Once-Daily Atomoxetine for Adult Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
November 2, 2022
Introduction
This study aimed to test whether Strattera given once a day, instead of twice a day, could effectively reduce ADHD symptoms in adults.
Researchers had previous established that Strattera twice a day works in adults.
This paper helped establish the effectiveness of once-a-day Strattera in adults, and provided valuable data to help us further understand the effects of Strattera.
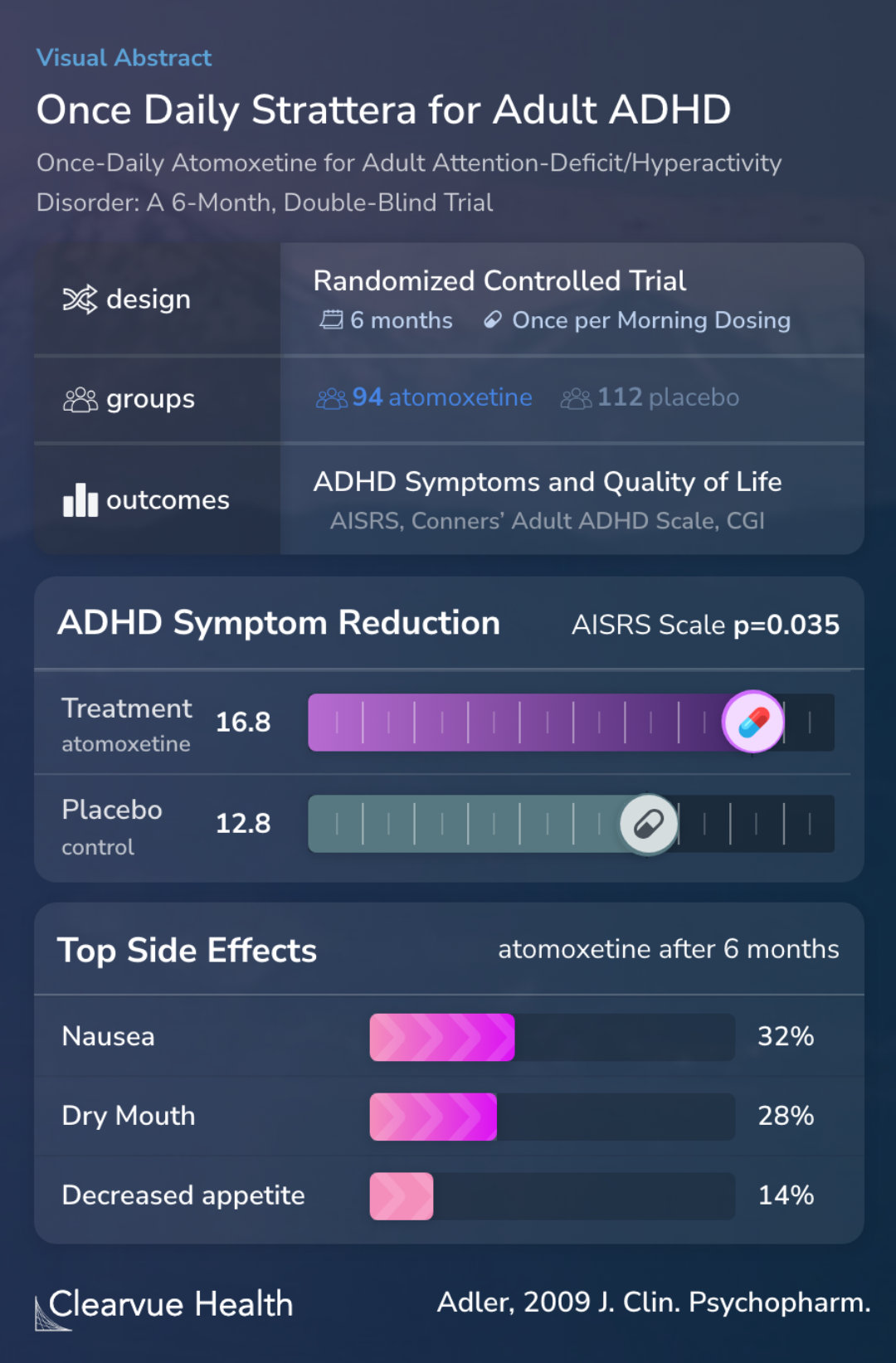
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 6-month trial examined the efficacy and safety of once-daily morning-dosed atomoxetine in adult patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and the efficacy of atomoxetine in ameliorating symptoms through the evening ho...
Methods
Researchers randomly selected patients to receive either Strattera or a placebo control. They measured the effectiveness of the medication by testing participants for ADHD symptoms and quality of life before and after the treatment.
Results
Overall, 94 patients randomized to atomoxetine and 112 patients randomized to placebo completed the study. On the AISRS total score, Conners' Adult ADHD Rating Scale-Investigator Rated: Screening Version evening index total score, Clinical Global Impressions-ADHD-Severity of Illness scor...
94 volunteers given Strattera and 112 given a placebo control completed the study. Those given Strattera had a higher quality of life and fewer ADHD symptoms than those given the control.
At 6 months, the chart below shows that those given Strattera had significantly greater symptom reduction than those given the control.
These data suggest that once-a-day Strattera can effectively reduce ADHD symptoms in adults.
Nausea, dry mouth, fatigue, decreased appetite, urinary hesitation, and erectile dysfunction were the treatment-emergent adverse events reported significantly more often with atomoxetine. Discontinuations due to adverse events were 17.2% and 5.6% for atomoxetine and placebo, respectively...
There were side effects found in the study.
Overall, 17.2% of those on Strattera left the study due to side effects, compared to 5.6% of those given the placebo control.
This suggests that for some, Strattera can cause notable side effects.
The most common side effects were nausea, dry mouth, fatigue, and decreased appetite. All of these side effects were significantly more common in the treatment group than the control group.
Conclusions
Based on the data above, researchers concluded that Strattera given once a day can effectively reduce ADHD symptoms throughout the entire day.
Once-daily morning-dosed atomoxetine is efficacious for treating ADHD in adults when measured 10 weeks and 6 months after initiating treatment. Atomoxetine demonstrated significant efficacy that continued into the evening. Adverse events were similar to previous trials.