Genetic contributions to the development of ADHD subtypes from childhood to adolescence
Genetics and ADHD Development from Childhood to Adolescence
Larsson H, Lichtenstein P, Larsson JO
Objectives
The study aimed to understand how genes affect the development of ADHD symptoms from childhood to adolescence. This investigation focused on the genetic influences on hyperactive-impulsive and inattentive symptoms, two key subtypes of ADHD.
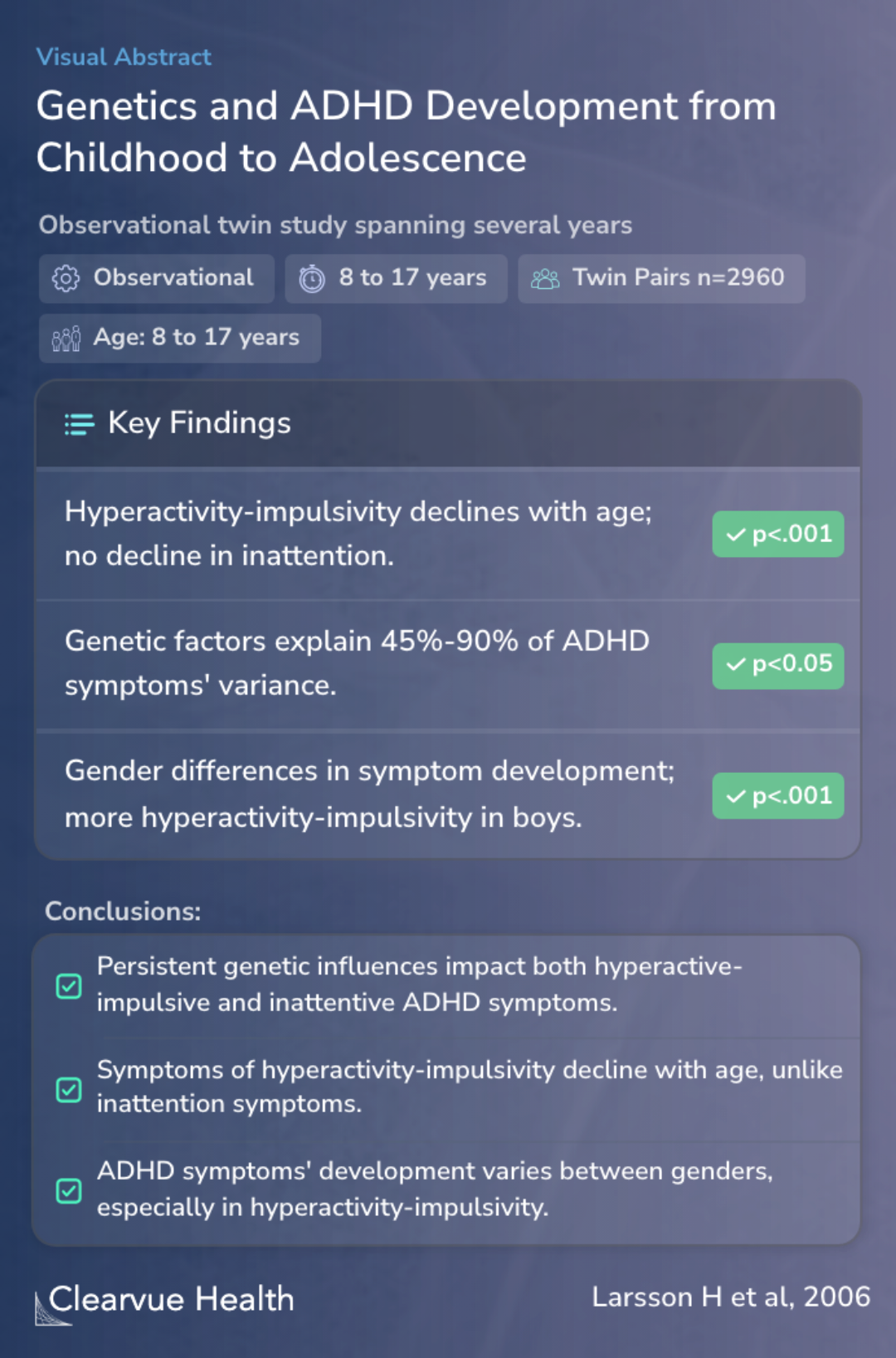
Little is known about how genes influence the development of symptoms included in the DSM-IV subtypes of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) from childhood to adolescence. The aim of this study was to examine genetic influences contributing to the development of hyperactive-i...
Methods
The authors conducted an observational twin study over several years to explore these genetic influences. They included 1,480 twin pairs from Sweden, born between May 1985 and December 1986. Parents of these twins provided information through questionnaires when the twins were aged 8 to 9, 13 to 14, and 16 to 17 years. This approach helped in tracking the changes in ADHD symptoms over time.
The sample included all 1,480 twin pairs born in Sweden between May 1985 and December 1986. Parents responded to mailed questionnaires on three occasions, when the twins were 8 to 9, 13 to 14, and 16 to 17 years old. The authors used dimensional scales of hyperactivity-impulsivity and in...
Results
The study revealed that hyperactivity-impulsivity symptoms tend to decrease as children grow older, while inattentive symptoms remain stable. A significant finding was that genetic factors account for 45% to 90% of the variance in these symptoms across different ages. Additionally, the study found that boys tend to exhibit more hyperactivity-impulsivity than girls, especially in younger years.
Symptoms of hyperactivity-impulsivity declined with increasing age, whereas there was no decline in symptoms of inattention. Persistent genetic influences explain between 45% and 90% of the total genetic variance in hyperactivity-impulsivity and inattention across age. Persistent genetic...
Conclusions
The conclusions of this study align with the genetic basis for the DSM-IV classification of ADHD subtypes. It was found that both cross-subtype (combined hyperactive-impulsive and inattentive) and subtype-specific genetic influences (mainly hyperactive-impulsive or inattentive) are persistent, supporting the idea that genetics play a crucial role in ADHD's development.
The finding of persistent cross-subtype (i.e., combined) and persistent subtype-specific genetic influences (i.e., primarily hyperactive-impulsive and primarily inattentive) are in line with a genetic basis for the DSM-IV classification of ADHD subtypes.
Key Takeaways
Context
The findings of this study add to the existing body of research, such as Wood et al. (2011), which explored the relationship between ADHD and cognitive abilities like IQ. Wood et al. found that while ADHD and IQ are both influenced by genetics and environment, the underlying factors for each are mostly separate. This suggests that ADHD's genetic influences are unique and not simply a byproduct of lower IQ.
Moreover, the research by Roy et al. (2016) provides context to the persistence of ADHD into adulthood. While most children with ADHD improve as they grow, some continue to experience symptoms into adulthood. This study's finding about the significant genetic influence on ADHD's persistence complements Roy et al.'s conclusion that factors like symptom severity and parental mental health are crucial in determining the continuation of ADHD symptoms.