Self-esteem in special education children with ADHD: relationship to disorder characteristics and medication use
Self-esteem and ADHD in School Children
R Bussing , B T Zima, A R Perwien
Objectives
This study examined self-esteem among those with ADHD in special education.
ADHD can create challenges for students in their lives at school. While ADHD is typically first noticed in the classroom, and most commonly associated with academic difficulties, it can also lead to social challenges:
All of these factors can affect self-esteem in those with ADHD.
To describe the level of self-esteem among the study population, to examine how self-esteem ratings may vary by disorder characteristics and medication use, and to identify predictors of low self-esteem while adjusting for sociodemographic factors.
Methods
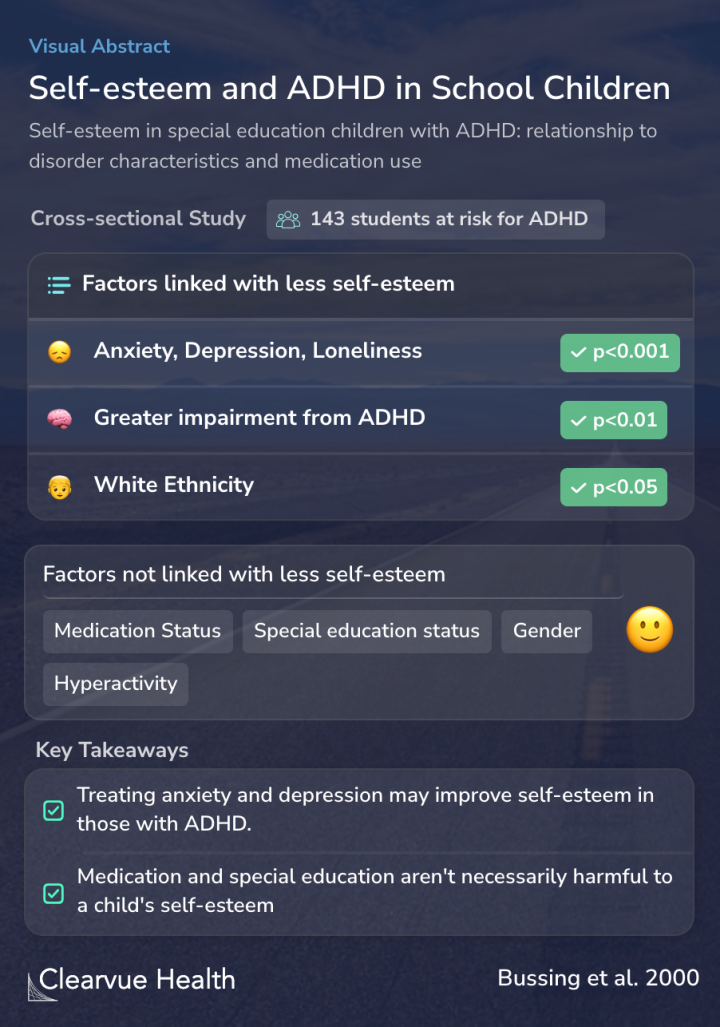
The study surveyed 143 students in special education who were at a high risk of developing ADHD.
They collected information on the participants' ADHD symptoms and medication usage.
In a school district-wide sample of children in special education programs, the authors assessed self-esteem with the Piers-Harris Self-Concept Scale among 143 students at high risk for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in the school year 1995, with an interview participati...
Results
The results showed that, in general, participants in special education didnot have lower levels of self-esteem.
Those with anxiety, depression, and/or loneliness had the highest risk of low self-esteem, followed by those affected the most by ADHD symptoms.
Other factors, such as whether the students were taking medication and whether they were in special education, were not linked with lower self-esteem. Neither were hyperactivity symptoms.
Self-esteem scores, on average, were in the normal range. However, across ADHD comorbidity profiles, children with ADHD and internalizing symptoms had significantly lower self-esteem scores, especially in the areas of anxiety and popularity, than children with ADHD alone or those with co...
Conclusions
These results suggest that anxiety and depression can dramatically lower self-esteem in those with ADHD. This is concerning, given how common anxiety is among those with ADHD:
Fortunately, those on ADHD medication and those in special education were not as strongly affected. This is encouraging, showing that proving effective treatment for children with ADHD doesn't necessarily lower their self-esteem.
Findings suggest that interventions for ADHD should be culturally sensitive as well as aimed at improving a child's functional level and associated internalizing symptoms. Medication use among this younger patient group was not related to self-esteem scores.