Support for an independent familial segregation of executive and intelligence endophenotypes in ADHD families
ADHD Genetics, IQ, and Executive Function
N N J Rommelse , M E Altink, J Oosterlaan, C J M Buschgens, J Buitelaar, J A Sergeant
Objectives
While challenges with attention and hyperactivity define ADHD, ADHD is also associated with other deficits as well, including cognition and executive function.
Executive function encompasses the higher-level thought processes in your brain, including sustained attention and self-control. These are areas that those with ADHD can struggle with.
This study wanted to examine the links between executive function and IQ among those with ADHD.
Researchers recruited twins and families for this study to see how IQ and executive function play out within families and whether there is evidence of a genetic link.
Impairments in executive functioning (EF) and intelligence quotient (IQ) are frequently observed in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The aim of this paper was twofold: first, to examine whether both domains are viable endophenotypic candidates for ADHD and ...
Methods
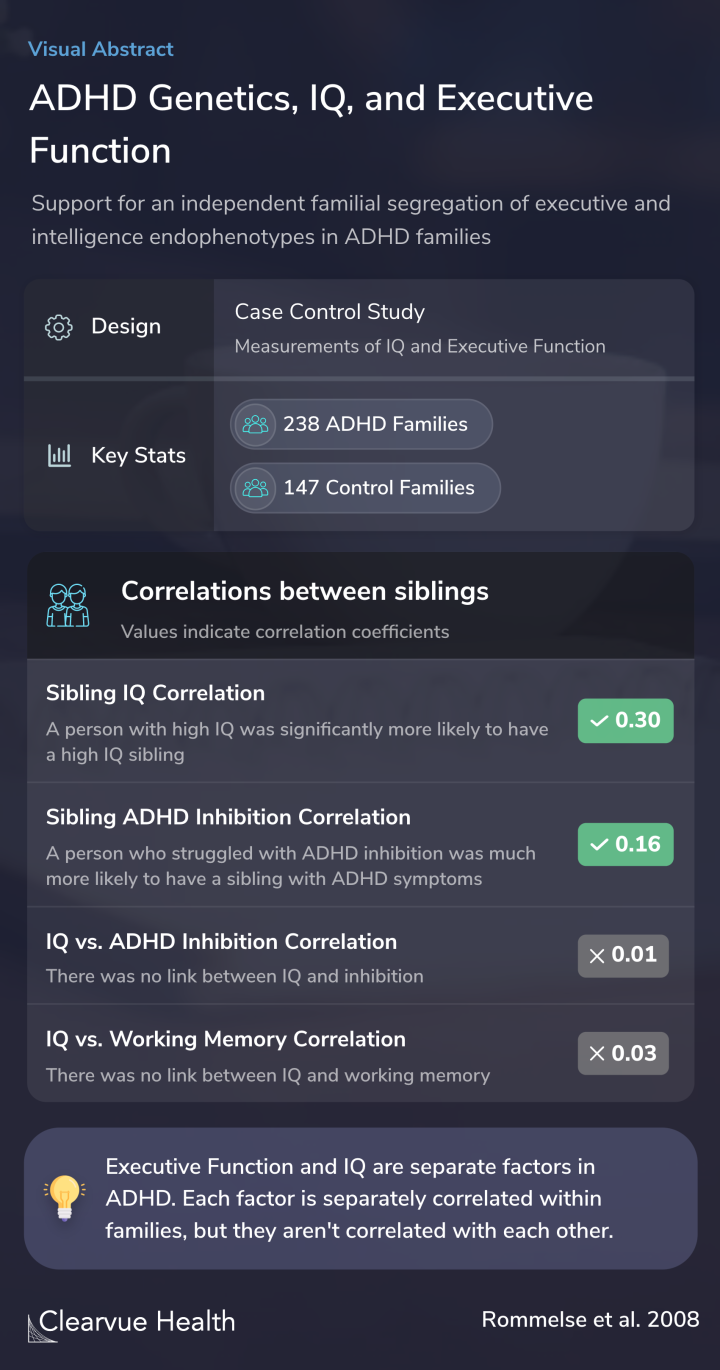
Researchers conducted a study on a group of 238 families with children with ADHD and a group of 147 families without ADHD as a comparison group.
Researchers conducted IQ and executive function tests on the participants and analyzed the data for statistical links.
A large family-based design was used, including 238 ADHD families (545 children) and 147 control families (271 children). Inhibition, visuospatial and verbal working memory, and performance and verbal IQ were analysed.
Results
Overall, researchers found that IQ was correlated between siblings. Having highly intelligent siblings increases the likelihood that a person is more intelligent. Similarly, there was a strong link in ADHD symptoms. Having siblings with ADHD increases the likelihood of having ADHD symptoms yourself.
However, there was no significant link found between IQ and ADHD. Having a sibling with ADHD or having ADHD did not lead to significant differences in IQ.
Using a sibling study, researchers could estimate how ADHD gets passed on through families.
There was a strong link in ADHD between siblings. Those with siblings with ADHD were more likely to have ADHD themselves. Even those who don’t have ADHD are more likely to experience ADHD symptoms if they have a sibling with ADHD.
Children with ADHD, and their affected and non-affected siblings were all impaired on the EF measures and verbal IQ (though unimpaired on performance IQ) and all measures correlated between siblings. Correlations and sibling cross-correlations were not significant between EF and IQ, thou...
Conclusions
Based on the study, researchers concluded that executive function and IQ are separate traits among those with ADHD. Just because someone has difficulty sustaining attention or using their working memory doesn’t mean someone has a lower IQ. Similarly, someone with a high IQ can still struggle with executive function.
Both of these factors are linked within families. Having siblings with difficulties increases the risk of having difficulties yourself. But, the two factors aren’t necessarily linked to each other.
The results supported the viability of EF and IQ as endophenotypic candidates for ADHD. Most findings support an independent familial segregation of both domains. Within EF, similar familial factors influenced inhibition and working memory. Within IQ, similar familial factors influenced ...