed significant differences and variances within the groups concerning their speech and language usage. Children with ADHD displayed more frequent speech interruptions and added extra words during pauses or corrections more often compared to the SLI group and those with typical development. On the other hand, children with SLI showed a lower variety of words, used shorter sentences, and had more difficulties with sentence structure and grammar. Notably, there was a considerable variation in the speaking rate across all groups.
Speech disruptions, often observed as linguistic mazes, involve moments when speech doesn't flow smoothly, marked by pauses, repetitions, or mid-sentence corrections. These disruptions can indicate underlying challenges in language processing or executive functioning.
High levels of within group variation were observed in children's speaking rate (words per minute).
Conclusions
The study's conclusions emphasize the distinct communication challenges faced by children with ADHD, SLI, and those with typical development. These differences have important implications for the differential diagnosis and understanding of developmental language disorders. By identifying specific speech and language characteristics unique to each group, the research contributes to a better understanding of how these conditions affect children's conversational abilities.
In the broader context of research on language impairments and ADHD, this study aligns with other findings that highlight the complex relationship between attention disorders, language development, and social communication skills. Such research underscores the necessity for tailored interventions and supports that address the specific language and communication needs of children with developmental challenges.
Implications for differential diagnosis and the establishment of phenotypes for developmental language disorders are discussed.
Key Takeaways
Context
The study underlines the importance of delving deeper into the language characteristics of children with ADHD, revealing similarities and differences in language skills when compared to their peers without ADHD. It supports the notion that while children with ADHD may have comparable vocabulary levels, their grammar and conversational abilities often lag behind, potentially impacting their social interactions and academic performance.
Furthermore, the research connects with findings from Staikova et al. in 2013, which investigated the social and language challenges faced by children with ADHD. This study suggested that the social difficulties experienced by children with ADHD might be partly attributed to their struggles with using language effectively in social contexts, highlighting the intertwined nature of language skills and social competence.