Validity of DSM-IV attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptom dimensions and subtypes
Evaluating ADHD Subtypes Validity in DSM-IV
Willcutt EG, Nigg JT, Pennington BF, Solanto MV, Rohde LA, Tannock R, Loo SK, Carlson CL, McBurnett K, Lahey BB
Objectives
The study aimed to assess the effectiveness of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th Edition (DSM-IV) in identifying and distinguishing between different types of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Specifically, it focused on evaluating the validity of the DSM-IV model for ADHD and its subtypes. This objective sets the stage for a detailed exploration of how ADHD is categorized and understood in clinical settings.
To evaluate the validity of DSM-IV model of ADHD and its subtypes.
Methods
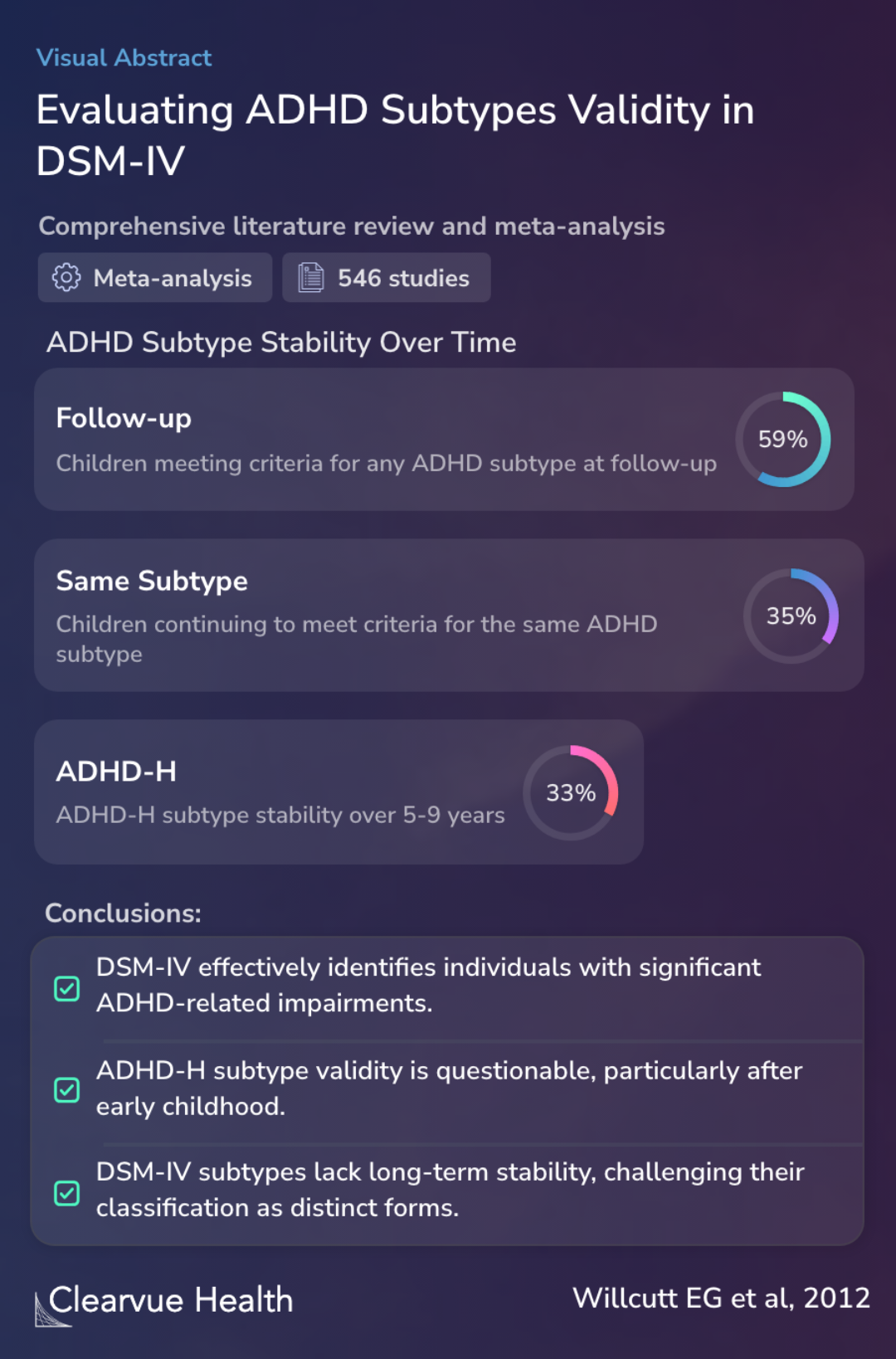
The authors conducted a comprehensive review and meta-analysis of 546 studies focusing on the DSM-IV criteria for ADHD. This methodical approach provided a broad and in-depth examination of existing literature, offering insights into the ADHD subtypes: ADHD-C (combined type), ADHD-H (hyperactive-impulsive type), and ADHD-I (inattentive type).
Literature review and meta-analysis of 546 studies on DSM-IV ADHD criteria.
Results
The results of the study revealed that while the DSM-IV criteria are effective in identifying individuals with significant ADHD impairments, they have certain limitations in distinguishing between the subtypes. Particularly, the study found varying levels of stability among the ADHD subtypes over time, with the ADHD-H subtype showing the least stability.
Additionally, the authors observed that ADHD-C and ADHD-I subtypes have similar long-term outcomes, indicating that the differences between these subtypes might not be as distinct as previously thought. This finding challenges the clear-cut categorization of ADHD subtypes in the DSM-IV.
DSM-IV criteria effectively identify individuals with significant ADHD impairments but have limitations in subtype distinctions.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the study suggests that while the DSM-IV provides a useful framework for understanding ADHD, its subtypes do not represent distinct groups with consistent long-term stability. The authors advocate for an alternative model that would use dimensional modifiers to reflect the number of inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity symptoms at the time of assessment. This approach could offer a more nuanced understanding of ADHD and its symptoms.
Overall, we conclude that the DSM-IV ADHD subtypes provide a convenient clinical shorthand to describe the functional and behavioral correlates of current levels of inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity symptoms, but do not identify discrete subgroups with sufficient long-term stabil...
Key Takeaways
Context
The context of ADHD as a disorder that persists into adulthood is crucial to understanding the study's significance. ADHD symptoms, including hyperactivity, often continue to impact individuals well into adulthood, though hyperactivity symptoms are more likely to improve first. This ongoing impact underscores the importance of accurate diagnostic criteria like those discussed in the study.
Similarly, the study's findings align with broader research indicating that while ADHD symptoms can improve with age, difficulties with attention often take longer to improve. Many children with ADHD will see improvements, yet they may continue to face challenges related to attention. This ties back to the study's conclusion on the need for a more flexible and dynamic model in the DSM for diagnosing and understanding ADHD.