Efficacy of Meta-Cognitive Therapy (MCT) for Adult ADHD
Mary V. Solanto, Ph.D., David J. Marks, Ph.D., Jeanette Wasserstein, Ph.D., Katherine Mitchell, Psy.D., Howard Abikoff, Ph.D., Jose Ma. J. Alvir, Dr.P.H., and Michele D. Kofman, Ph.D.
Objectives
This study wanted to evaluate whether Meta-Cognitive Therapy could help improve outcomes in adults with ADHD.
Cognitive Behavior Therapy has been previously shown to improve outcomes in ADHD.
This study wanted to test the effectiveness of a specific type of therapy designed to provide skills that help those withADHD accomplish tasks in their daily life.
To examine the efficacy of a 12-week manualized Meta-Cognitive Therapy (MCT) group designed to enhance time-management, organization, and planning in adults with AD/HD.
Methods
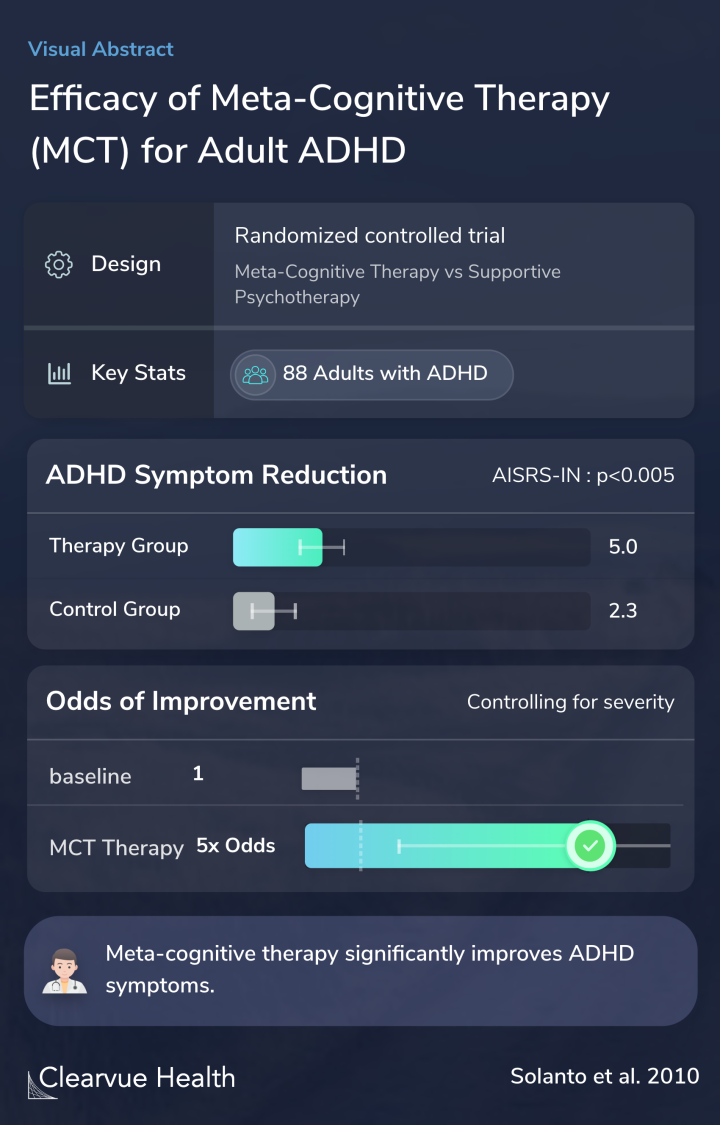
Researchers recruited 88 adults with ADHD and conducted a randomized trial to test the effectiveness of Meta-Cognitive Therapy.
They provided MCT to a randomly selected subset of participants and supportive psychotherapy to the rest of the participants as a comparison control group.
By doing so, researchers can test whether meta-cognitive therapy provides benefits above and beyond supportive therapy.
Eighty-eight clinically referred adults who met DSM-IV criteria for ADHD based on clinical and structured diagnostic interviews and standardized questionnaires were stratified vis-à- vis ADHD medication use and otherwise randomly assigned to receive MCT or supportive psychotherapy in a g...
Results
Researchers found that both groups experienced a significant reduction in their ADHD symptoms after therapy. This is consistent with previous studies that have shown the effectiveness of therapy in ADHD.
There was a significantly greater reduction in ADHD symptoms in the meta-cognitive therapygroup compared to the supportive therapy group, suggesting that meta-cognitive therapy carries benefits beyond psychological support.
Those in the meta-cognitive therapy group were far more likely to experience a significant response to therapy as well
It is important to note that even supportive therapy, without the specific structure of Meta-Cognitive Therapy, was still found to reduce ADHD symptoms. This is consistent with other studies that have demonstrated the effectiveness of therapy in ADHD.
General linear models, comparing change from baseline between treatments, revealed statistically significant effects for independent evaluator, self-report, and collateral ratings of DSM-IV inattentive symptoms. Employing dichotomous indices of therapeutic response, a significantly great...