Temporal stability of ADHD in the high-IQ population: results from the MGH Longitudinal Family Studies of ADHD
High IQ ADHD Children as Teenagers
Kevin M Antshel , Stephen V Faraone , Katharine Maglione , Alysa Doyle , Ronna Fried , Larry Seidman , Joseph Biederman
Objectives
ADHD is typically associated with students who struggle in school. As a result, there is some controversy over whether high-IQ teens can have ADHD. Studies have shown that students with high IQ and ADHD can potentially perform reasonably well in school by compensating for their ADHD with intelligence.
This study wanted to understand more about how children with ADHD and high IQ perform as they grow into teenagers. Do they have the same struggles and challenges as average students with ADHD?
The diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in high-IQ youths remains controversial.
Methods
Researchers studied a group of high-IQ students with ADHD and compared them to a group of high-IQ students without ADHD. They followed all the students for four years in high school.
To further explore the diagnostic validity of ADHD in this population, we studied two cohorts of high-IQ youths, both with and without ADHD, across a 4.5-year period.
Results
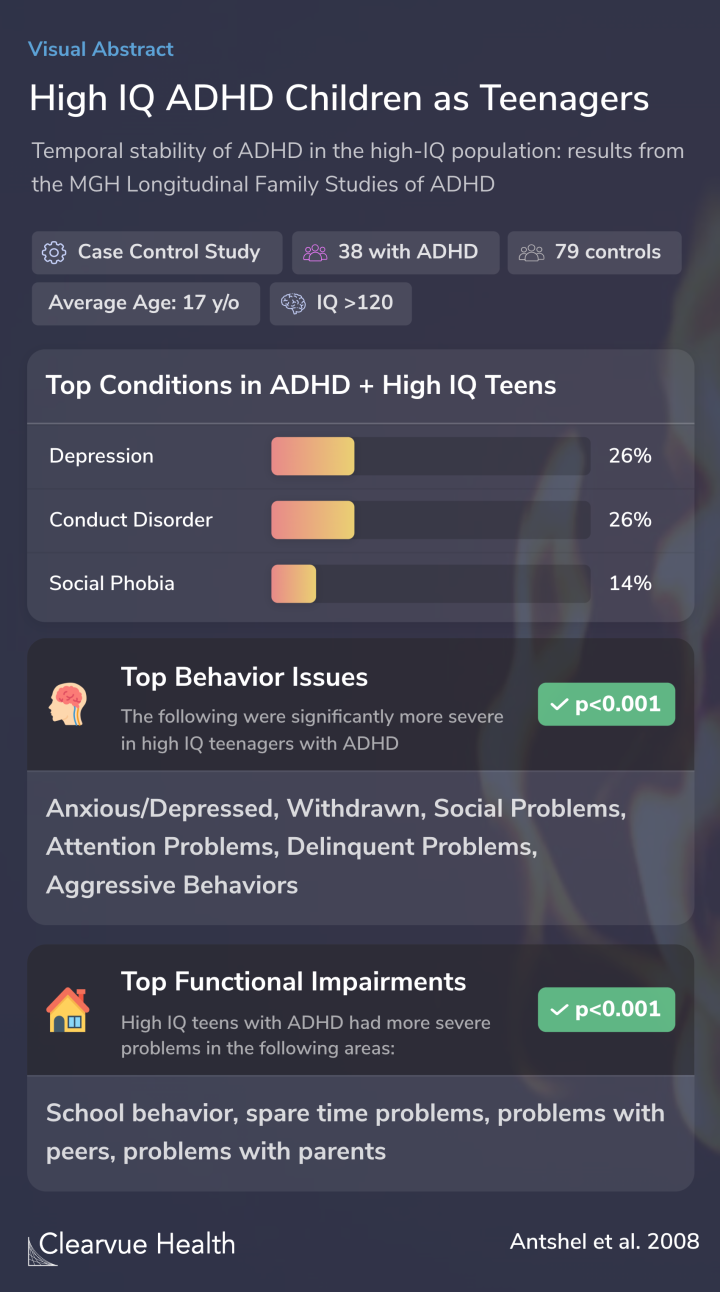
Teenagers with ADHD face more issues at home and school. They were more likely to experience anxiety, social problems, and behavioral issues.
They also had more difficulties with their peers and their parents.
Those with high IQ and ADHD had higher rates of other psychiatric conditions. Compared to the general population, they were at a higher risk of developing conduct disorder, major depressive disorder, and social anxiety.
ADHD is known for its links with other psychiatric conditions. Previous studies have shown that gifted children with ADHD have high rates of other psychiatric conditions. This study confirms that gifted teenagers also experience this link.
However, there were some differences between gifted teenagers with ADHD and other teenagers with ADHD. ADHD is typically associated with higher rates of drug addiction and smoking in teenagers. Teenagers with high IQs and ADHD did not have higher rates of substance abuse, despite their higher rates of psychiatric disorders.
Compared to those without ADHD, high-IQ youths with ADHD had significantly higher rates of mood, anxiety, and disruptive behavior disorders at follow-up. In addition, ADHD status was a significant predictor for higher impairments across most social, academic, and family functional domain...
Conclusions
Based on the study results, researchers concluded that gifted teenagers with ADHD have significant mental health struggles like other teenagers with ADHD. They are more likely to develop mood and behavioral disorders and experience relationship challenges.
These findings confirm that ADHD can be a valid diagnosis even among gifted teenagers.
These results provide further support for the predictive validity of ADHD in high-IQ youths.