Empathy and social perspective taking in children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
Empathy and Social Skills in ADHD
Imola Marton , Judith Wiener, Maria Rogers, Chris Moore, Rosemary Tannock
Objectives
ADHD has been linked to difficulties in social and personal lives among children with ADHD, including among gifted children:
This study focused on empathy and social skills in children with ADHD. Are children with ADHD able to understand the perspectives of others and empathize with their feelings?
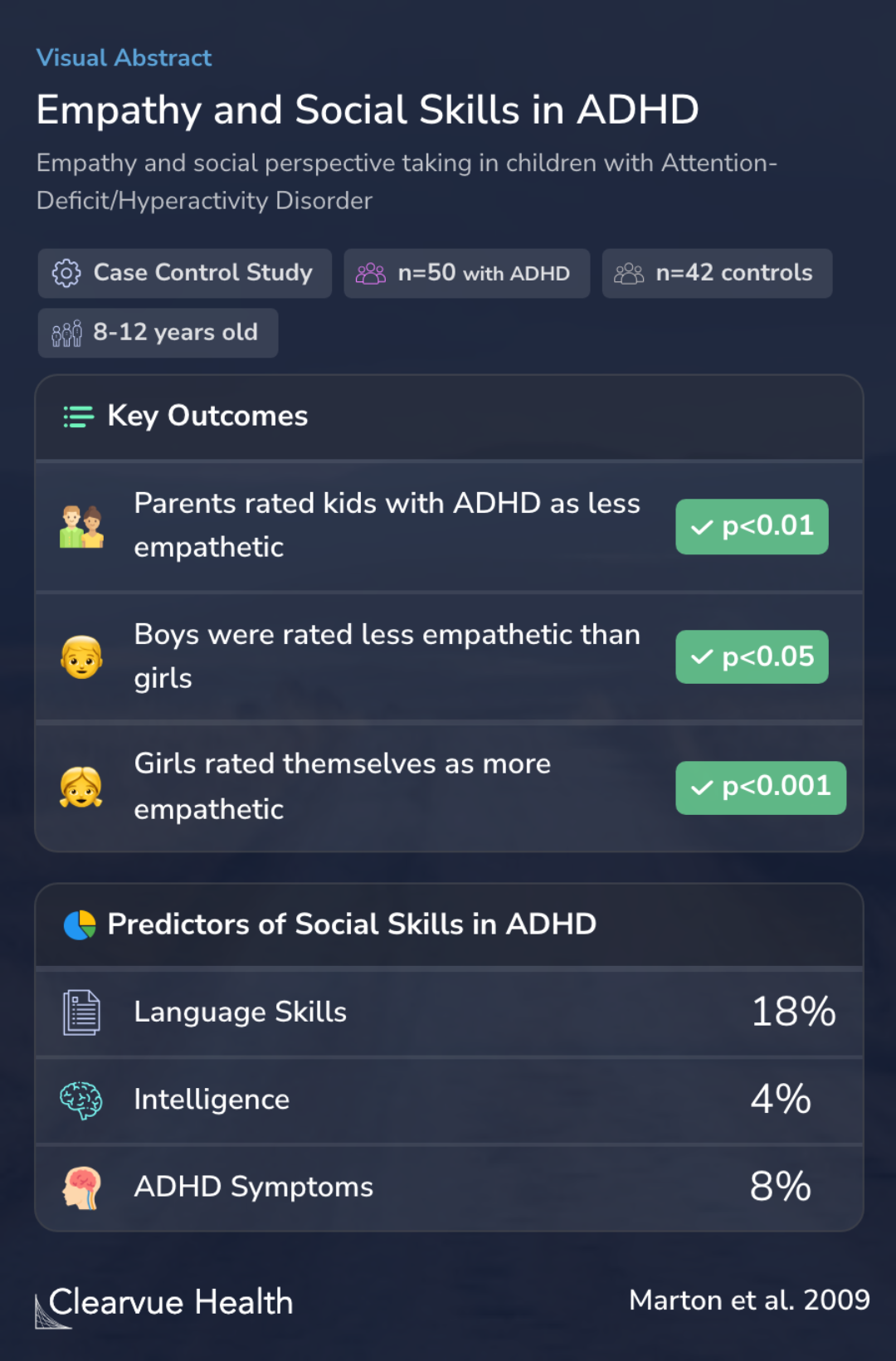
This study explored empathy and social perspective taking in 8 to 12 year old children with and without Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
Methods
Researchers compared 50 children with ADHD to 42 children without ADHD. By comparing two closely matched groups, where the main difference was the presence of ADHD, researchers are able to better isolate links between ADHD and social skills.
The sample comprised 92 children, 50 with a diagnosis of ADHD and 42 typically developing comparison children.
Results
Researchers found that children with ADHD were less likely to be rated as empathetic by their parents.
Boys with ADHD were less empathetic than girls with ADHD.
This was consistent with self-evaluations. Boys generally saw themselves as less empathetic as well.
Children with ADHD were less able to understand and take the perspectives of others in the study:
Interestingly, there was a link between IQ, language skills, and social skills. Kids with stronger language skills and more intelligence were more likely to have better social-perspective taking skills and empathy.
One possible explanation for the differences between boys and girls may be that girls have more support and discussions around emotions than boys. This may help them mature socially and emotionally:
Although children with ADHD were rated by their parents as less empathic than children without ADHD, this difference was accounted for by co-occurring oppositional and conduct problems among children in the ADHD sample. Children with ADHD used lower levels of social perspective taking co...
Conclusions
This study is consistent with previous studies showing difficulties with social skills for those with ADHD.
The data does suggest that intelligence and language skills can help improve social skills for those with ADHD.
Implications for research and practice are discussed.