Influence of Ethanol and Gender on Methylphenidate Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Ritalin: The effects of gender and alcohol
Summarized by Charles Li, MD
February 20, 2023
Study Objectives
ADHD has been linked with heavy drinking in both teenagers and adults. Those with ADHD may be more likely to develop drinking disorders:
The study examined whether drinking alcohol can increase methylphenidate (Ritalin) in the blood
It also aimed to study whether this effect affects women differently than men.
This study explores the hypotheses that: (1) ethanol will interact with dl-Methylphenidate (MPH) to enantioselectively elevate plasma d-MPH, and primarily yield l-ethylphenidate as a transesterification metabolite; (2) women will exhibit lower relative bioavailability of MPH than men; a...
Methods
Researchers studied ten men and ten women in a randomized crossover study, where they ran different experiments on the same participants. Researchers gave the participants methylphenidate (Ritalin) and also provided some of them with alcohol, either before or after they took the methylphenidate.
They then measured the blood levels of methylphenidate and surveyed them on how they felt.
dl-MPH HCl (0.3 mg/kg) was administered orally 30 min before ethanol, 30 min after ethanol (0.6 gm/kg), or without ethanol, in a randomized, normal subject three-way crossover study of 10 men and 10 women. Pharmacokinetic parameters were compared. Subjective effects were recorded using v...
Results
They found that alcohol affects how your body processes Ritalin.
Taking methylphenidate (Ritalin) with alcohol increased the maximum blood concentration of methylphenidate, regardless of whether participants were given alcohol before or after taking methylphenidate.
This can increase the risk of Ritalin (methylphenidate) abuse and dependence for those who combine methylphenidate and drinking.
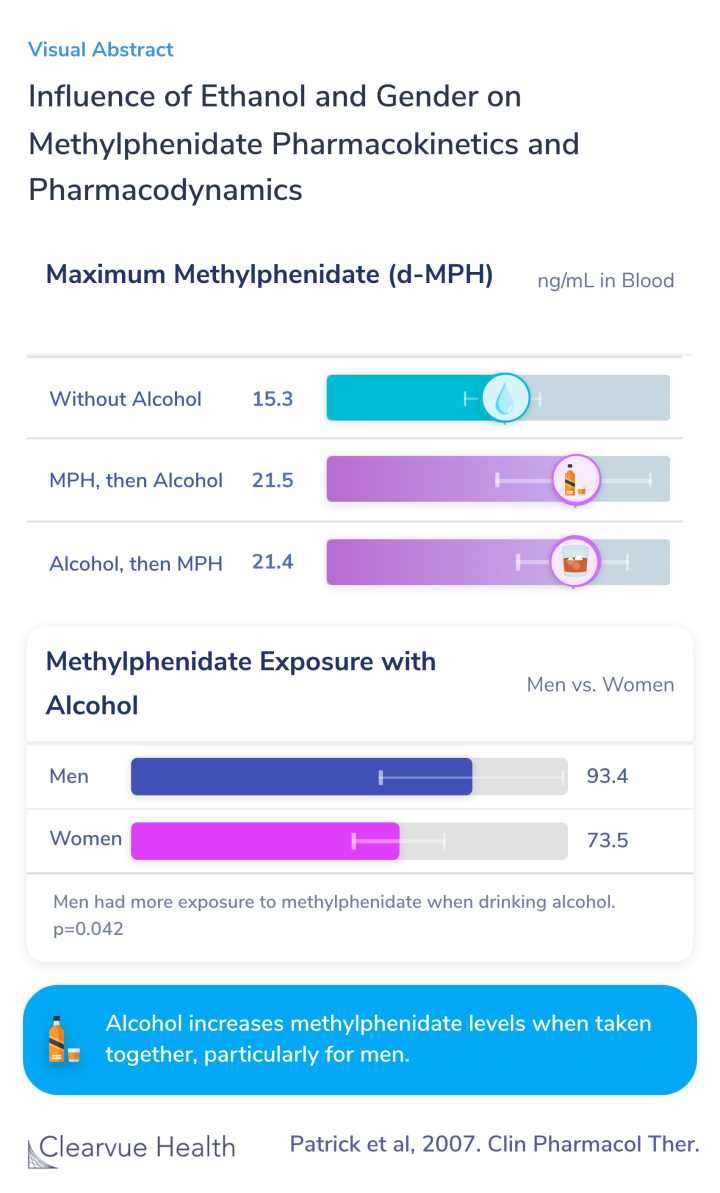
Figure: Blood Levels of Methylphenidate with Alcohol
In the chart below, from the original paper, you can see that individuals who were given methylphenidate and alcohol had a higher concentration of methylphenidate in their blood over the course of the experiment.

Participants who were provided with methylphenidate (Ritalin) and Alcohol had significantly higher exposure to methylphenidate.
Ethanol after or before MPH significantly (P<0.0001) elevated the geometric mean for the maximum d-MPH plasma concentration (Cmax (±SD)) from 15.3 (3.37) ng/ml to 21.5 (6.81) and 21.4 (4.86), respectively, and raised the corresponding geometric mean for the area under the concentration–t...
Methylphenidate, Alcohol, and Gender
This effect was particularly strong in men with higher blood levels of methylphenidate when given alcohol and Ritalin.
However, when participants were asked how strongly they felt the effects of the drug, women were more likely to describe feeling stronger effects than men.
Conclusions
This study provides evidence that alcohol affects how our bodies process Ritalin. When we use alcohol with Ritalin, we can potentially increase the amount of Ritalin in our blood.
While both alcohol and Ritalin can be used as part of a moderate lifestyle, they can potentially increase the risk of addiction when combined.
This effect is particularly strong in men, though women report feeling more effects when provided with alcohol and methylphenidate.
There are other risks as well when combining ADHD medication with alcohol, including rare cases of mortality:
If the poor metabolizer of MPH proves to be a distinct phenotype, determining the genetic mechanism may be of value for individualizing drug therapy. The more pronounced stimulant effects experienced by women have sex-based abuse liability implications.