Physical Activity, Affect, and Cognition in Children With Symptoms of ADHD
Caterina Gawrilow , Gertraud Stadler , Nadine Langguth , Alexander Naumann , Antje Boeck
Objectives
Exercise has a wide array of benefits for mental health, along with its known benefits for physical health.
The study wanted to examine the effects of exercise on children with ADHD to see whether it could benefit their symptoms and overall mental well-being.
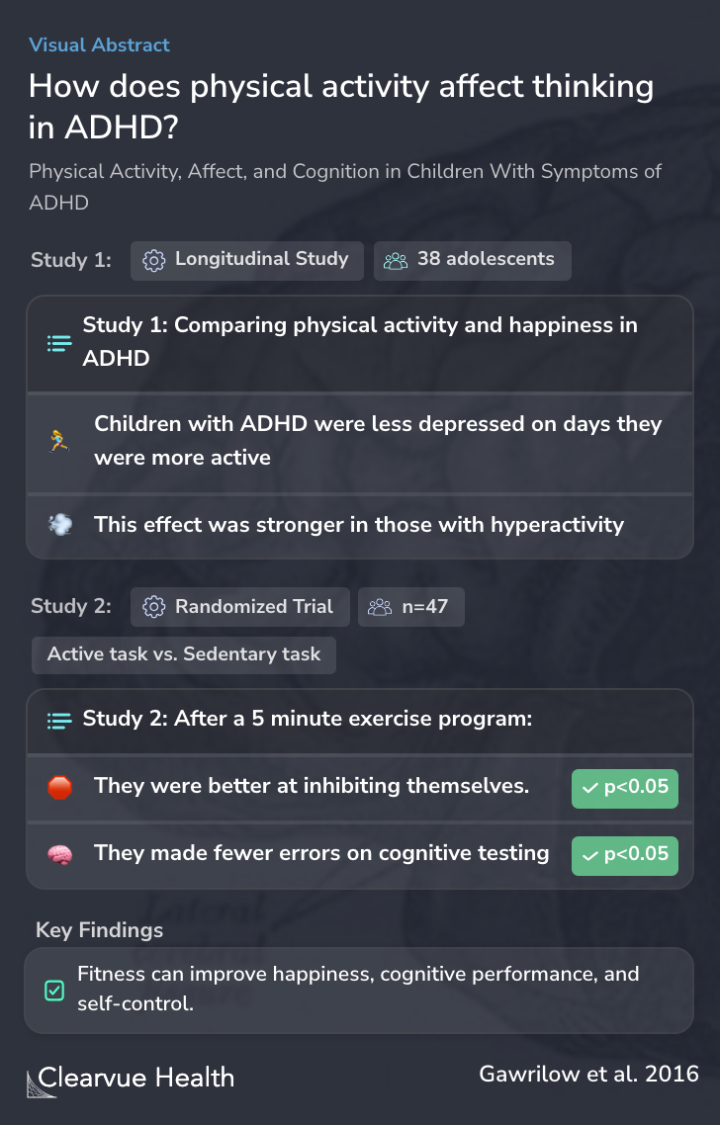
To examine the role of physical activity in determining the affect and executive functioning of children with symptoms of ADHD.
Methods
Researchers first gathered data from a group of adolescents with ADHD to see whether there are any links between exercise and their day-to-day mental health.
They then conducted a small trial where they assigned some children to receive an exercise program and compared them to children who did not receive an exercise program.
In Study 1, the association between physical activity and affect in the daily lives of children with varying degrees of hyperactivity was examined. In Study 2, children with ADHD were randomly assigned a physical activity or a sedentary task before working on a task requiring executive c...
Results
Children with ADHD reported being less depressed on days when they exercised.
Those who are more active in the daytime felt less depressed at night.
This effect was stronger for children with stronger hyperactivity symptoms of ADHD.
After a five-minute exercise program, researchers found that children were better at inhibiting themselves on a cognitive test. They also made fewer errors, suggesting exercise could improve cognition for those with ADHD.
Lack of physical activity was shown to relate to depressed affect, more strongly in participants with severe hyperactivity symptoms (Study 1). The physically active participants showed improved executive functioning after only 5 min of vigorous activity; the sedentary control participant...
Conclusions
These results demonstrate the benefits of exercise on ADHD symptoms.
Previous studies have linked exercise with improved ADHD symptoms:
This study adds to this research by providing evidence that even short periods of exercise can lead to real improvements in cognition and mood.
These results indicate that interventions to increase the level of physical activity in children with and without ADHD might improve affect and executive functioning.