Multiple deficits in ADHD: executive dysfunction, delay aversion, reaction time variability, and emotional deficits
Effects of ADHD on Cognition and Emotion
Douglas Sjöwall , Linda Roth, Sofia Lindqvist, Lisa B Thorell
Objectives
Experts have increasingly recognized that ADHD can affect more than just attention and hyperactivity. It’s been linked to cognition, behavior, and even mood differences.
This study wanted to examine how ADHD affects children's minds beyond its core symptoms, including its effects on emotions and behavior.
The notion that ADHD constitutes a heterogeneous disorder is well accepted. However, this study contributes with new important knowledge by examining independent effects of a large range of neuropsychological deficits. In addition, the study investigated whether deficits in emotional fun...
Methods
The study conducted standardized tests on 102 children with ADHD and a closely matched group without ADHD as a comparison.
The tasks tested the children’s neurological and psychological functioning.
Researchers also asked their parents about how well the children handled their emotions.
The study included children with ADHD (n = 102; 7-13 years) and a control sample individually matched with regard to age and gender. The administered tasks were designed to tap into three different neuropsychological domains: executive functions (i.e., working memory, inhibition, and shi...
Results
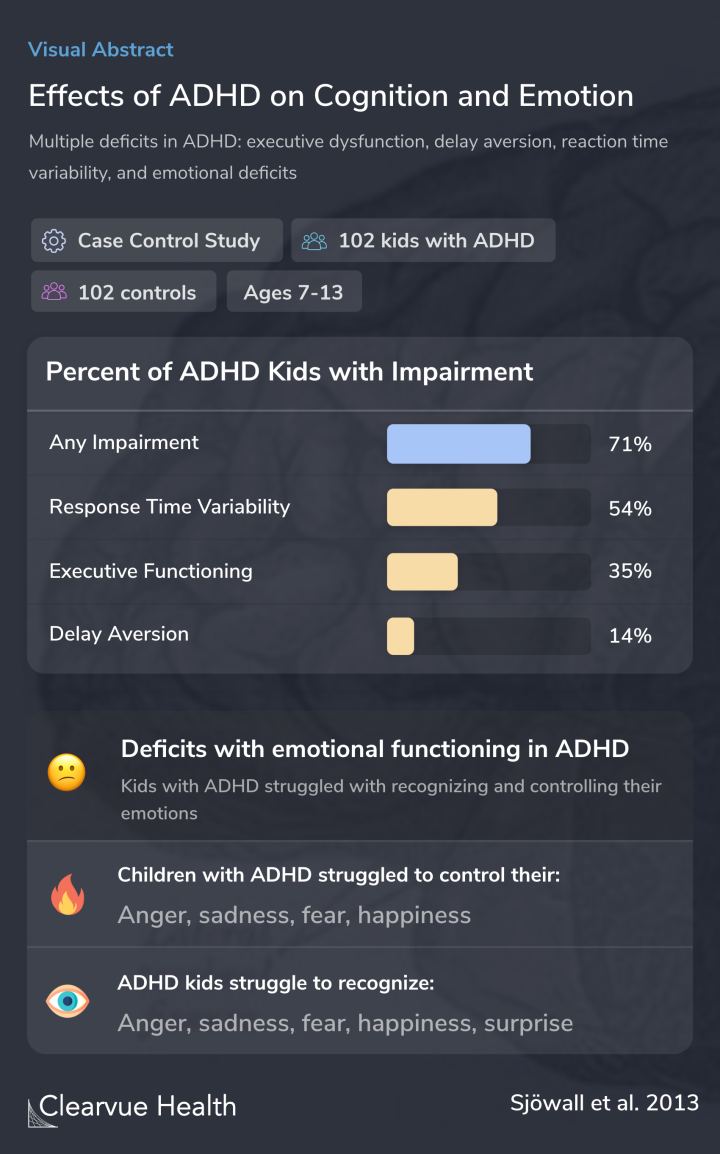
The results showed that over 2/3 of the children with ADHD in the study experienced cognitive impairments.
Around half experienced response time variability, the most common impairment in the study. For kids with ADHD, this can often indicate difficulties with attention and focus.
Executive function impairments were also common, consistent with other studies on executive functioning. ADHD.
There was also evidence that children struggled with emotions.
Children with ADHD tended to struggle with recognizing emotions, such as anger, sadness, fear, happiness, and surprise.
They also struggled to regulate their emotions.
These difficulties with recognition and regulation of emotions were significantly tied to ADHD status.
Children with ADHD differed significantly from controls on all measures, except for delay aversion and recognition of disgust. No main effects of gender or interaction effects of gender and group were found. More importantly, executive functioning, reaction time variability, and emotiona...
Conclusions
This study helped demonstrate the wide range of cognitive and emotional challenges faced by those with ADHD.
The cognitive tests showed widespread challenges with response time, which can affect how children perform on tests.
There was also evidence of significant emotional challenges, consistent with previous studies on ADHD and emotion.
The current study supports the view of ADHD as a heterogeneous disorder related to multiple neuropsychological deficits. In addition, emotional functioning appears to be an area of importance for ADHD that needs to be incorporated into future theoretical models.