Prevalence of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in substance use disorder patients: A meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis
ADHD and substance use disorder prevalence
Katelijne van Emmerik-van Oortmerssen, Geurt van de Glind, Wim van den Brink, Filip Smit, Cleo L Crunelle, Marije Swets, Robert A Schoevers
Background
Previous studies have shown a link between substance use disorder and ADHD. ADHD can potentially affect the risk and the impact of addiction.
Those with ADHD are more likely to drink heavily and develop drinking disorders:
Researchers in the study aimed to use meta-analysis to estimate how frequently those with addiction also have ADHD.
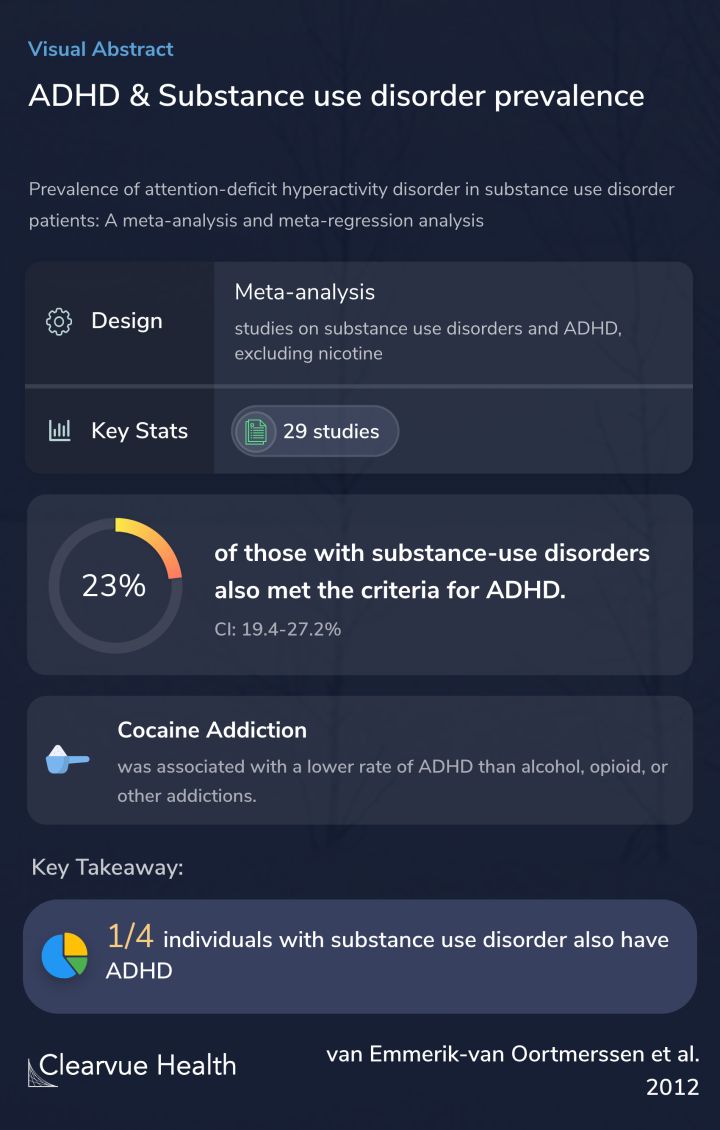
Context: Substance use disorders (SUD) are a major public health problem. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a comorbid condition associated with both onset and prognosis of SUD. Prevalence estimates of ADHD in SUD vary significantly.
Methods
Researchers collected studies that contained data on ADHD and addiction. They excluded data on nicotine addiction and smoking.
They ended up with 29 studies, from which they extracted the data and ran a meta-analysis.
Data sources: A literature search was conducted using MEDLINE, PsycINFO and EMBASE. Search terms were ADHD, substance-related disorders, addiction, drug abuse, drug dependence, alcohol abuse, alcoholism, comorbidity, and prevalence. Results were limited to the English language.
Results
Overall, slightly fewer than a quarter of individuals with substance use disorders in the 29 studies had ADHD.
Researchers looked at age, gender, ethnicity, timeframe, and setting to see whether these factors affected ADHD rates.
The rate of ADHD in those struggling with addiction is surprisingly stable at 23%, irrespective of most factors studied.
The main notable difference they found in the study was substance type.
Those addicted to cocaine had a lower rate of ADHD than those addicted to alcohol or opioids.
Data synthesis: Overall, 23.1% (CI: 19.4-27.2%) of all SUD subjects met DSM-criteria for comorbid ADHD. Cocaine dependence was associated with lower ADHD prevalence than alcohol dependence, opioid dependence and other addictions. Studies using the DICA or the SADS-L for the diagnosis of ...
It is not entirely clear why those with cocaine addiction have lower rates of ADHD compared to other substances.
One theory the authors suggested is that those with ADHD may be more likely to self-medicate with substances that calm them, such as alcohol and opioids.
Given the significant overlap between substance use disorder and ADHD, the results offer a compelling reason to study further how we can better treat ADHD and addiction together. ADHD treatments should be considered part of a comprehensive treatment strategy, especially for those who suffer from addiction due to self-medicating their ADHD symptoms.
These results are consistent with other studies that have found higher rates of substance use disorders among those with ADHD: