Is adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder a valid diagnosis in the presence of high IQ?
ADHD in high IQ adults
K M Antshel , S V Faraone, K Maglione, A Doyle, R Fried, L Seidman, J Biederman
Objectives
Traditionally, ADHD has been associated with individuals who have trouble at school, or at work.
There is some controversy over whether highly intelligent individuals can have ADHD, particularly when it comes to college students. Some might ask if a student is performing well, can they have a learning disability?
The study aimed to validate ADHD among adults with high IQ and purported ADHD to see if high IQ adults with ADHD experience disability and challenges.
Because the diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in higher education settings is rapidly becoming a contentious issue, particularly among patients with high IQs, we sought to assess the validity of diagnosing ADHD in high-IQ adults and to further characterize the ...
Methods
Researchers define a high IQ as an IQ above 120. They recruited groups of high-IQ adults, including those with ADHD and those without ADHD, to see what differences they could find between the groups.
We operationalized high IQ as having a full-scale IQ120. We identified 53 adults with a high IQ who did not have ADHD and 64 adults with a high IQ who met diagnostic criteria for ADHD. Groups did not differ on IQ, socio-economic status or gender.
Results
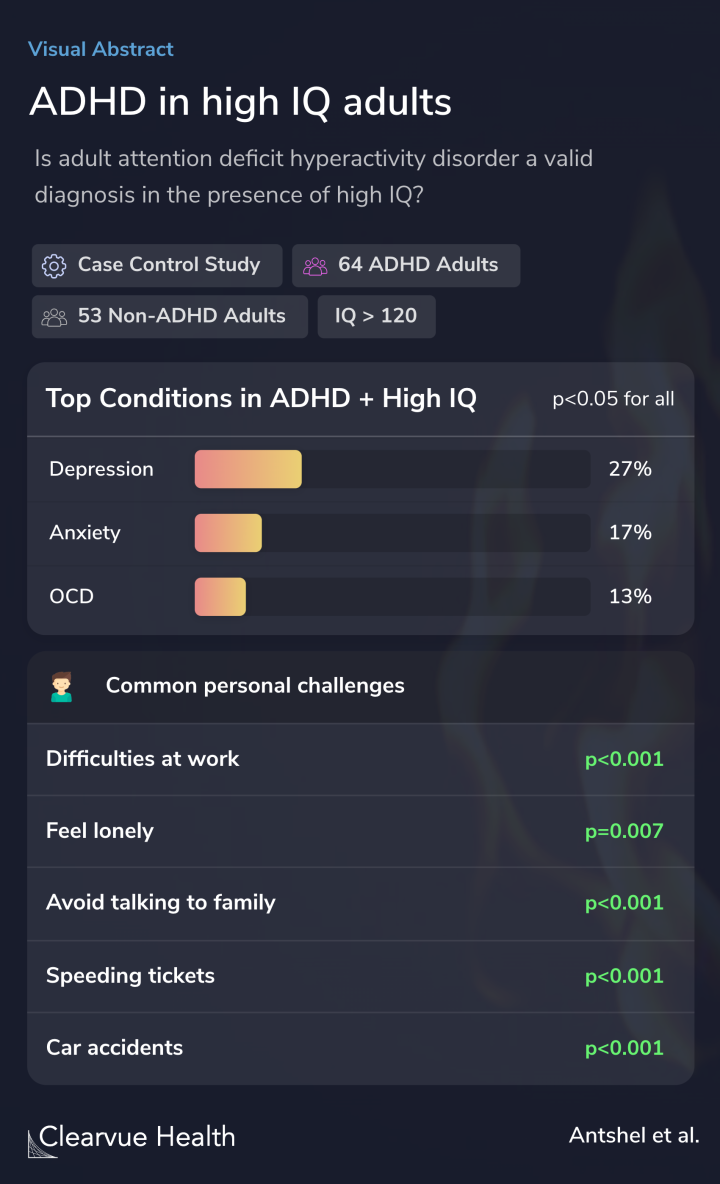
Across-the-board, adults with high IQ and ADHD reported a lower quality of life than those without ADHD.
They were likelier to have other psychiatric conditions, most commonly depression, anxiety, and OCD.
They also experienced significantly more challenges at home and work. Compared to those without ADHD, they were likelier to feel lonely, avoid talking to family, and underperform at work.
ADHD symptoms and high IQ
There are many symptoms that make up ADHD.
They are generally split up into challenges with attention and difficulties with hyperactivity.
For adults with high IQ, there were symptoms of all types. The symptoms below were found to be the most common.
Beyond just having symptoms and impact in their lives, those with ADHD and high IQ were also more likely to have family members with ADHD, suggesting that their ADHD also had a genetic component.
High-IQ adults with ADHD reported a lower quality of life, had poorer familial and occupational functioning, and had more functional impairments, including more speeding tickets, accidents and arrests. Major depressive disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder and generalized anxiety disor...
Conclusions
Based on the results, the author concluded that high-IQ individuals with ADHD have similar challenges as adults with ADHD in general.
They had impairments from ADHD, higher rates of psychiatric disorders, and a higher likelihood of having ADHD run in the family.
These factors support adult ADHD as a legitimate diagnosis and disorder in high-IQ adults.
Our data suggest that adults with ADHD and a high IQ display patterns of functional impairments, familiality and psychiatric co-morbidities that parallel those found in the average-IQ adult ADHD population.