Effects of IQ on executive function measures in children with ADHD
E Mark Mahone , Kathleen M Hagelthorn, Laurie E Cutting, Linda J Schuerholz, Shelley F Pelletier, Christine Rawlins, Harvey S Singer, Martha B Denckla
Objectives
One of the key differences in how children with ADHD think is executive function. This refers to the advanced thought processes that help us plan, inhibit ourselves, and remain attentive. These are all areas that those with ADHD can struggle with.
Researchers wanted to see how children with ADHD perform on tests of executive function and whether performance was correlated with IQ.
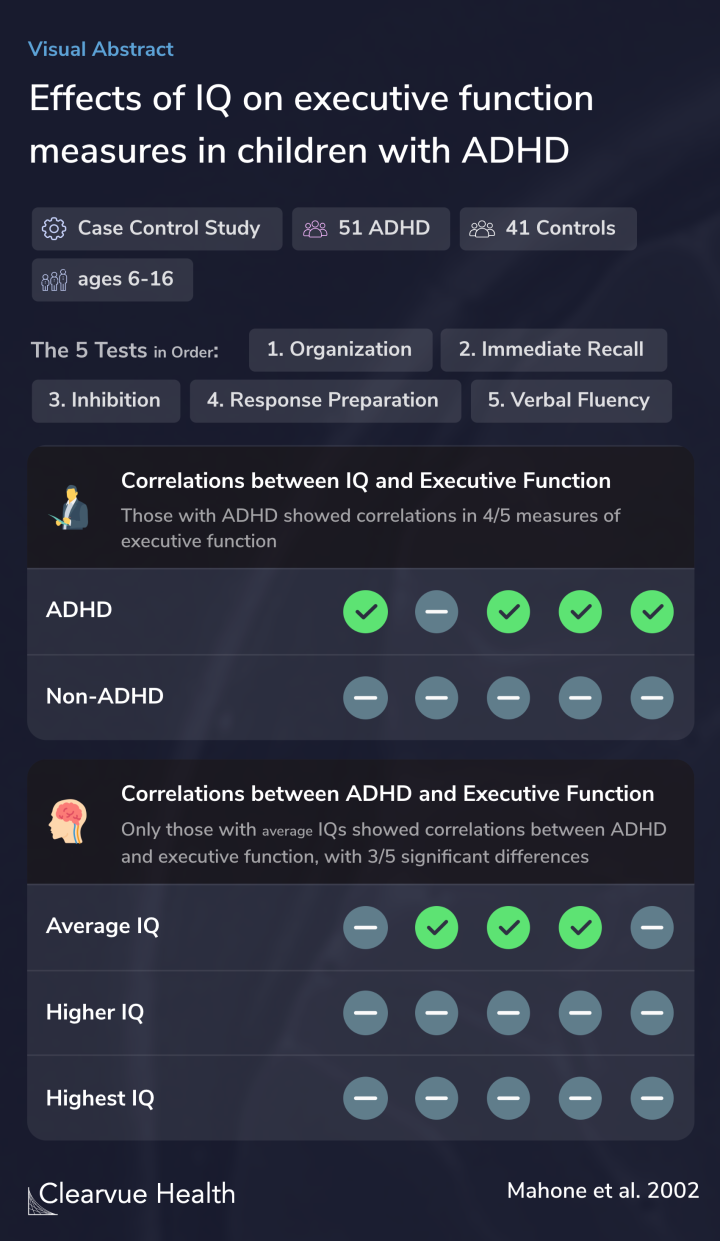
The present study compared children with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and controls on a selected set of clinical measures of executive function (EF).
Methods
Researchers compared 51 children with ADHD and 41 children without ADHD on a set of executive function tests to see whether there were differences in executive function.
A total of 92 children (51 ADHD, 41 control), ages 6-16, completed measures chosen from a larger neuropsychological battery to illustrate diverse components of the EF construct (planning, inhibitory control, response preparation, memory search).
Results
They tested children's abilities in organization, immediate recall, inhibition, response, preparation, and verbal fluency. Each of these is a commonly used metric within executive function. The charts below show results in the test order above.
Executive Function and IQ in ADHD
IQ and executive function showed significant correlations on 4 out of 5 tests among those with ADHD. Those with higher IQs tended to perform better on tests of executive function.
This relationship was not seen in children without ADHD.
In healthy children, IQ test results do not correlate with executive function test results:
Executive Function in High IQ
The relationship between IQ and executive function among those with ADHD depends on the child’s IQ.
Very bright children perform relatively well on IQ tests regardless of ADHD symptoms.
The selected measures were moderately correlated with one another, and moderately correlated with IQ. After controlling for age, sex, presence of learning disability (LD), ADHD, and IQ test version, Full Scale IQ was significantly related to four of the five selected EF measures. A secon...
Conclusions
The link between ADHD and executive function has been well documented. However, this study suggests it may be more complex than we previously thought.
Children with high IQs may be able to perform well on executive function tests, regardless of their ADHD symptoms. They may be compensating for their ADHD symptoms with their raw intellect.
This and similar studies show that we may be under-diagnosing ADHD among gifted children.
These results suggest that clinical measures of EF may differ among children with ADHD and controls at average IQ levels, but there is poorer discriminatory power for these measures among children with above average IQ.