Evaluation of group cognitive behavioral therapy for adults with ADHD
Group CBT for Adult ADHD
Jessica Bramham , Susan Young, Alison Bickerdike, Deborah Spain, Denise McCartan, Kiriakos Xenitidis
Objectives
Cognitive behavioral therapy is a commonly used and validated treatment for ADHD. Previous studies have shown that it works particularly well if combined with medication.
This study wanted to see whether group CBT could significantly improve outcomes in adult ADHD compared to medication alone.
If so, group CBT can be a cost-effective treatment option to enhance medication therapy for ADHD.
Just a bit of background, CBT is a therapy designed to help patients cope with symptoms, pursue healthier ways of thinking, and develop helpful behavior patterns.

A brief cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) group intervention was designed to treat comorbid anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem and self-efficacy in adults with ADHD. It was hypothesised that participants would gain knowledge about ADHD, experience a reduction in comorbid symptoms,...
Methods
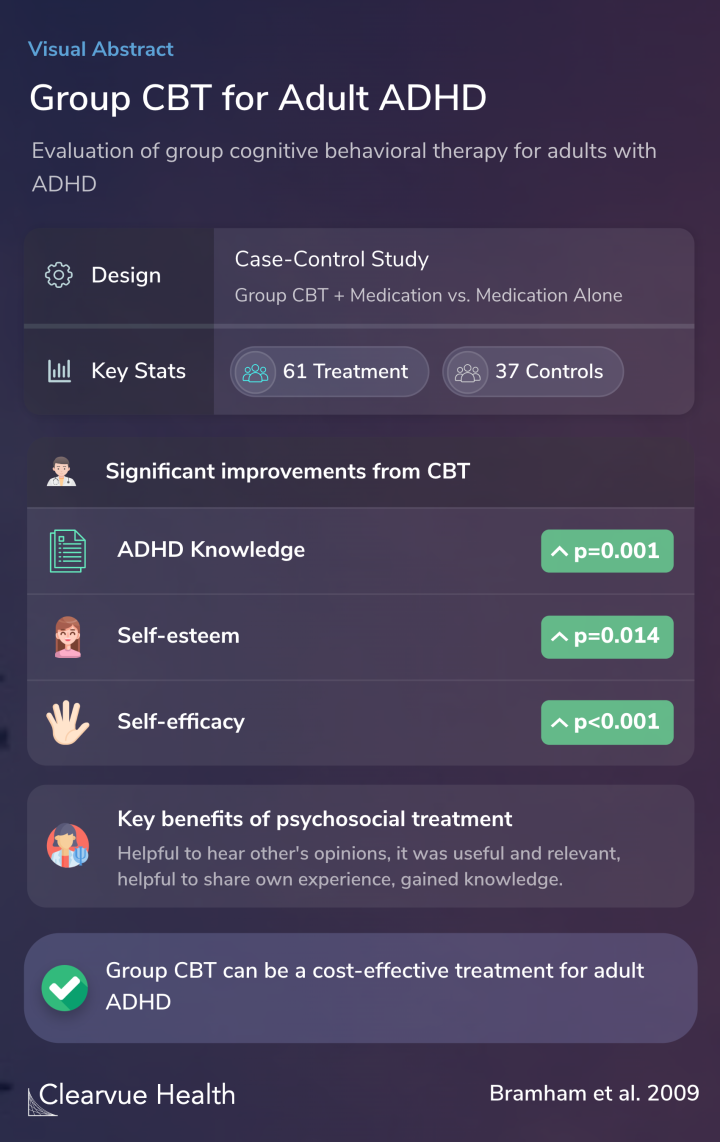
Researchers conducted a case-control study to evaluate group CPT for adult ADHD.
Researchers recruited 61 adults with ADHD and treated them with group CBT. Most of the adults were also receiving medication at the time.
They compared the results to 37 adults in the same clinic receiving medication but not CBT.
The program they developed aimed to teach participants about ADHD and help them develop strategies to deal with the impact of ADHD.
The specific program was designed around the particular advantages of a group setting. Being part of a group allowed for more ideas and practice with communication.
Participants in the study formed a CBT treatment group that attended six workshops and a waiting list control group. The intervention was evaluated with measures assessing knowledge about ADHD, psychological symptoms, and support received. The groups were compared using repeated measures...
Results
Researchers found that those in the treatment group showed significantly improved self-esteem, self-efficacy, and ADHD knowledge compared to those who only received medication.
These improvements were calculated with standardized evaluations provided to those in the treatment and control groups.
The evaluations from the participants showed that they believed they benefitted from being in a group setting.
Many felt that hearing others’ opinions and sharing their experiences was helpful.
These results suggest inherent advantages to being in a group setting.
The CBT group had significantly greater improvement on measures of knowledge about ADHD, self-efficacy, and self-esteem than the control group. Participants' evaluations of the sessions suggested that sharing personal experiences with other adults with ADHD was an important aspect of the...
Conclusions
The results showed that brief group CBT interventions could help treat adult ADHD alongside medication.
Group CBT is cost-effective compared to one-on-one therapy and offers some advantages unique to a group setting.
This study was small, and further research will be needed to confirm these findings. The researchers did not closely match the controls and the treatment groups. The control group also had a relatively low response rate, which can skew the results.
Brief CBT group treatments may be an acceptable and cost-effective intervention for adults with ADHD.