Ritalin for ADHD
Visual Abstract
Cognitive effects of methylphenidate in healthy volunteers: a review of single dose studies
Effects of methylphenidate on cognition
Reviewed by Charles Li, MD
July 15, 2024
author
Linssen AM, Sambeth A, Vuurman EF, Riedel WJ
journal
Int J Neuropsychopharmacol
Date Published
2014 Jun
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The researchers wanted to find out if methylphenidate (MPH) improves cognitive performance in healthy people.
💡
What They Found
They found that single doses of MPH improve working memory and speed of processing in healthy people, and to a lesser extent, verbal learning and memory, attention, vigilance, and reasoning.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that MPH enhances working memory and processing speed in healthy individuals, aligning with current evidence that it impacts ADHD and cognitive functions.
Study Summary
Background
Abstract: background
Methylphenidate (MPH), a stimulant drug with dopamine and noradrenaline reuptake inhibition properties, is mainly prescribed in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, is increasingly used by the general population, intending to enhance their cogni...more
🧠
Mechanism of Action
Blocks norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake, increasing their synaptic concentration, affecting cognitive domains.
💊
Cognitive Enhancement
Off-label use for cognitive enhancement is increasing despite primary approval for ADHD and narcolepsy.
👀
Monitoring for Side Effects
Regular monitoring for cardiovascular, psychiatric, and growth issues is vital when using methylphenidate.
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers combed through various studies to see how MPH affected cognitive performances, such as memory and attention, in people without ADHD. They looked at the percentages of studies that reported improvements after taking MPH. They also examined how different doses of MPH—low, medium, and high—impacted these cognitive abilities.
Abstract: methods
We present a novel way to determine the extent to which MPH enhances cognitive performance in a certain domain. Namely, we quantify this by a percentage that reflects the number of studies showing performance enhancing effects of MPH. To evaluate whe...more

Study Summary
Results
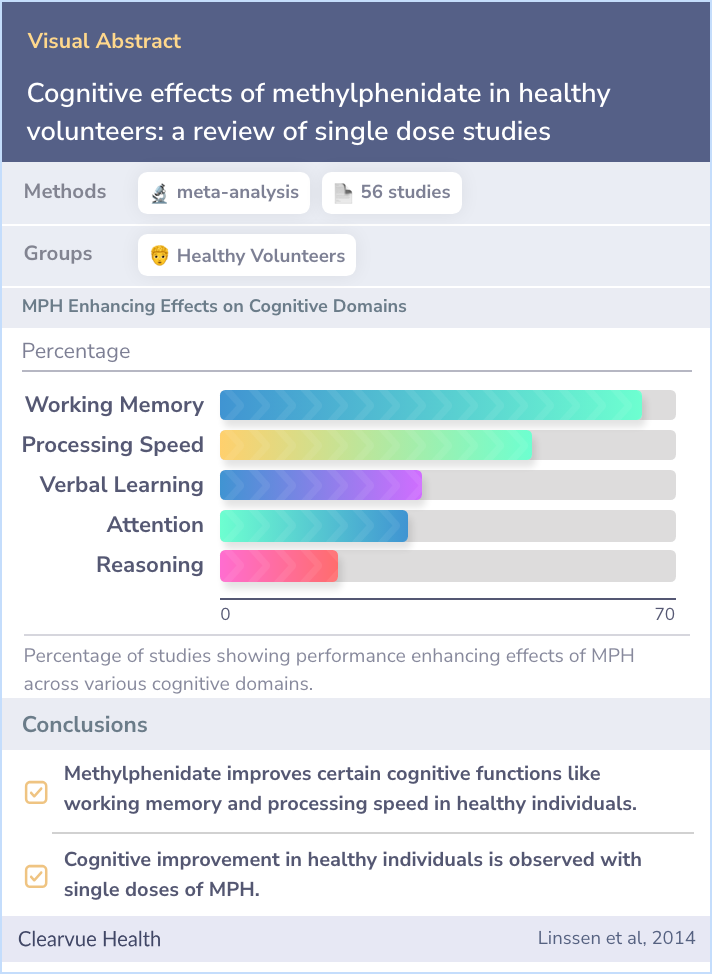
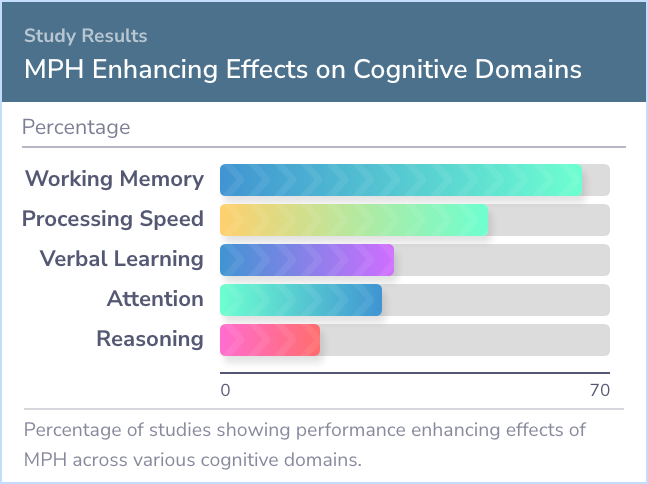
The findings revealed that MPH seems to boost certain aspects of brain function. About 65% of the studies showed improvements in working memory, and 48% reported faster processing speeds. Other areas like verbal learning and memory (31%), attention and vigilance (29%), and reasoning and problem solving (18%) also saw some improvements. However, MPH didn't help with visual learning and memory. The effects of MPH varied greatly depending on the dose, suggesting that how much you take matters. But it's not all good news: using MPH comes with potential side effects and risks, including the possibility of misuse.
Abstract: results
The studies reviewed here show that single doses of MPH improve cognitive performance in the healthy population in the domains of working memory (65% of included studies) and speed of processing (48%), and to a lesser extent may also improve verbal l...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
In conclusion, methylphenidate can enhance certain cognitive functions such as working memory and speed of processing in healthy individuals. However, its benefits are not uniform across all cognitive domains and depend significantly on the dosage. While some aspects of brain function may improve with MPH use, it doesn't benefit visual memory and poses risks of side effects and abuse. Future research should weigh these benefits against the risks to fully understand MPH's value as a cognitive enhancer.
Abstract: conclusions
MPH use is associated with side effects and other adverse consequences, such as potential abuse. Future studies should focus on MPH specifically to adequately assess its benefits in relation to the risks specific to this drug.

Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Effects of methylphenidate on cognition
The findings suggest that MPH can enhance certain cognitive functions in a healthy population, primarily working memory and speed of processing.
This aligns with the broader clinical understanding that ADHD, a common neuropsychiatric disorder, frequently persists into adulthood, necessitating ongoing intervention.
Current professional guidelines recommend combining stimulant medications with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to target executive dysfunction in adults.
Stimulant medications are shown to be effective and provide immediate clinical benefits, which is particularly relevant given the dose-dependent effects of MPH on cognitive domains highlighted in the abstract.
Furthermore, meta-analyses suggest stimulants have greater short-term efficacy compared to nonstimulants.
Studies also indicate that extended-release stimulants may have a lower potential for abuse, which could be significant when considering long-term ADHD management strategies.
This aligns with the broader clinical understanding that ADHD, a common neuropsychiatric disorder, frequently persists into adulthood, necessitating ongoing intervention.
Current professional guidelines recommend combining stimulant medications with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to target executive dysfunction in adults.
Stimulant medications are shown to be effective and provide immediate clinical benefits, which is particularly relevant given the dose-dependent effects of MPH on cognitive domains highlighted in the abstract.
Furthermore, meta-analyses suggest stimulants have greater short-term efficacy compared to nonstimulants.
Studies also indicate that extended-release stimulants may have a lower potential for abuse, which could be significant when considering long-term ADHD management strategies.

Evidence Summary
ADHD and Variability in Reaction Times
Building upon the paper's exploration of MPH's effects on different cognitive domains, individuals with ADHD often experience slower and more variable reaction times.
These differences are potentially influenced by genetic factors.
This cognitive aspect is an important consideration when evaluating the overall impact of ADHD.
These differences are potentially influenced by genetic factors.
This cognitive aspect is an important consideration when evaluating the overall impact of ADHD.

Evidence Summary
Strategies to Aid Task Management in ADHD
Building upon the findings that MPH enhances cognitive functions across various domains,
individuals with ADHD face challenges with complex tasks due to difficulties in response inhibition and sustained attention.
Implementing organizational strategies and structured support can significantly enhance their ability to manage these tasks and improve academic performance.
individuals with ADHD face challenges with complex tasks due to difficulties in response inhibition and sustained attention.
Implementing organizational strategies and structured support can significantly enhance their ability to manage these tasks and improve academic performance.

Evidence Summary
Exercise and Cognitive Function in ADHD Children
Building upon the analysis of MPH's effects on cognitive performance, a 10-week exercise program demonstrates considerable improvements in children with ADHD.
Improvements include better attention, reduced impulsivity, and decreased anxiety.
This suggests exercise positively impacts both mental and physical well-being in children with ADHD.
Improvements include better attention, reduced impulsivity, and decreased anxiety.
This suggests exercise positively impacts both mental and physical well-being in children with ADHD.
