Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy v. treatment as usual in adults with ADHD: a multicentre, single-blind, randomised controlled trial
Mindfulness CBT for ADHD
Lotte Janssen , Cornelis C Kan , Pieter J Carpentier , Bram Sizoo , Sevket Hepark , Melanie P J Schellekens , A Rogier T Donders , Jan K Buitelaar , Anne E M Speckens
Objectives
Studies have shown that medication can be a highly effective treatment for ADHD, but it’s not a cure.å
For many, medication only offers an improvement in symptoms rather than a full resolution.
For others, it may not work at all.
Previous studies have shown that cognitive behavioral therapy can reduce ADHD symptoms, particularly when used alongside medication.
This study wanted to test a mindfulness-based version of cognitive behavioral therapy for treating ADHD.
There is a high need for evidence-based psychosocial treatments for adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) to offer alongside treatment as usual (TAU). Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) is a promising psychosocial treatment. This trial investigated the efficacy of...
Methods
Researchers conducted a randomized trial where they gave a group of participants mindfulness-based cognitive behavioral therapy alongside their normal ADHD treatment. They then compared the group to a second group that only received their normal ADHD treatment.
Researchers used a standard mindfulness-based therapy program modified specifically for adult ADHD. The patient education modules were rewritten to include ADHD education, and the other modules were redesigned to meet the needs of adults with ADHD better.
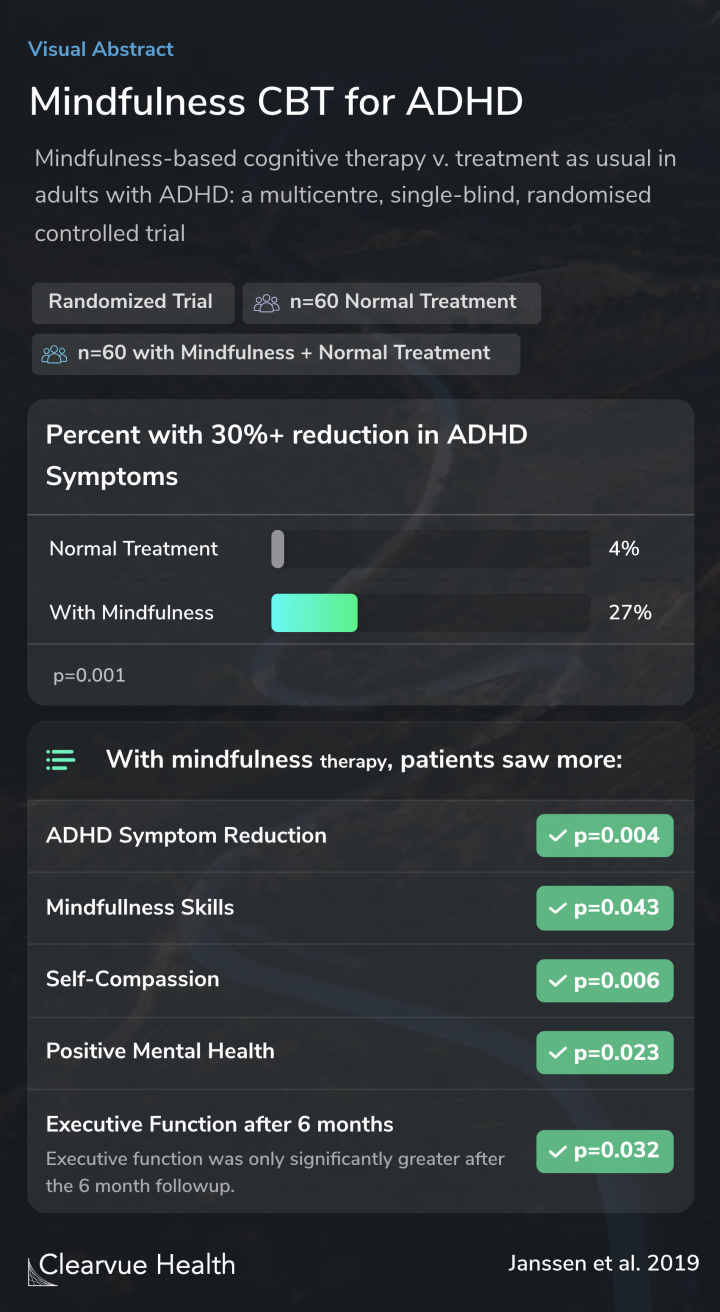
A multicentre, single-blind, randomised controlled trial (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02463396). Participants were randomly assigned to MBCT + TAU (n = 60), an 8-weekly group therapy including meditation exercises, psychoeducation and group discussions, or TAU only (n = 60), which reflected ...
Results
Overall, researchers found that patients who received mindfulness therapy were significantly more likely to experience improvement in their ADHD symptoms.
Both groups received normal ADHD treatment, which typically includes medication. These results suggest that mindfulness may be a useful addition to common ADHD treatment regimens.
Those who received mindfulness training also experienced fewer ADHD symptoms over time. Though the treatment program was short, the chart below shows that the program led to long-term improvements. With the new skills acquired in therapy, patients continued to improve long after the program concluded.
In addition to improvements in ADHD symptoms, patients reported improvements in mindfulness, self-compassion, and mental health.
Those who received therapy reported better executive function, though the improvement was not noticeable until six months after the study.
In MBCT + TAU patients, a significant reduction of clinician-rated ADHD symptoms was found at post-treatment [M difference = -3.44 (-5.75, -1.11), p = 0.004, d = 0.41]. This effect was maintained until 6-month follow-up. More MBCT + TAU (27%) than TAU participants (4%) showed a ⩾30% redu...
Conclusions
The results showed that mindfulness-based therapy may be a good addition to typical ADHD therapies such as medication.
Medication therapy remains a key part of ADHD treatment. This study suggests that adding mindfulness can make it even more effective.
MBCT might be a valuable treatment option alongside TAU for adult ADHD aimed at alleviating symptoms.