Comorbidity in adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Lucy Cumyn, PhD, Lisa French, PhD, and Lily Hechtman, MD, FRCP

Objective
Researchers in this study wanted to see how frequently individuals with ADHD also suffered from other psychiatric conditions.
In particular, they were interested in seeing whether there were different rates of acute psychiatric conditions, such as depression and anxiety, and personality disorders. These disorders are sometimes referred to as Axis I and II, respectively.
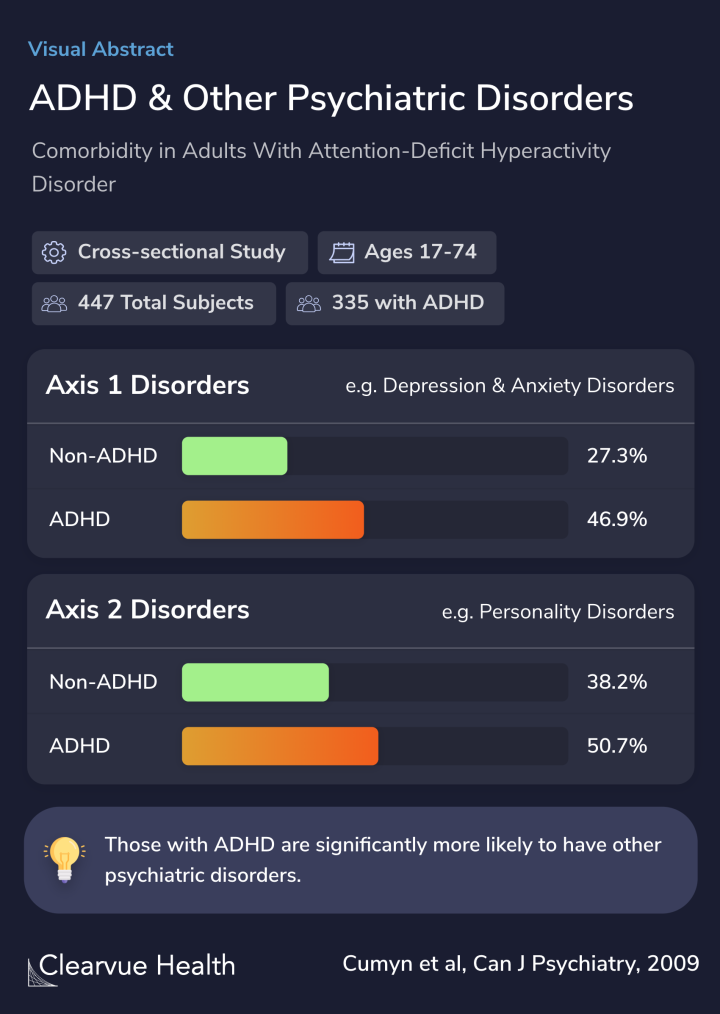
To examine the prevalence of comorbid Axis I (current and lifetime) and II disorders in adult men and women with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Method
In order to study this, researchers conducted comprehensive testing for ADHD and other psychiatric conditions on 447 adults with ADHD.
Among these patients was a mix of individuals who had inattentive ADHD, hyperactive ADHD, or both.
They ran statistical analyses to estimate links between ADHD and other disorders.
Adult patients (n = 447; 266 men, 181 women) received comprehensive assessments for ADHD and Axis I and II disorders. Adults were aged between 17 and 74 years. Among the patients diagnosed with ADHD (n = 335), there were those with ADHD inattentive subtype (ADHD-I) (n = 199), hyperactive...
Results
Researchers found that adults with ADHD had higher rates of psychiatric conditions of all types.
The difference was most pronounced in Type I disorders, encompassing most mental conditions that aren’t personality disorders, such as depression and anxiety.
There were also significant differences in personality disorders:
Rates of certain conditions differed by gender. Men, for example, were more likely to experience drug addiction and antisocial personality disorder. Women were more likely to experience anorexia, bulimia, and panic disorder.
Adults with ADHD, compared with those without ADHD, had higher rates of Axis I (46.9% and 27.31%) and Axis II (50.7% and 38.2%) disorders. Adults with ADHD-C were more likely to have mood disorder, anxiety, conduct disorder, and substance use disorder as well as obsessive-compulsive pers...
Conclusions
Researchers concluded that mental health conditions of all types were common among those with ADHD.
The findings in this study were consistent with other studies on ADHD and mental health that found higher rates of mental health conditions in those with ADHD.
One interesting finding in this study was the gender difference in how often people experienced mental health conditions with ADHD. Certain conditions were more common in men, and others were more common in women. This is consistent with known gender differences in ADHD. For example, boys and men have a much higher risk of developing ADHD than girls and women:
This finding reinforces the fact that everyone experiences mental health differently. What works for one patient might not work for another.
Adults with ADHD have very high rates of comorbid Axis I and II disorders, with differences found between men and women on certain comorbid disorders.