Attention and executive functions profile in drug naive ADHD subtypes
ADHD's Impact on Executive Functions and Attention
Pasini A, Paloscia C, Alessandrelli R, Porfirio MC, Curatolo P
Objectives
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, or ADHD, is a condition often linked with difficulties in executive functioning, sustained attention, and the ability to divide attention among tasks. To shed light on this, the authors of the study investigated specific executive functions and attention deficit patterns across different clinical subtypes of ADHD.
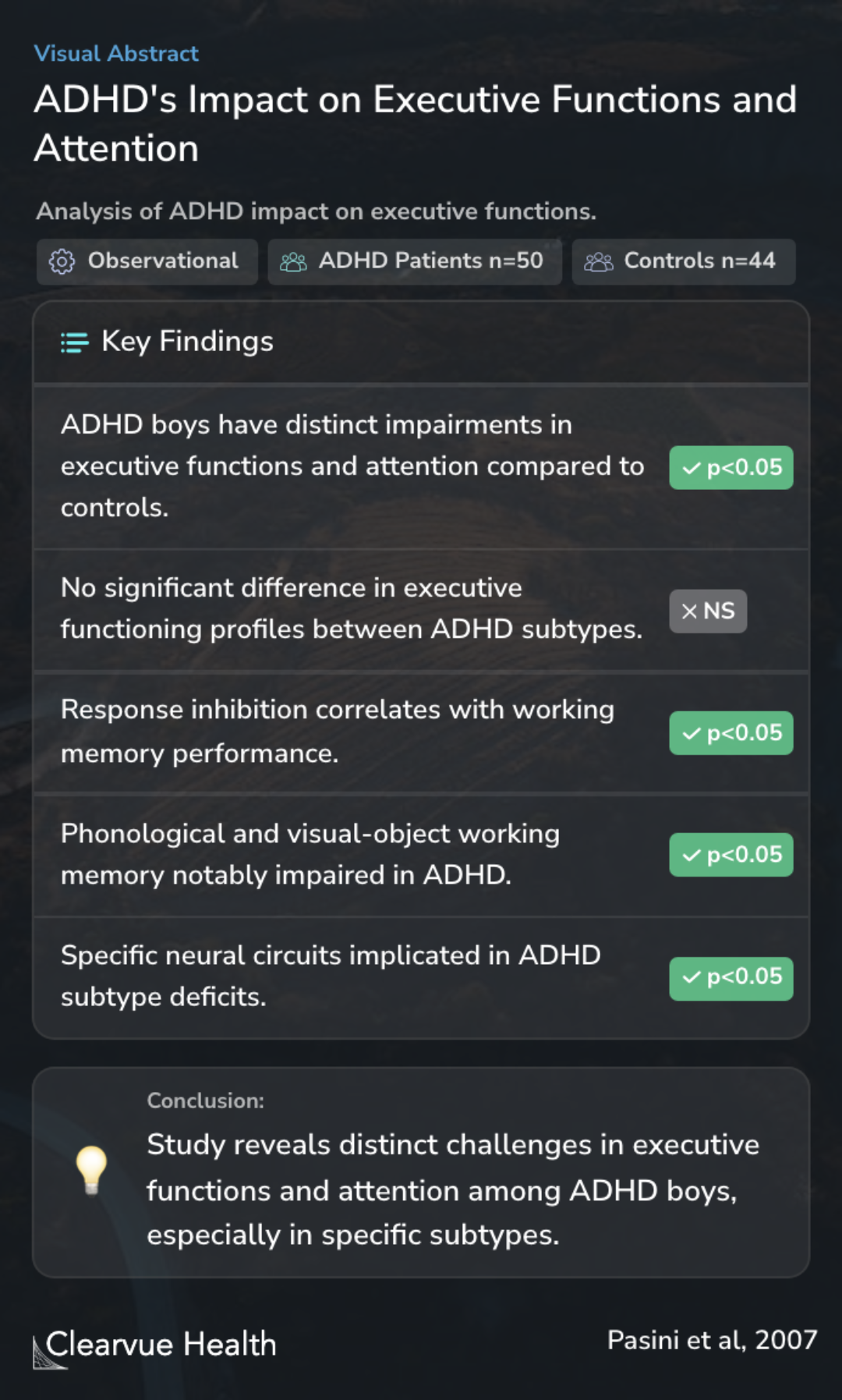
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) has been associated with executive functioning and sustained and divided attention deficits. In order to clarify the questions on neurocognitive impairment in ADHD, we investigated the presence of specific executive functions (EFs) and atte...
Methods
The study assessed 50 ADHD patients and 44 control subjects, all boys, using a comprehensive clinical-psychopathological and neuropsychological battery. This involved examining five key areas of executive functions and attention.
50 patients with ADHD and 44 controls were evaluated. All subjects were boys and performed a clinical-psychopathological and neuropsychological battery. Five main domains of EFs and attention were studied. Executive functions-related neurocognitive abilities were used as control tasks.
Results
The results revealed that boys with ADHD, particularly those with inattentive and combined subtypes, showed distinct challenges in areas such as response inhibition, divided attention, and working memory. This was measured using tasks like the Continuous Performance Test (CPT). Interestingly, when comparing different ADHD subtypes, the study found no significant differences in their executive functioning profiles. However, response inhibition was seen to correlate with working memory performance. This suggests that while ADHD boys face challenges in executive functions and attention tasks, these challenges do not vary significantly between ADHD subtypes.
ADHD patients, inattentive and combined subtypes differ from controls on response inhibition, divided attention, phonological, and visual object working memory and on variability of reaction times measured with CPT. Comparison of ADHD subtypes, in five main domains of EFs, did not show e...
Conclusions
The study concludes that boys with ADHD exhibit selective impairments in executive functions and attention tasks. This indicates the involvement of specific neural circuits in ADHD subtypes, particularly in phonological and visual-object working memory. These findings highlight the importance of understanding the unique challenges faced by boys with different ADHD subtypes.
ADHD boys exhibit a selective impairment on executive functions and attention tasks, suggesting the involvement of specific neural circuits in ADHD subtypes. The study also highlights the impairment in phonological and visual-object working memory as potential neuropsychological traits i...
Key Takeaways
Context
While this study focused on children, it is important to note that adults with ADHD often have different symptoms:
Furthermore, Barkley et al.'s 2010 research connected executive function with job performance, suggesting that self-management and time management skills, where individuals with ADHD may struggle, are crucial for success in the workplace: