Simulated Driving Performance of Adults with ADHD: Comparisons with Alcohol Intoxication
Driving with ADHD and Alcohol
Jessica Weafer, Daniel Camarillo, Mark T. Fillmore, Richard Milich, and Cecile A. Marczinski
Objectives
ADHD is known to lead to attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity issues.
These can all interfere with driving. Previous studies have found significant links between ADHD and driving challenges.
Those with ADHD also have a higher risk of heavy drinking and drinking disorders:
The study wanted to conduct a laboratory experiment to see how ADHD impairs driving compared with alcohol intoxication.
Previous research has demonstrated that adults with ADHD are more likely to experience driving-related problems, which suggests that they may exhibit poorer driving performance. However, direct experimental evidence of this hypothesis is limited. The current study involved two experiment...
Results
Researchers first established that their experiments could reliably capture driving difficulties caused by alcohol.
The researchers then tested adults with ADHD and adults without ADHD under different levels of intoxication on a driving simulator.
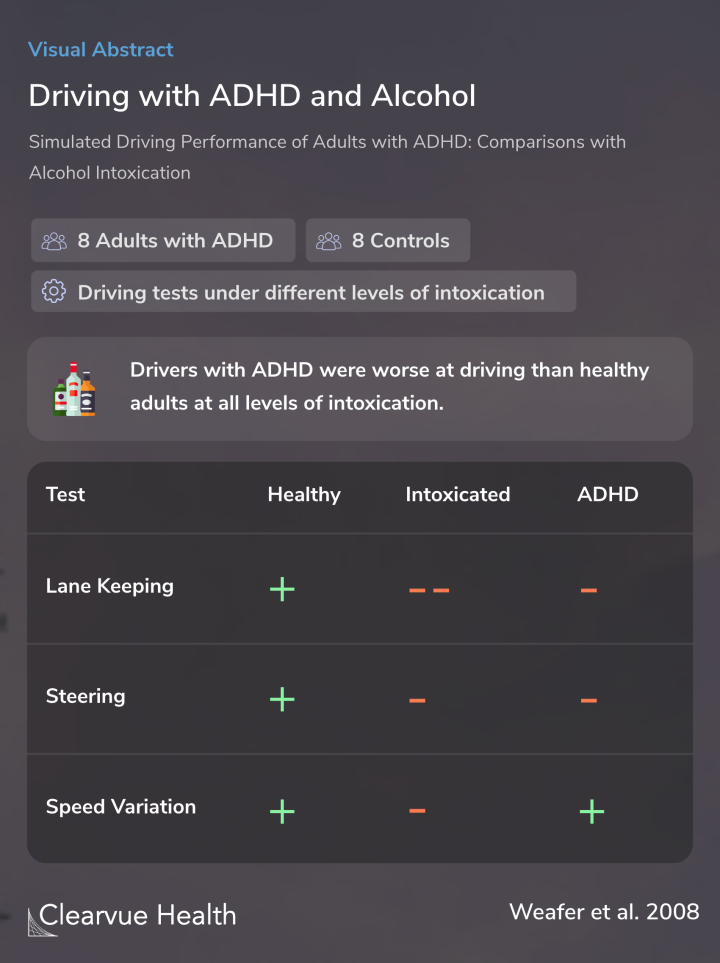
The results showed that, generally, those with ADHD drove significantly worse than those without ADHD at every level of intoxication. No matter how much someone drinks, these results suggest that ADHD worsens their driving if they choose to drive.
When they examined the driving ability of those with ADHD while sober, they found that their driving skills were in some ways comparable to healthy adults while drunk.
Both groups struggled with staying in the lane and with stable steering.
To make matters worse, those with ADHD also overestimate their driving ability and underestimate how drunk they may be. This, combined with the deficit shown in driving ability, help explain why those with ADHD time to get into more car accidents.
Experiment 1 compared the simulated driving performance of 15 adults with ADHD to 23 adult control participants, who performed the task both while sober and intoxicated. Results showed that sober adults with ADHD exhibited decrements in driving performance compared to sober controls, an...
Conclusions
These results show that, generally, those with ADHD are worse at driving at any level of intoxication. ADHD makes drinking and driving more dangerous.
This research offers some evidence that the effect of ADHD on driving ability is similar to alcohol in some ways.
While this was a small study and more research is needed to confirm the results, the study is consistent with our understanding of the adverse effects of ADHD on driving.
This research suggests it is particularly important for those with ADHD to avoid drinking while driving.
Together the findings provide compelling evidence to suggest that the cognitive and behavioral deficits associated with ADHD might impair driving performance in such a manner as to resemble that of an alcohol intoxicated driver. Moreover, alcohol might impair the performance of drivers w...