Atomoxetine in Adults with ADHD: Two Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Studies
December 9, 2022
Background
Atomoxetine (Strattera) is a newer treatment for adult ADHD. Unlike Adderall and Ritalin, atomoxetine isn't a stimulant. For those who don't tolerate or don't improve on stimulants, atomoxetine can be a good alternative to consider.
Background: Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) has been less studied in adults than in children, and the treatment studies reported to date have been small, single-center trials. To assess the efficacy of atomoxetine, a new and highly selective inhibitor of the norepi...
Methods
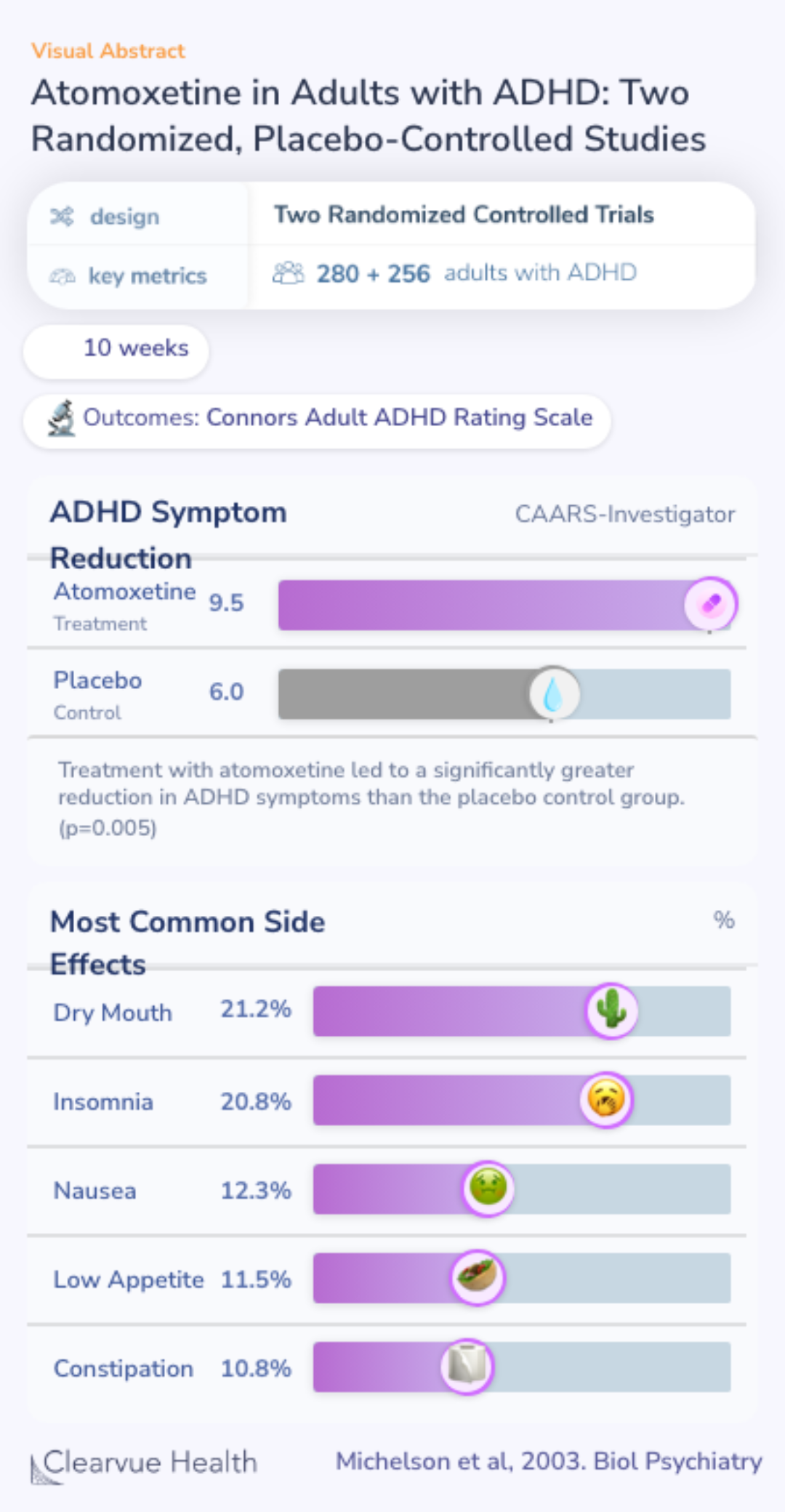
This study was one of the first clinical trials published on atomoxetine. Researchers ran two parallel clinical trials, identical in design, to see whether atomoxetine could reduce ADHD symptoms in adults.
Researchers randomized adult ADHD patients to take either atomoxetine or a placebo control. The primary outcome of the trial was theConners’ Adult ADHD Rating Scale, a standardized ADHD symptom rating scale.
Two identical studies using randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled designs and a 10-week treatment period were conducted in adults with DSM-IV- defined ADHD as assessed by clinical history and confirmed by a structured interview (study I, n = 280; study II, n = 256). The primary ou...
Results
Researchers found that atomoxetine (Strattera) was able to successfully reduce ADHD symptoms after 10 weeks of treatment. This was found with an ADHD test performed by a clinician, as well as the patients' own reports.
Both the identical trials found that patients on atomoxetine had significantly more improvement in their ADHD symptoms than patients given the control.
Of note, only the larger of the two studies is presented in the chart below.
In each study, atomoxetine was statistically superior to placebo in reducing both inattentive and hyperactive and impulsive symptoms as assessed by primary and secondary measures. Discontinuations for adverse events among atomoxetine patients were under 10% in both studies.
Side Effects
Generally, the side effects of atomoxetine, aka Strattera, were mild in this study. One way that doctors measure the intensity of side effects is by comparing how many people drop out of a certain study.
In this study, fewer than 10% of participants on atomoxetine left due to side effects. This was not significantly higher than those who left in the control group, who did not receive atomoxetine.
Most Common Side Effects
The most common side effects reported in the two trials were dry mouth, insomnia, nausea, low appetite, and constipation.
Of note, these side effects were more common in the treatment group, suggesting that these may be caused by atomoxetine.
Conclusion
Based on the data in these two trials, researchers concluded that atomoxetine can be an effective treatment for adult ADHD.
Unlike stimulants, atomoxetine is not typically used for drug abuse. It doesn't have the addictive or euphoric potential of stimulants which makes it a great option.
Atomoxetine appears to be an efficacious treatment for adult ADHD. Its lack of abuse potential may be an advantage for many patients.