A possible effect of methylphenidate on state anxiety: A single dose, placebo controlled, crossover study in a control group
Ritalin may reduce anxiety in anxious adults without ADHD
Aviv Segev , Hila Zahava Gvirts , Kevin Strouse , Naama Mayseless , Hagar Gelbard , Yael Doreen Lewis , Yael Barnea , Kfir Feffer , Simone G Shamay-Tsoory , Yuval Bloch
Objectives
Studies have shown that Ritalin can potentially help reduce anxiety in those with ADHD.
This study wanted to see whether methylphenidate, generic Ritalin, could reduce anxiety in those without ADHD.
Methylphenidate affects state-anxiety in ADHD patients. The current study examines the effect of Me- thylphenidate on state-anxiety in healthy subjects.
Methods
This study conducted a small clinical trial on 36 healthy individuals without ADHD.
In a cross-over, randomized, controlled, double-blind study, 36 healthy subjects received either Methylphenidate or placebo.
Results
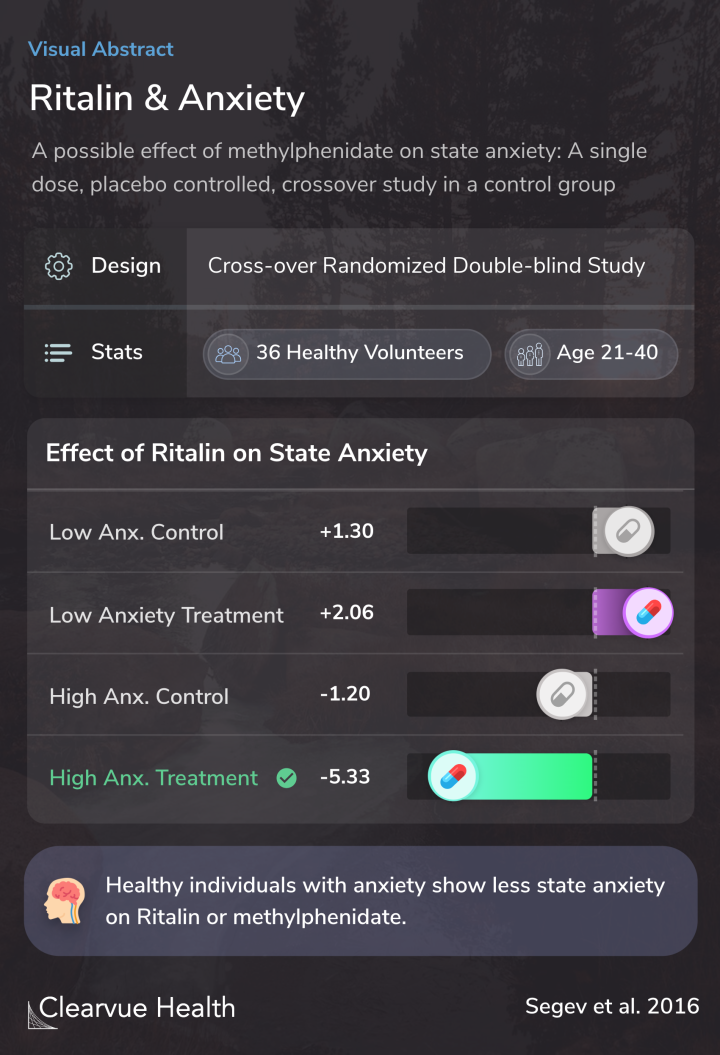
As a group, healthy individuals did not show decreased anxiety on methylphenidate (Ritalin).
When researchers split up the group based on baseline or preexisting anxiety levels, they found a significant difference.
Those with low baseline anxiety showed no significant changes after being given methylphenidate (Ritalin).
However, those with high baseline anxiety showed a significant decrease in anxiety during the test on methylphenidate.
As a group, no change in state- anxiety was detected with Methylphenidate. However, participants reporting higher anxiety levels ex- perienced a significant and specific state-anxiety reduction following Methylphenidate. Moreover, a strong negative correlation was found between the initi...
Conclusions
Many without ADHD have taken Adderall and Ritalin for their purported cognitive benefits. While this practice is dangerous and illegal in many cases, this study shows why some without ADHD feel stimulants can help.
The results show that those with anxiety can experience some benefits of anxiety reduction, even if they don’t have ADHD.
The authors confirmed that the effect on anxiety was independent of any impact on attention.
It is important to note that stimulant medications are not indicated for anxiety treatment or are particularly effective in treating anxiety.
If you or a loved one have test anxiety, but do not have ADHD, talk to your doctor to see what treatment options are available specifically for anxiety.
These data are also particularly helpful in helping us understand the mechanism of Ritalin. For those with ADHD, it can be difficult to tell the cause of improvement.
Since these study subjects did not have ADHD, researchers determined that Ritalin has some effect in reducing anxiety.
Our results point to the state- dependent effects of Methylphenidate on anxiety.