Bupropion for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults (Review)
Summarized & Visualized by Charles Li, MD
July 25, 2022
Background
While there are many good treatments for ADHD, not every adult responds well to ADHD treatment. The current options don't work for everyone.
Most treatments prescribed for ADHD are stimulants such as Adderall and Ritalin. These work exceptionally well for many.
Experts have explored alternative options such as Wellbutrin (bupropion) for those who don't do well on stimulants. Bupropion is currently used for depression and to help smokers quit smoking.
However, there is some evidence that it might also help with ADHD. While it's not officially approved as an ADHD treatment by the FDA, it is being used as an ADHD treatment off-label.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a prevalent neurobiological condition, characterised by behavioral and cognitive symptoms such as inattention, impulsivity and/or excessive activity. The syndrome is commonly accompanied by psychiatric comorbidities and is associated wit...
Methods and Objectives
Researchers searched for the best studies looking at bupropion as a treatment for adult ADHD.
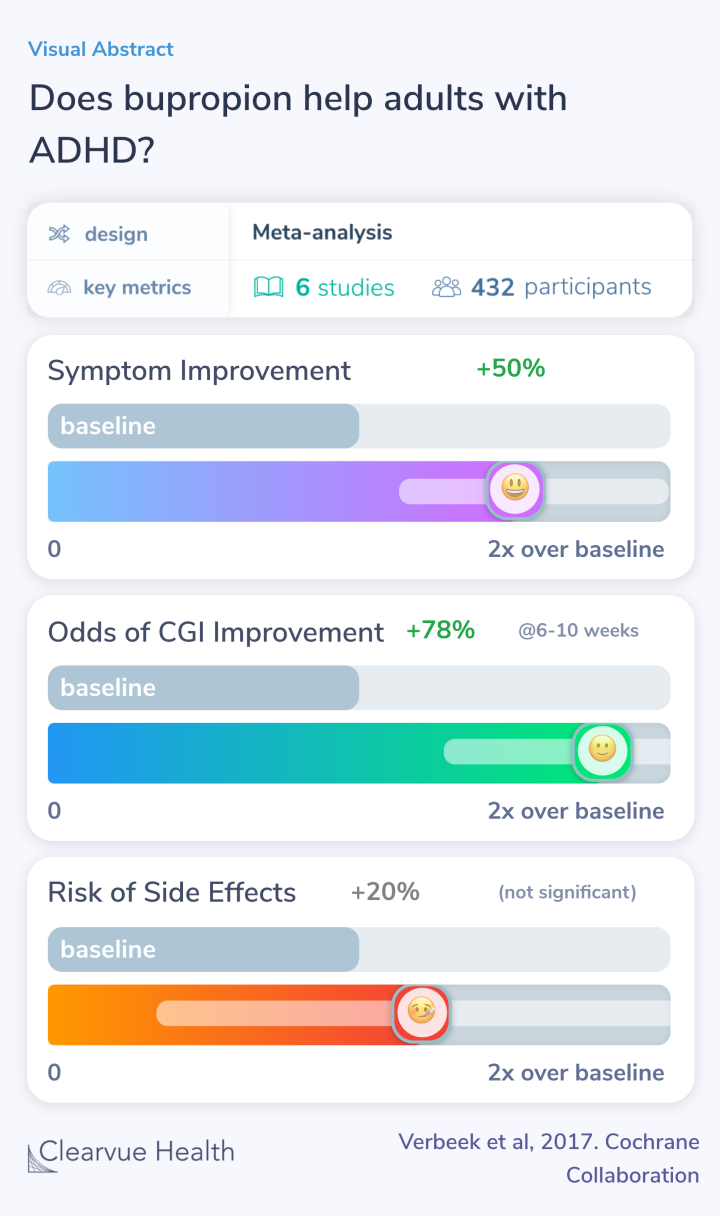
They found 6 studies that compared bupropion to placebo, a control group used in medical studies.
The authors of this study extracted data from these studies and combined them into a single analysis.
They then assessed how reliable the data was, and whether there was any potential for bias in the data.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, Embase, and seven other databases in February 2017. We also searched three trials registers and three online theses portals. In addition, we checked references of included studies an...
Result: Improvement of ADHD Symptoms
Researchers found out that patients given bupropion were 50% more likely to experience some level of symptom improvement than the control group.
They defined symptom improvement as either improvement noted by the clinician or a 30% improvement in ADHD symptoms.
In controlled trials such as those analyzed here, participants are compared against individuals given a control. Individuals in the control group, given a placebo such as a sugar pill, often can experience improvement even though they aren't given an active medication. Researchers use this as the baseline for evaluating the effectiveness of a particular treatment.
Main results: We included six studies with a total of 438 participants. Five studies were conducted in the USA, and one in Iran. All studies evaluated a long-acting version of bupropion, with the dosage ranging from 150 mg up to 450 mg daily. Study intervention length varied from six to ...
Individuals given bupropion were 78% more likely to experience improvement noted by their doctor or clinician, as represented by the CGI scale. This is a more restrictive definition of improvement that may be more specific than the previous definition.
While fewer patients reached this level of improvement, the ones that did were much more likely to have been taking bupropion than a placebo control.
The authors noted that the studies however may have been biased. Several of the studies and authors were funded by pharmaceutical companies. The sample sizes were also relatively small, which can potentially affect the accuracy and generalizability of the results.
Side Effects
Generally, bupropion appears to be safe and well-tolerated as a treatment for ADHD. Individuals who have been given bupropion were not significantly more likely to withdraw from trials.
However, the data is inconsistent with large margins of error. We'll need more studies and larger studies before we know for sure just how risky bupropion is as a treatment for ADHD.
Author's Conclusions
The authors concluded that there is some evidence that bupropion can reduce symptoms of ADHD. However, as noted above, the quality of the evidence is low.
They believe that this conclusion can potentially change as more research is conducted on bupropion and ADHD.
There's also little information on the long-term effects of bupropion as an ADHD treatment.
Since bupropion is not approved as an ADHD treatment, it's particularly important to talk to your doctor before using bupropion to treat ADHD symptoms.
Authors' conclusions: The findings of this review, which compared bupropion to placebo for adult ADHD, indicate a possible benefit of bupropion. We found low-quality evidence that bupropion decreased the severity of ADHD symptoms and moderately increased the proportion of participants ac...
Visual Abstract