Self-Esteem Evaluation in Children and Adolescents Suffering from ADHD
Self-esteem in Children with ADHD
Luigi Mazzone,,* Valentina Postorino, Laura Reale, Manuela Guarnera, Valeria Mannino, Marco Armando, Laura Fatta, Lavinia De Peppo, and Stefano Vicari
Objectives
Many studies have examined the connection between ADHD and self-esteem. But the link is not yet clear.
In this study, researchers examined self-esteem among children and teenagers with ADHD. In particular, they examined the link between self-esteem and ADHD symptoms and treatment.
Several recent studies investigated the relationship between self-esteem and ADHD, however, the results are still controversial. In the present study we analyze the characteristics of self-esteem in a sample of children and adolescents suffering from ADHD, with a particular focus on the ...
Methods
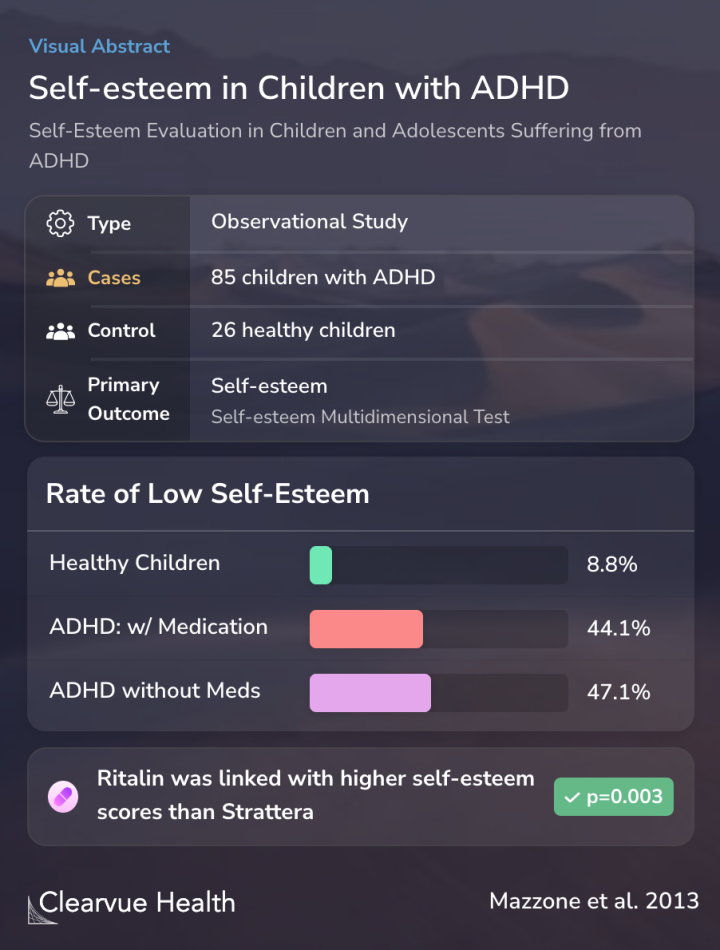
The researchers gathered 85 individuals with ADHD, some on medication and some not, along with 26 healthy individuals. They used a specific test called the Self-esteem Multidimensional Test (TMA) to measure and analyze the self-esteem levels of everyone involved in the study.
A total of 85 patients with ADHD (44 drug-free and 41 drug-treated, 23 of which atomoxetine-treated and 18 Methylphenidate-treated) and 26 healthy controls were enrolled in the study in order to evaluate self-esteem using the Self-esteem Multidimensional Test (TMA).
Results
The results showed that those with ADHD had lower levels of self-esteem on every test that was used.
Nearly half of children with ADHD had low self-esteem. Only 8.8% of healthy children had low self-esteem using the same criteria.
Interestingly, Ritalin was linked with higher self-esteem than Strattera in this study.
ADHD subjects revealed lower scores on all self-esteem domains compared to controls. Both ADHD drug-free (47.1%) and ADHD drug-treated (44.1%) groups showed significantly higher rates of subjects in the pathological range as compared to normal control group (8.8%) (p <.001) with a higher...
Conclusions
Based on these results, researchers concluded that those with ADHD are more likely to have lower self-esteem.
One possible reason may be that ADHD affects our ability to interact with our friends and maintain our relationships. This can lower self-esteem:
Fortunately, research shows that social skills can be trained in those with ADHD:
A lower self-esteem profile is more common in subjects suffering from ADHD than in healthy controls, suggesting the importance of an early detection of psychological well-being in these children in order to reduce the ADHD symptoms long-term impacts.