Comorbid anxiety and depression in school-aged children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and self- reported symptoms of ADHD, anxiety, and depression among parents of school-aged children with and without ADHD
Anxiety and depression among children with ADHD and their parents
Weiping XIA, Lixiao SHEN, Jinsong ZHANG
Background
ADHD is a common disorder among children around the world. It has been linked with difficulties at home and school. From many, it can continue into adulthood.
Previous studies have linked ADHD with a higher risk of depression and anxiety.
This particular study wanted to get more information on depression and anxiety and school kids with ADHD and to see whether their parents had similar symptoms,
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a common psychiatric disorder in children that can extend into adulthood and that is often associated with a variety of comorbid psychiatric disorders.
Methods
Researchers screened children at a hospital in Shanghai for ADHD. They tested children for ADHD symptoms, anxiety disorders, and depressive disorders.
They also performed similar tests for one of the parents of each child.
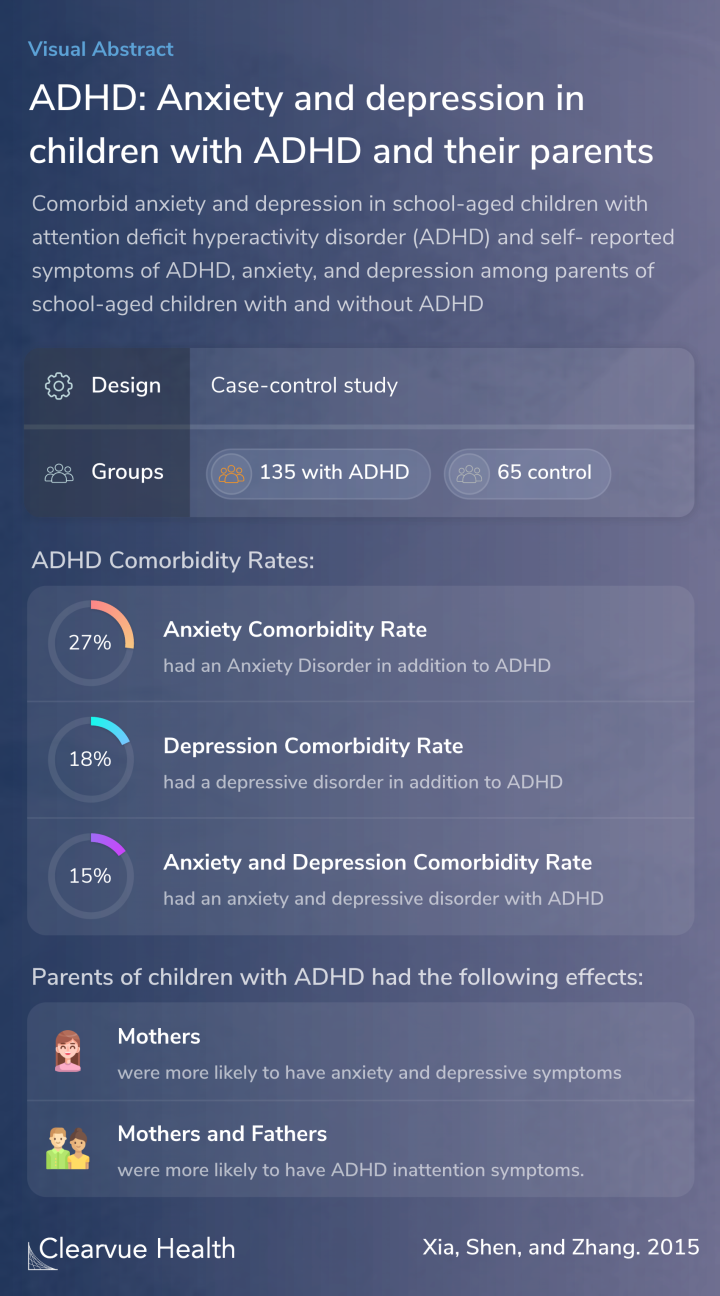
A two-stage screening process identified children 7-10 years of age with and without ADHD treated at the Xin Hua Hospital in Shanghai. ADHD and other DSM-IV diagnoses were determined by a senior clinician using the Schedule for Affective Disorder and Schizophrenia for School-Aged Childre...
Results
27% of the children in the study, who all had ADHD, also had an anxiety disorder. 18% had a depressive disorder, and 15% had both an anxiety and a depressive disorder.
These findings are similar to previous studies that have found higher rates of anxiety and depression in ADHD.
The parents of children with ADHD had higher rates of inattentive ADHD symptoms themselves.
Mothers of children with anxiety or depression also had higher rates of anxiety and depression. The severity of the symptoms in mothers was correlated with the severity of the symptoms in children.
Among the 135 children with ADHD, 27% had a comorbid anxiety disorder, 18% had a comorbid depressive disorder, and another 15% had both comorbid anxiety and depressive disorders. Parents of children with ADHD self-reported more severe ADHD inattention symptoms than parents of children wi...
Conclusion
This study provides further evidence that children with ADHD are more likely to have anxiety and depression.
The study also finds a curious link between ADHD symptoms in children and symptoms in parents. At least some of this link may be driven by genetics, but we will need more research to understand the driving factors behind this link fully.
School-aged children with ADHD commonly suffer from comorbid anxiety and depressive disorders, and the severity of these symptoms parallels the level of anxiety and depressive symptoms in their parents. Self-reported symptoms of ADHD are significantly more common in parents of children w...