The IQs of children with ADHD are normally distributed
IQs of Children with ADHD
B J Kaplan, S G Crawford, D M Dewey, G C Fisher
Objectives
This study wanted to analyze the IQ scores of children with ADHD. In the past, some have theorized that children with ADHD may be unusually intelligent.
This study wanted to test his theory by analyzing the IQ scores of children with ADHD, excluding those with reading problems.
The purpose of this investigation was to determine whether or not attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)-when there was an absence of reading problems-was associated with having a high IQ.
Methods
Researchers administered standard IQ tests to the volunteers. They separated students with reading difficulties as a separate analysis. This allowed the study to isolate the effects of ADHD better.
The vocabulary and block design short forms of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Third Edition were administered to 63 children with ADHD, 69 children with reading difficulties (RD), and 68 children with comorbid ADHD + RD.
Results
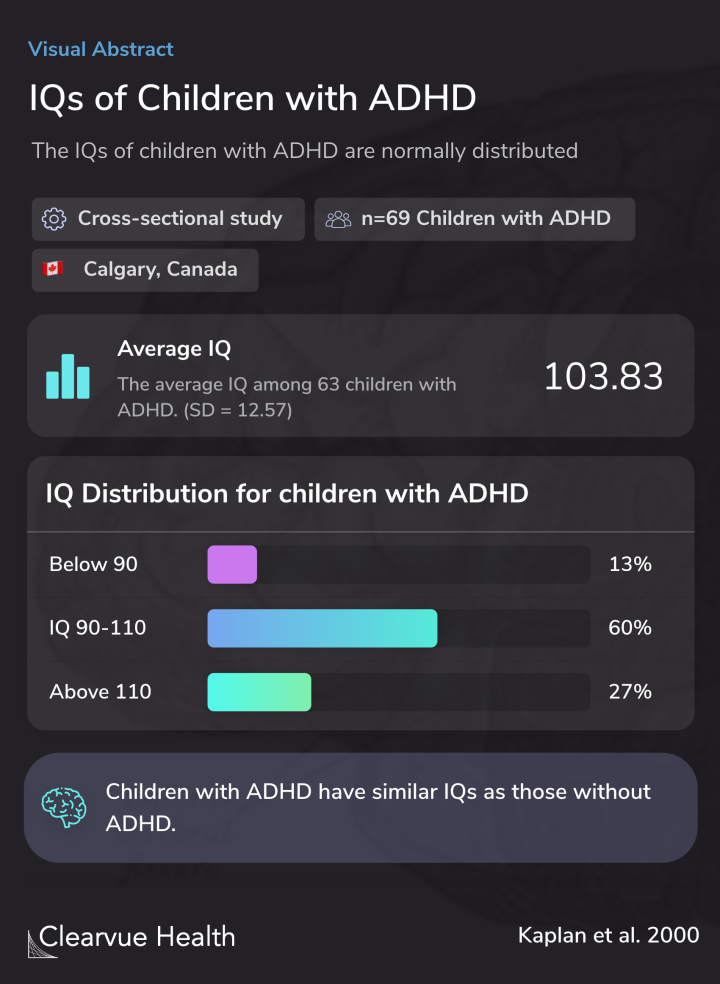
Researchers found that the IQ scores of those with ADHD followed a generally normal distribution. There were some students with unusually high IQs, but there were also students with low IQs.
Most students had near-average IQs.
The average IQ found in the study was around the average for everyone.
Results indicated that the distributions of estimated Full Scale IQs (FSIQ) for each of the three groups of children did not differ significantly from a normal distribution, with the majority of children (more than 50%) in each group scoring in the average range. The percentage of childr...
Conclusions
Based on the study results, researchers concluded that those with ADHD are not necessarily more likely to be unusually intelligent. Their IQ scores are similar to what we expect in children without ADHD. There are brilliant children with ADHD and less intelligent children with ADHD. But, statistically, most are average, just like typical children.
Of note, the researchers did exclude a few students with exceptional intellectual challenges, as the students would have skewed the results. The study also used an abbreviated test correlated with full IQ scores but did not administer a full IQ test.
Nonetheless, the study does offer interesting evidence that children of all intellectual capabilities can develop ADHD. This finding has been confirmed in subsequent studies as well.
It was concluded that children with ADHD are no more likely to have an above-average IQ than are other children.