Methylphenidate but not atomoxetine or citalopram modulates inhibitory control and response time variability
Ritalin, reaction time, and response inhibition in healthy adults
L Sanjay Nandam, Robert Hester, Joe Wagner, Tarrant D R Cummins, Kelly Garner, Angela J Dean, Bung Nyun Kim, Pradeep J Nathan, Jason B Mattingley, Mark A Bellgrove
Objectives
Response inhibition plays a pivotal role in conditions such as ADHD. It refers to our ability to stop ourselves from following every impulse. It is a part of executive function that allows us to step back and think about things.
We know that ADHD medication can dramatically improve ADHD symptoms. But it’s still not entirely clear how they work.
This study aimed to help further understand how medications affect response time. Doing so helps us understand how ADHD medications work.
Response inhibition is a prototypical executive function of considerable clinical relevance to psychiatry. Nevertheless, our understanding of its pharmacological modulation remains incomplete.
Methods
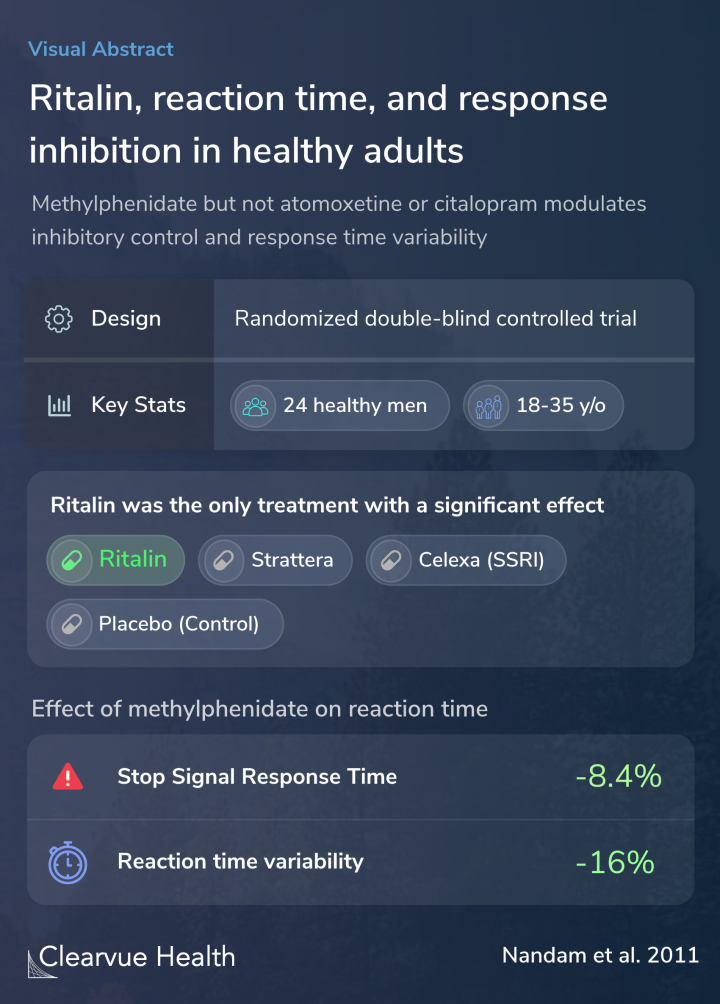
Researchers conducted a small clinical trial comparing the generic forms of Ritalin, Strattera, and Celexa.
To test the effects of the medication, researchers performed a stop signal inhibition test, a cognitive test used to evaluate response inhibition.
We used a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover design to examine the effect of an acute dose of methylphenidate (MPH) (30 mg), atomoxetine (ATM) (60 mg), citalopram (CIT) (30 mg), and placebo (PLAC) (dextrose) on the stop signal inhibition task in 24 healthy, right-han...
Results
The results showed that methylphenidate was uniquely effective in improving response inhibition.
In this test, participants were rated on their ability to respond to stop signals, which those with ADHD and impulsivity struggle to do.
Participants who were given Ritalin showed a significant improvement in their ability to inhibit themselves.
They also showed less variability in their results, an effect that is linked to better attention:
Of note, those on Ritalin didn’t necessarily work faster overall; they were just better at responding to stop signals.
This suggests that the effects of Ritalin don’t necessarily come from speeding up our brains. Rather, it helps us inhibit our impulses, a key challenge for those with ADHD.
Methylphenidate led to a reduction in both response time variability and stop-signal reaction time (SSRT), indicating enhanced response inhibition compared with all other drug conditions. Crucially, the enhancement of response inhibition by MPH occurred without concomitant changes in ove...
Conclusions
This study tells us more about the mechanism behind Ritalin’s effectiveness. Medications like Strattera are also effective, but their mechanisms are different.
In the case of Ritalin and possibly Adderall, these data tell us that improving our ability to control our impulses and reactions is a key part of how they work.
An acute dose of MPH but not ATM or CIT was able to improve SSRT and reduce response time variability in nonclinical participants. Improvements in response inhibition and response variability might underlie the reported clinical benefits of MPH in disorders such as attention-deficit/hype...