A two-site randomized clinical trial of integrated psychosocial treatment for ADHD-inattentive type
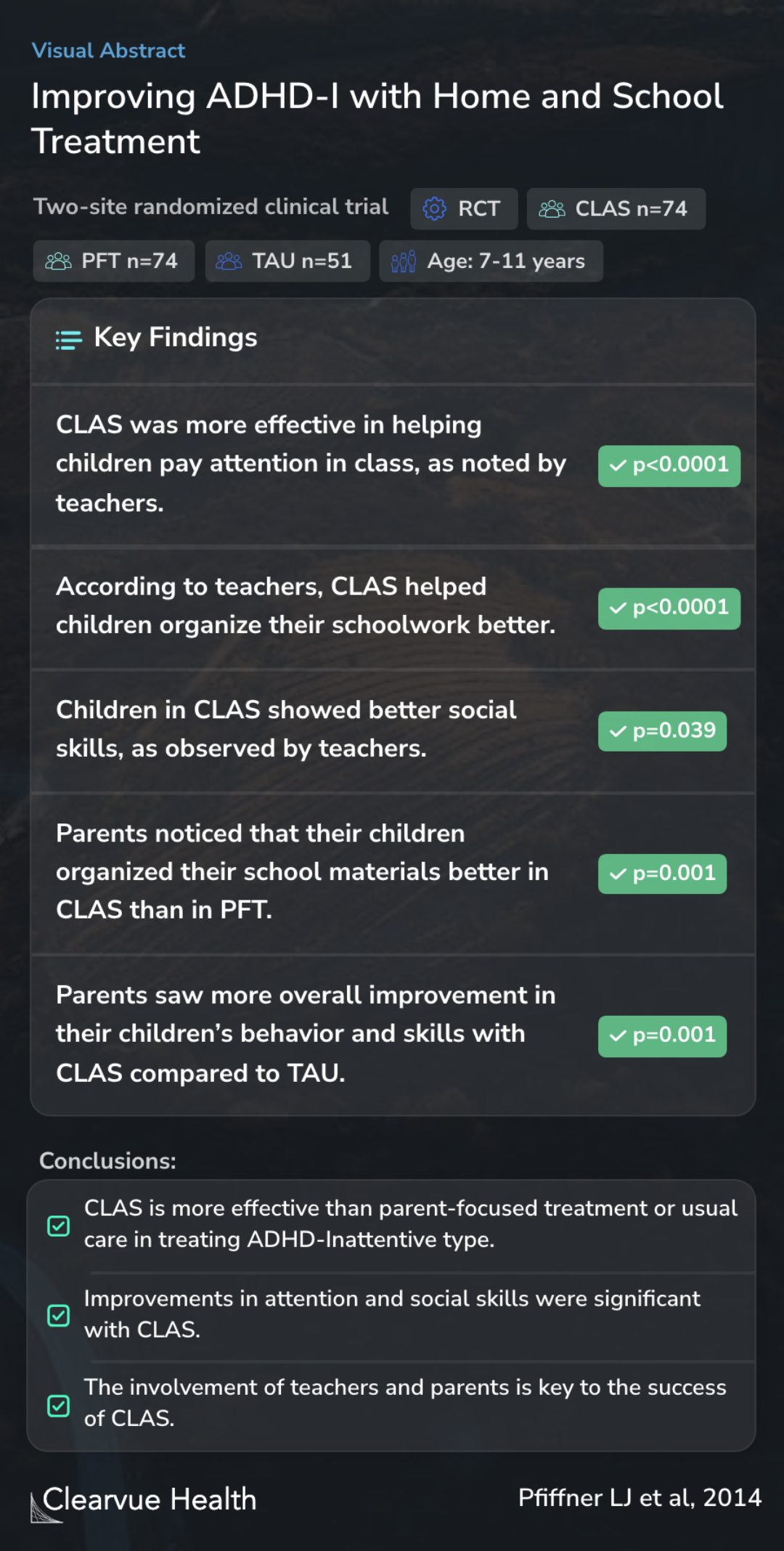
Improving ADHD-I with Home and School Treatment
Pfiffner LJ, Hinshaw SP, Owens E, Zalecki C, Kaiser NM, Villodas M, McBurnett K
Objectives
The study focused on the Child Life and Attention Skills (CLAS) program, designed to help children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder-inattentive type (ADHD-I). CLAS is a behavioral treatment that works across both home and school environments. It's meant to address the challenges that kids with ADHD-I face, especially with homework. These challenges can include problems with organizing and completing assignments, as well as managing time efficiently. Such issues are more pronounced in students with ADHD compared to their peers, often leading to lower academic achievements.
This study evaluated the efficacy of the Child Life and Attention Skills (CLAS) program, a behavioral psychosocial treatment integrated across home and school, for youth with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder-inattentive type (ADHD-I).
Methods
In this study, 199 children between the ages of 7 and 11 were randomly assigned to one of three groups: CLAS, parent-focused treatment (PFT), or treatment as usual (TAU). The aim was to compare the effectiveness of these approaches in addressing inattention, organizational skills, social skills, and overall improvement.
The CLAS program is comprehensive, involving not just the children, but also their parents and teachers. It includes strategies for managing ADHD-I at home, developing social skills and self-management for the children, and classroom management techniques for teachers. The program emphasizes a collaborative approach among all parties involved.
In a 2-site randomized controlled trial, 199 children (ages 7-11 years) were randomized to CLAS (N = 74), parent-focused treatment (PFT, N = 74), or treatment as usual (TAU, N = 51). We compared groups on parent and teacher ratings of inattention symptoms, organizational skills, social s...
Results
Teachers reported that children in the CLAS program showed better attention in class, improved organization of schoolwork, and better social skills compared to those in the other PFT and TAU groups. These improvements were statistically significant, meaning they were likely not due to chance. Parents also noticed that their children in the CLAS program had better organizational skills and overall behavior than those in PFT and TAU groups. This suggests that CLAS effectively brought about positive changes in these children.
CLAS resulted in greater improvements in teacher-reported inattention, organizational skills, social skills, and global functioning relative to both PFT and TAU at posttreatment. Parents of children in CLAS reported greater improvement in organizational skills than PFT and greater improv...
Conclusions
The study concludes that CLAS is more effective than just parent-focused treatment or the usual care for treating children with ADHD-Inattentive type. The involvement of teachers and parents in the CLAS program is crucial for its success, leading to significant improvements in attention and social skills. These findings underscore the importance of a coordinated approach that includes parents, teachers, and children for effectively managing symptoms associated with ADHD-I.
These findings extend support for CLAS across 2 study sites, revealing that integrating parent, teacher, and child treatment components, specifically adapted for ADHD-I, is superior to parent training alone and to usual care. Direct involvement of teachers and children in CLAS appears to...
Key Takeaways
Context
To understand how this study fits into broader research, we can look at other studies. One such study focused on the Homework, Organization, and Planning Skills (HOPS) intervention for students with ADHD. It found that using a structured binder system significantly improved students' organization, planning, and homework management skills. This highlights the importance of structured and organized approaches in assisting students with ADHD.
Another study looked at the effects of Ritalin (methylphenidate) on organizational skills in children with ADHD. While the medication did improve these skills and reduce ADHD symptoms, some children still faced challenges. This suggests that while medication can be helpful, additional treatments or interventions, like CLAS, might be necessary for better outcomes. These studies, when viewed alongside the current research on CLAS, provide a comprehensive picture of the various methods available to support children with ADHD in their academic and social development.