Mindfulness vs psychoeducation in adult ADHD: a randomized controlled trial
E Hoxhaj , C Sadohara , P Borel , R D'Amelio , E Sobanski , H Müller , B Feige , S Matthies , Alexandra Philipsen
Objectives
This study wanted to see whether mindfulness can be a good treatment for ADHD.
Therapy and education about ADHD are validated and commonly used techniques for ADHD treatment. Studies have shown that they can improve outcomes when combined with medication.
Mindfulness is also a promising approach for ADHD treatment, but it has not been tested in comparison with traditional psychoeducation techniques.
The study ran a small trial comparing mindfulness with psychoeducation to see whether mindfulness is effective and how well it compares with psychoeducation.
Mindfulness training is a promising treatment approach in adult ADHD. However, there has not yet been a randomized controlled trial comparing mindfulness to an active control condition. In this study, we assessed the efficacy of a mindfulness training program (MAP) compared to structure...
Methods
Researchers recruited adults with ADHD who were not on medication. They randomly assigned some adults to receive mindfulness training and others to receive psychoeducation.
At the beginning and end of the study, they measured the symptoms and general well-being of the participants.
After randomization 81 medication-free adult ADHD patients participated either in an 8-week MAP or PE group program. At baseline (T1), after 8 weeks (T2) and after 8 months (T3), severity of ADHD and associated symptoms (depression, general psychopathology, quality of life) were measured...
Results
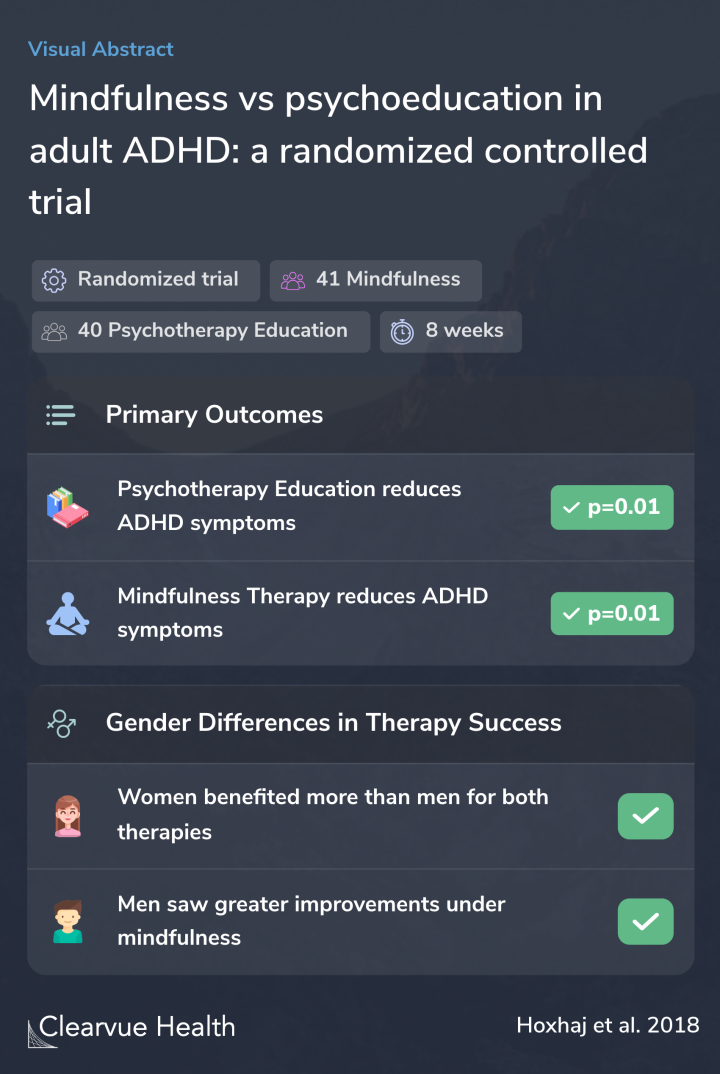
The results showed that psychotherapy education and mindfulness therapy reduced ADHD symptoms similarly. Both therapies were significantly and similarly effective.
These benefits extend beyond just ADHD symptoms. Participants also experienced improvements in their mental health, depression, and general well-being.
There were small differences seen when researchers analyzed results by gender. Generally, women responded better to both types of therapy than men.
Men were more likely to improve with mindfulness therapy than with psychoeducation.
Within the mindfulness program, researchers found that certain aspects of mindfulness correlated with specific improvements, as outlined below:
Both groups showed significant pre-post improvements in observer-rated Inattention scale (p < .001, partial η2 = 0.18) and in associated symptomatology, which persisted through 6 months of follow-up. There were no significant differences regarding symptom reduction between the treatment ...
Conclusions
Researchers concluded that both types of therapy were effective in treating ADHD. There’s no evidence that one is necessarily better than the other. These results suggest that patients with difficulty with medication may want to consider trying one or both of these therapies.
In the current study, MAP was not superior to PE regarding symptom reduction in adult ADHD. Both interventions, mindfulness meditation and PE, were efficacious in reducing symptom load in adult ADHD. Furthermore in exploratory post hoc tests the study provides evidence for a potential ge...