Working memory deficits can be overcome: Impacts of training and medication on working memory in children with ADHD.
Medication and Training for Working Memory in ADHD
Joni Holmes, Susan E Gathercole, Maurice Place, Darren L Dunning, Kerry A Hilton, Julian G Elliott
Objectives
Previous studies have linked ADHD with difficulties in working memory. It is one of the most common cognitive deficits in ADHD.
This study wanted to examine whether brain training and medication could improve working memory for those with ADHD.
This study evaluated the impact of two interventions—a training program and stimulant medication—on working memory (WM) function in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Methods
Researchers tested working memory in a group of 25 children with ADHD before and after medication; and before and after a brain training program.
The training program asked participants to perform exercises to improve their working memory and problem-solving abilities.
Twenty-five children aged between 8 and 11 years participated in training that taxed WM skills to the limit for a minimum of 20 days, and completed other assessments of WM and IQ before and after training, and with and without prescribed drug treatment.
Results
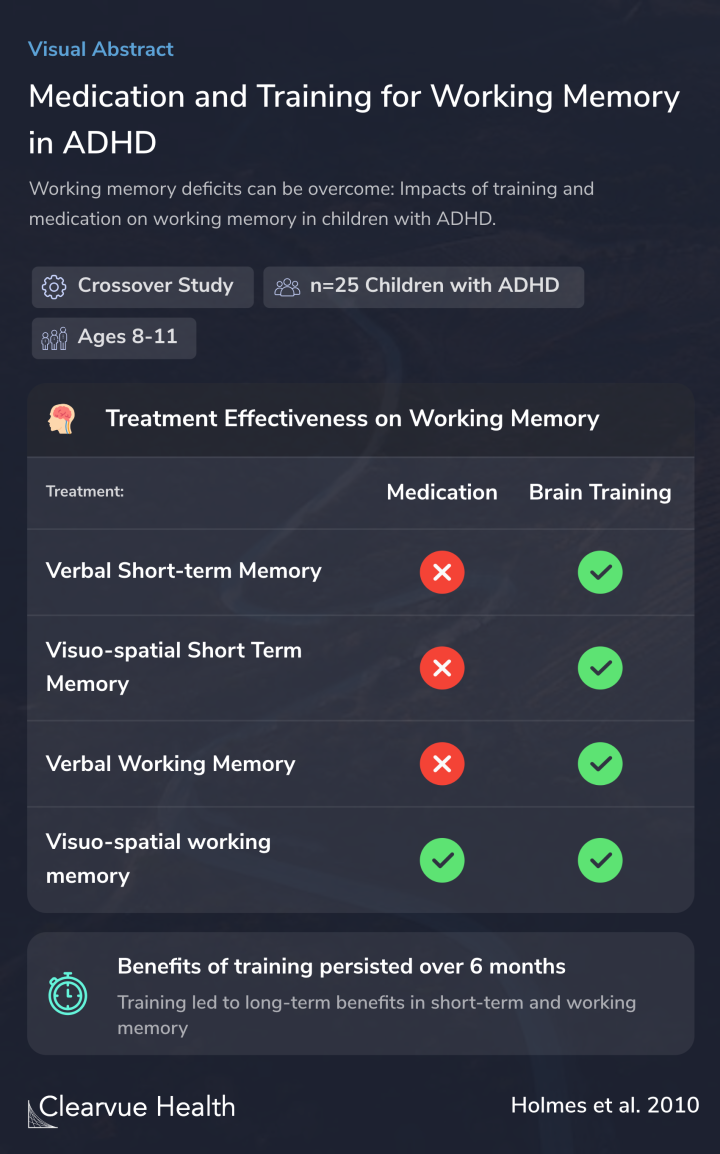
The results showed that medication significantly improved visuospatial working memory but did not significantly improve other measures.
However, brain training led to significant gains across all measures studied.
Additionally, when researchers followed up over six months, they found that participants had sustained long-term improvements, even after the training concluded.
While medication significantly improved visuo-spatial memory performance, training led to substantial gains in all components of WM across untrained tasks. Training gains associated with the central executive persisted over a 6- month period. IQ scores were unaffected by either intervent...
Conclusions
The study provides evidence that brain training may help improve some cognitive deficits for those with ADHD.
In this study, the brain training results were better than the results from medication.
However, the study does have some shortcomings. The study did not have a control group, making it difficult to tell how much of the effectiveness was due to the placebo effect or the treatment. The study also performed both treatments in the same patients in the same order, which makes it less clear how much each treatment contributed to the outcome.
Nonetheless, it does provide evidence that working memory in those with ADHD can improve with the proper treatment.
These findings indicate that the WM impairments in children with ADHD can be differentially ameliorated by training and by stimulant medication.