Anxiety as a Predictor and Outcome Variable in the Multimodal Treatment Study of Children with ADHD (MTA)
Effect of Anxiety on ADHD Treatment
John S. March, James M. Swanson, L. Eugene Arnold, Betsy Hoza, C. Keith Conners, Stephen P. Hinshaw, Lily Hechtman, Helena C. Kraemer, Laurence L. Greenhill, Howard B. Abikoff, L. Glen Elliott, Peter S. Jensen, Jeffrey H. Newcorn, Benedetto Vitiello, Joanne Severe, Karen C. Wells, and William E. Pelham
Objective & Methods
ADHD and anxiety are closely related conditions:
There is some evidence that the level of anxiety in a child with ADHD affects the chances that a child will respond to different types of ADHD treatment.
The study wanted to find out more about the effect of anxiety and ADHD treatment response and to see whether conduct disorder played a role in ADHD treatment response as well.
Initial moderator analyses in the Multimodal Treatment Study of Children with ADHD (MTA) suggested that child anxiety ascertained by parent report on the Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children 2.3 (DISC Anxiety) differentially moderated the outcome of treatment. Left unanswered were ...
Results
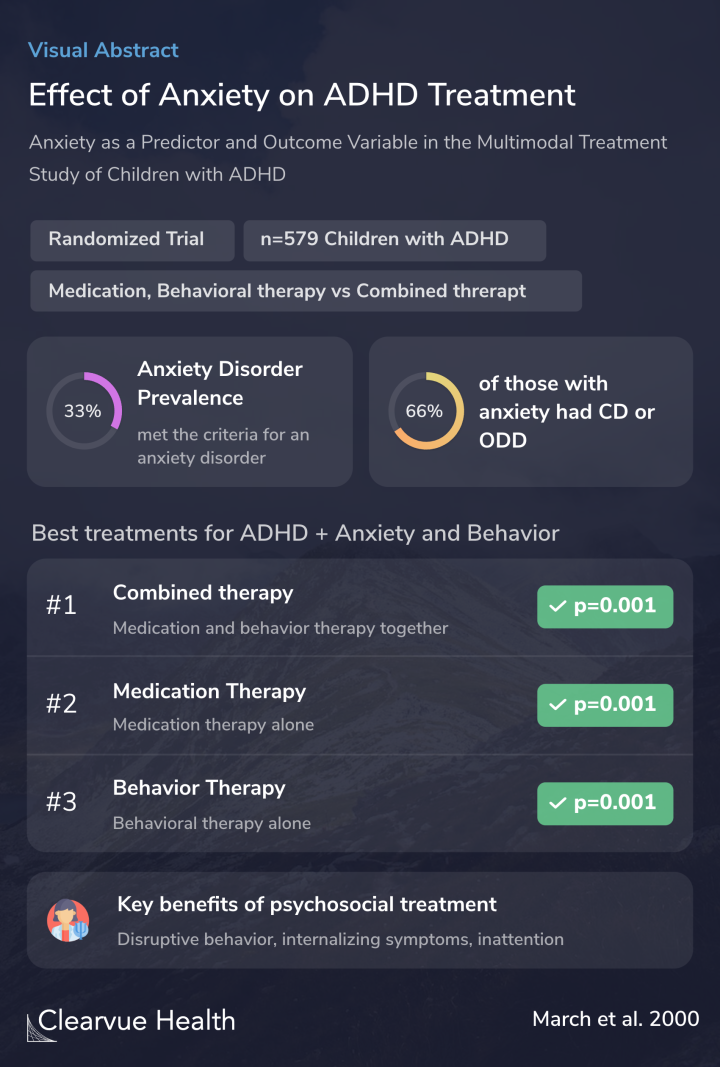
In this study of children with ADHD, anxiety was quite common. Consistent with previous studies, around a third of participants had an anxiety disorder and ADHD.
Of those with ADHD, and anxiety, 2/3 also had conduct disorder or oppositional defiant disorder.
Conduct disorder is a common disorder in ADHD characterized by a lack of respect for other's rights and feelings.
In terms of therapy, researchers studied medication, therapy, behavioral therapy, and a combination of medication and behavioral therapy.
While all three therapies worked for those with ADHD and anxiety, there were significant differences.
A combination of medication and behavioral therapy was significantly more effective than medication or behavioral therapy alone.
Medication alone was more effective than behavioral therapy alone.
Of note, there was no evidence that medication for ADHD made the anxiety worse, an effect that some experts are concerned about.
Thirty-three percent of MTA subjects met DSM-III-R criteria for an anxiety disorder excluding simple phobias. Of these, two-thirds also met DSM-III-R criteria for comorbid oppositional-defiant or conduct disorder whereas one-third did not, yielding an odds ratio of approximately two for ...
Conclusions
Based on the results of this study, researchers concluded that it’s important to consider anxiety and conduct when diagnosing and treating ADHD. Having different disorders can affect how well certain treatments can work.
When treating ADHD, it is important to search for comorbid anxiety and negative affectivity and to adjust treatment strategies accordingly.