Anxiety in young people with ADHD: clinical and self-report outcomes
Anxiety and ADHD in children
Tracey W Tsang , Michael R Kohn , Daryl Efron , Simon D Clarke , C Richard Clark , Christopher Lamb , Leanne M Williams
Objective
Anxiety and ADHD have been known to occur together frequently. There’s also been evidence that having anxiety can lead to differences in the effects of ADHD.
Researchers wanted to find how common anxiety was in young ADHD patients. They also want to gather information on how parents and the participants themselves perceived anxiety symptoms and the effects of anxiety.
(a) To determine the prevalence of comorbid anxiety disorder in ADHD, defined by diagnostic criteria and (b) to compare anxiety as reported by parents and participants with clinician assessment.
Method
This was a relatively simple study in which researchers asked parents and children to assess anxiety symptoms and ADHD symptoms in the subject for comparison.
All the participants were already diagnosed with ADHD. The researchers evaluated participants for anxiety disorders during the study.
Children with ADHD were assessed for comorbid anxiety disorder using the Anxiety Disorder Interview Schedule for Children. Parent report (Conners' Parent Rating Scale-Revised: Long version) and self-report (State-Trait Anxiety Inventory and Brain Resource Inventory for Screening Cases-Ch...
Results
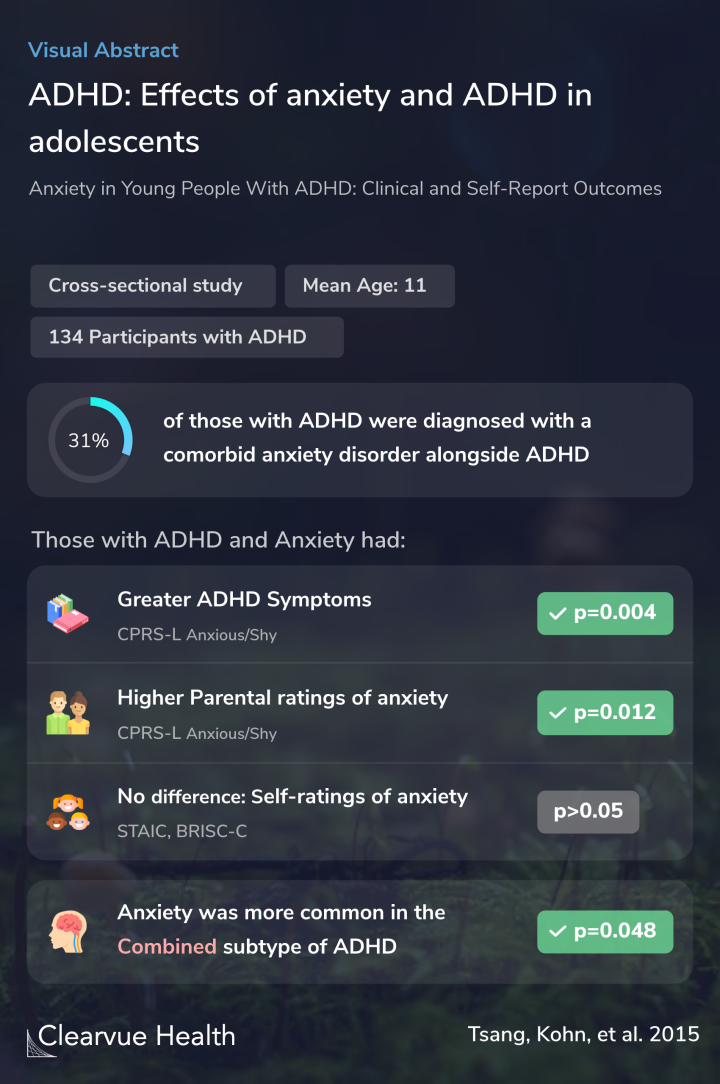
Overall, slightly fewer than a third of the participants had an anxiety disorder and ADHD.
The most common disorder found was generalized anxiety disorder, followed by Social Anxiety Disorder.
Those with ADHD and anxiety had significantly more severe ADHD symptoms than those with only ADHD.
The parent's ratings of their child’s anxiety symptoms generally correlated with their child’s anxiety disorder test results.
However, the children were not very good at detecting their anxiety symptoms. There’s no significant correlation between a child’s self-assessment of anxiety and their actual anxiety diagnosis.
Among the different subtypes of ADHD, those with the combined type were more likely to be diagnosed with an anxiety disorder.
The combined type of ADHD refers to children with persistent attention challenges and hyperactivity. This particular type has been associated with worse outcomes in other studies.
Of 134 participants (11.0 ± 2.6 years), 31.3% had comorbid anxiety disorder. Comorbid anxiety disorder was associated with greater severity of ADHD. Anxiety symptoms from parent reports (p < .05) but not from child/self-report (p > .05) correlated with clinician assessment.
Conclusion
This study highlights an additional challenge in assessing and treating ADHD. Consistent with previous studies, those with ADHD and anxiety show differences compared to those with anxiety alone. This study's data provides evidence that those with anxiety and ADHD have more severe ADHD symptoms.
The study also shows the importance of gathering information from parents when assessing children. The parents in the study knew their children better than their children knew themselves when it came to anxiety symptoms.
Assessment for comorbid anxiety disorder and inclusion of parent rating in this assessment are important components of ADHD treatment in children and adolescents.