Executive functioning in adult ADHD: a meta-analytic review
A Marije Boonstra, Jaap Oosterlaan, Joseph A Sergeant, Jan K Buitelaar
Objectives
Executive function is believed to play a key role in ADHD.
It encompasses functions such as staying attentive and impulse control. These are areas where those with ADHD can struggle.
However, ADHD is a broad condition linked with many symptoms. As a result, the researchers in the study wanted to see how strong the link between ADHD and executive function was.
Several theoretical explanations of ADHD in children have focused on executive functioning as the main explanatory neuropsychological domain for the disorder. In order to establish if these theoretical accounts are supported by research data for adults with ADHD, we compared neuropsychol...
Methods
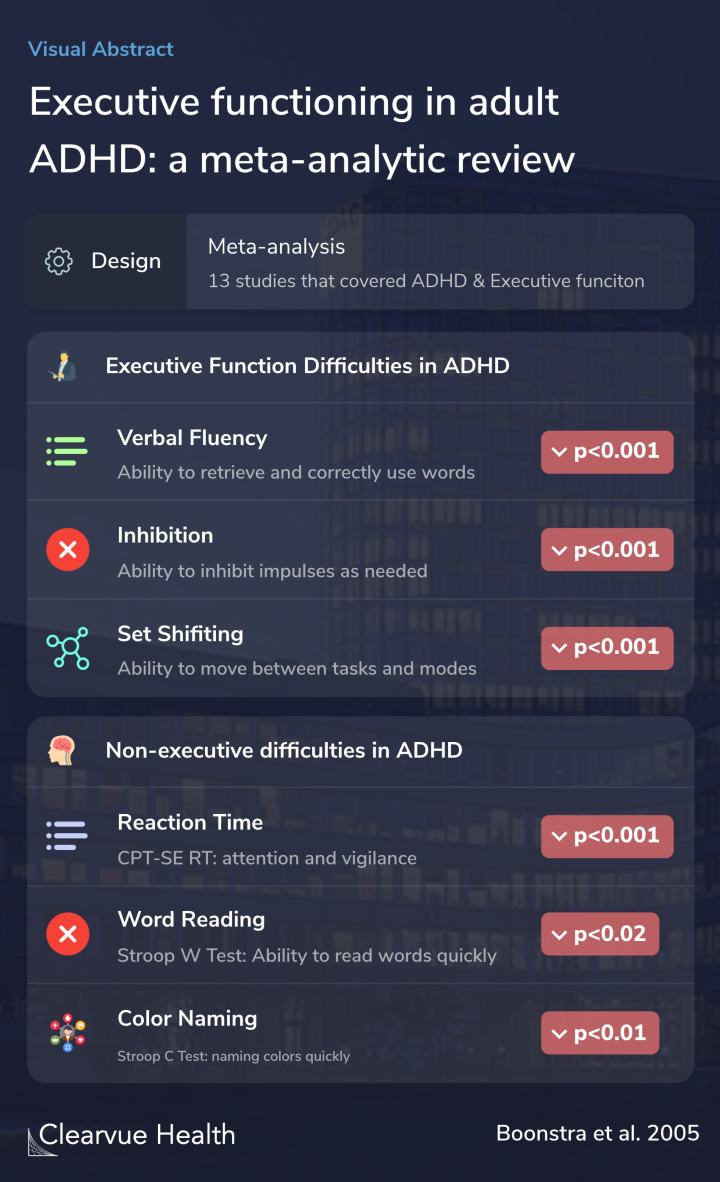
The researchers conducted a meta-analysis covering 13 studies that compared adults with ADHD and adults without ADHD.
We compared 13 studies that (1) included at least one executive functioning measure, (2) compared the performance of an adult ADHD group with that of an adult normal control group, (3) provided sufficient information for calculation of effect sizes, and (4) used DSM-III-R or DSM-IV crit...
Results
As expected, researchers found that those with ADHD had more trouble with tasks involving executive function. These included tasks involving verbal fluency, inhibition, and set-shifting.
Each area involved a specific test designed to differentiate strengths and weaknesses. For example, set shifting was tested with the trail-making test, a standardized test detailed below:
The results showed that those with ADHD also struggled with tests outside of executive function. This suggests that cognitive deficits in ADHD may extend further than previously thought.
We found medium effect sizes both in executive functioning areas [verbal fluency (d= 0-62), inhibition (d = 0-64 and d = 0.89), and set shifting (d = 0.65)] and in non-executive functioning domains [consistency of response (d = 0.57), word reading (d = 0.60) and color naming (d = 0.62)].
Conclusions
Based on the study's results, the researchers concluded that cognitive issues in ADHD may be broader than we previously thought.
One ambiguity in the results is that some of the tests for non-executive functions may still involve some level of executive function. For example, the color naming and word reading tasks require a fair amount of focus and sustained attention, which are executive functions.
At this point, it’s hard to tell whether the results of non-executive function tests truly reflect deficits outside of executive function. The authors state in the conclusion that these results highlight the need for more research and for better tests of executive function.
Neuropsychological difficulties in adult ADHD may not be confined to executive functioning. The field is in urgent need of better-designed executive functioning tests, methodological improvements, and direct comparisons with multiple clinical groups to answer questions of specificity.