The effect of fidget spinners on fine motor control
Do Fidget Spinners Help Hand Control?
Cohen EJ, Bravi R, Minciacchi D
Objectives
The study explored the intriguing relationship between fidgeting, a common behavior among individuals with ADHD, and motor control. Fidgeting, which often manifests as small, restless movements born out of nervousness or impatience, is a hallmark of ADHD. Although predominantly a motor activity, its impact on motor control remains largely unexplored. The researchers posited that engaging in fidgeting, particularly through manipulating objects like fidget spinners, could potentially hone motor skills. This hypothesis stems from the understanding that both repetitive actions and practice play crucial roles in developing motor abilities. Therefore, the repetitive use of fidget spinners might not only be a mere pastime but could also serve as a beneficial tool for enhancing motor control.
Fidgeting, defined as the generation of small movements through nervousness or impatience, is one of cardinal characteristic of ADHD. While fidgeting is, by definition, a motor experience still nothing is known about the effects of fidgeting on motor control. Some forms of fidgeting invo...
Methods
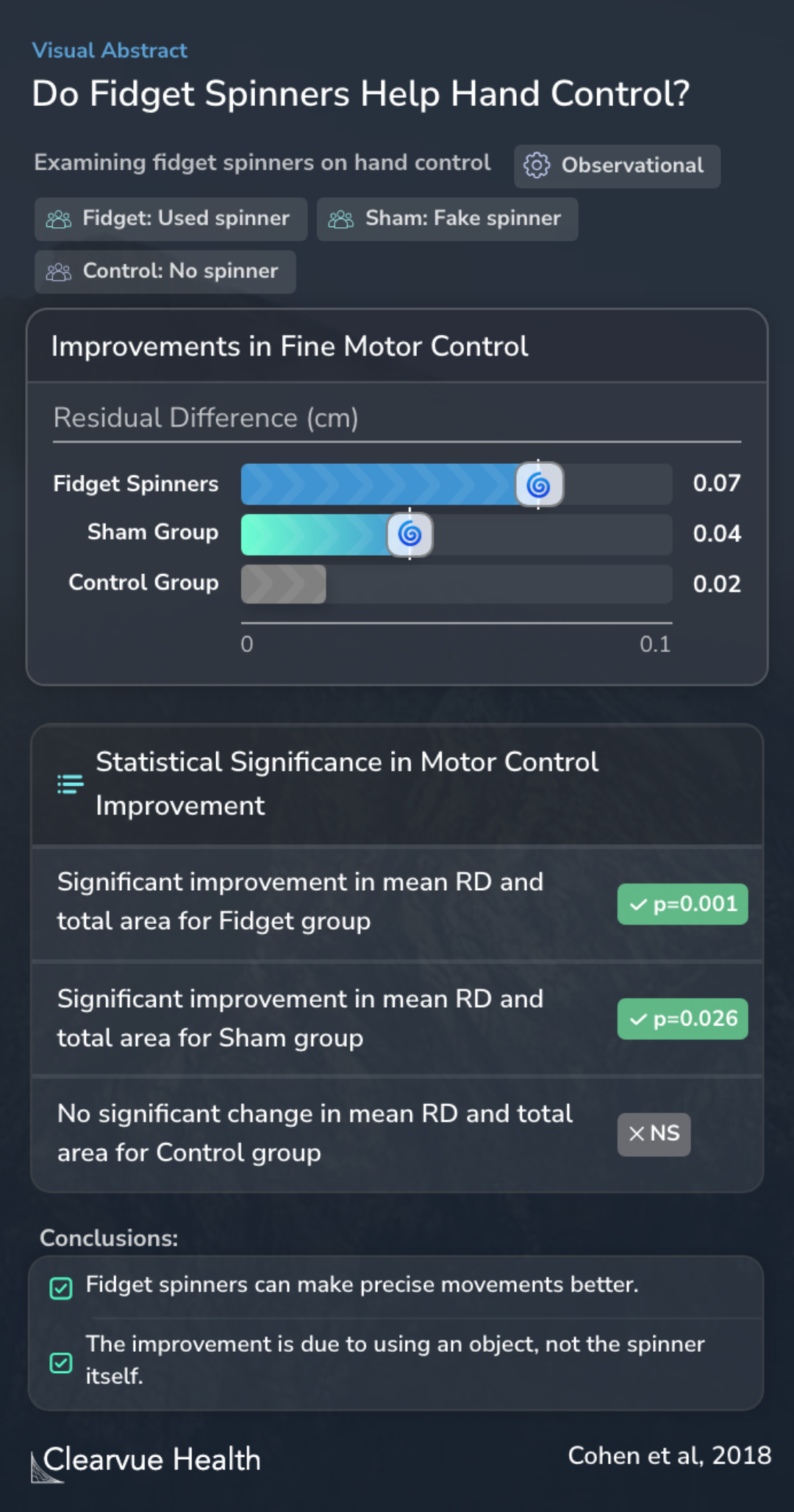
The study employed a spiral-tracing task to gauge fine motor control. This task was instrumental in assessing how the use of fidget spinners, compared to a sham (fake spinner) and no spinner at all, influences the precision and coordination of hand movements. The inclusion of a visual abstract served to encapsulate the study's methodology, offering a clear and concise overview of the experimental design.
In this study we examine the effect of fidget spinners on fine motor control, evaluated by a spiral-tracing task.
Results
Both the groups assigned fidget spinners and sham spinners exhibited notable improvements in their ability to perform the spiral-tracing task, a stark contrast to the control group that saw no significant enhancement. These improvements were quantified and presented in a visual abstract, highlighting the residual difference in performance among the groups. Further statistical analysis underscored the significance of these findings, particularly for the sham group, suggesting that the act of object manipulation, rather than the fidget spinner per se, was instrumental in enhancing fine motor control.
We show that the use of fidget spinner indeed seems to have a favorable effect on fine motor control, at least in the short term, although this effect does not seem to be in any way inherent to fidget spinners themselves as much as to object manipulation in general.
Conclusions
The study concludes that while fidget spinners themselves may not be inherently beneficial for motor control, the act of manipulating an object could be. This finding is particularly relevant given the widespread popularity of fidget spinners, making them an enjoyable tool for potentially improving fine motor skills. The broader implications of these results suggest that engaging in activities that involve object manipulation could be a valuable strategy for enhancing motor control, especially in populations prone to fidgeting, such as those with ADHD.
However, due to their widespread usage, fidget spinner may have the advantage of being an enjoyable means for improving fine motor control.
Key Takeaways
Context
Hyperactive ADHD is a serious issue that should be diagnosed and treated. While fidget spinners are a fun toy, with some potential benefits, they don't substitute for professional diagnosis and management.
Fortunately, as the article below expands upon, hyperactive symptoms are the most likely to resolve as children get older.