Structured group psychotherapy in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: results of an open multicentre study
Structured Group Psychotherapy for ADHD
Alexandra Philipsen , Harald Richter, Julia Peters, Barbara Alm, Esther Sobanski, Michael Colla, Mirka Münzebrock, Corinna Scheel, Christian Jacob, Evgeniy Perlov, Ludger Tebartz van Elst, Bernd Hesslinger
Objectives
ADHD is one of the most common psychiatric conditions among children and adults. Studies have shown that therapy can improve ADHD symptoms with or without medication.
This study wanted to build upon a previous study to see if skills-training-focused therapy could improve ADHD symptoms among a larger patient population across different medical centers.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a serious mental disorder that often persists in adulthood. In a pilot study, a structured skills training group program for adult ADHD led to significant symptomatic improvements
Methods
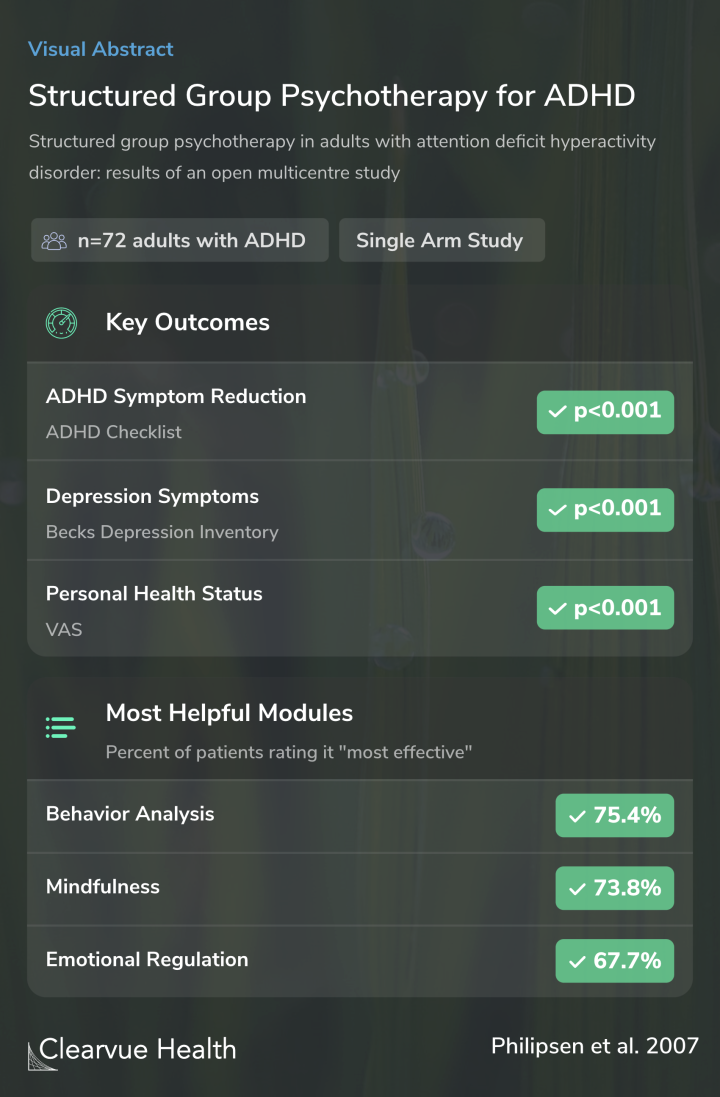
Researchers performed the therapy program on 72 adults with ADHD across four sites/
They measured the symptoms and well-being of the participants before and after therapy to estimate the effectiveness of the therapy.
Of note, the study did not use a control group.
The present study evaluated the program's effectiveness, feasibility, and patient acceptability in a multicenter setting. Seventy-two adult ADHD patients were assigned to 13 two-hour weekly sessions at 4 different therapy sites.
Results
The results showed that participants experienced significant improvements in their ADHD symptoms after therapy compared to where they started. They also had fewer depression symptoms.
This study was a single-arm study without a control or comparison group. Based on this data, we can see that this therapy program likely works better than nothing. Still, it’s difficult to say whether it works better than any other therapy, doctor’s visit, or discussion program.
Among the different modules in the program, participants found the behavior analysis, mindfulness, and emotional regulation modules the most effective.
This is consistent with studies that have shown the benefits of mindfulness therapy in ADHD:
The therapy was well tolerated and led to significant improvements of ADHD, depressive symptoms, and personal health status (p < 0.001). The factors treatment site and medication did not contribute to the overall improvement. Patients regarded the program topics "behavioral analyses," "m...
Conclusions
Based on the results of this study, researchers concluded that group therapy is a promising approach for treating ADHD.
Since this is a single-arm study, further studies with comparison groups will be needed better to understand the effectiveness of skills-based therapy programs in ADHD.
Other similar studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of this type of therapy in ADHD, consistent with these results.
In this multicenter study, the therapy program showed therapist-independent effects and seemed to be disorder-specific. This warrants the effort of organizing further controlled studies.