Evidence for higher reaction time variability for children with ADHD on a range of cognitive tasks including reward and event rate manipulations
ADHD and Response Time Variability
Jeffery N Epstein , Joshua M Langberg , Paul J Rosen , Amanda Graham , Megan E Narad , Tanya N Antonini , William B Brinkman , Tanya Froehlich , John O Simon , Mekibib Altaye
Objectives
ADHD has been linked to cognitive challenges in addition to its effects on attention and hyperactivity.
One of the most robust links has been with reaction time variability. On cognitive tests, those with ADHD tend to have a broader range of response times. Those with ADHD can take much longer to respond to some questions while taking less time for others.
This study wanted to examine whether this phenomenon was consistent across different tests. They also wanted to see whether the ADHD subtype and different test scenarios affected reaction time variability.
The purpose of the research study was to examine the manifestation of variability in reaction times (RT) in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and to examine whether RT variability presented differently across a variety of neuropsychological tasks, was present ...
Methods
This study compared children with ADHD and matched controls without ADHD on several standardized tasks designed to test reaction time variability under different conditions.
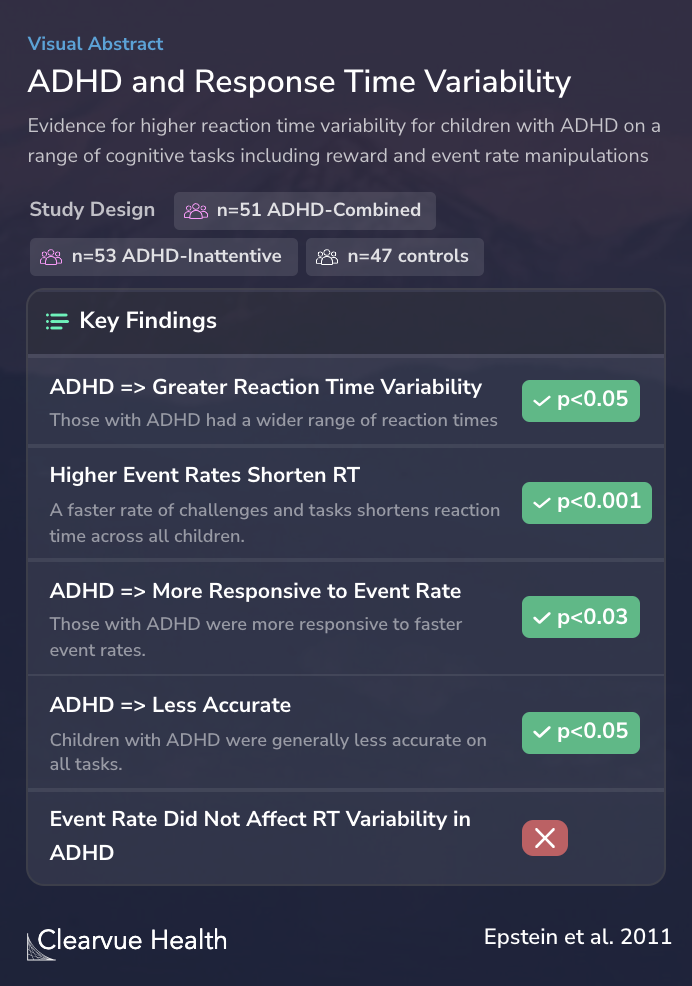
Children with ADHD-combined type (n = 51), ADHD-predominantly inattentive type (n = 53), and 47 controls completed five neuropsychological tasks (Choice Discrimination Task, Child Attentional Network Task, Go/No-Go task, Stop Signal Task, and N-back task), each allowing trial-by-trial as...
Results
The results showed that children with ADHD had much more variability in the response times than children without ADHD.
Those with ADHD had a wider range of response times on various tests covering working memory, attention, and response inhibition.
These results suggest that response time variability is a core effect of ADHD, consistent with previous studies on response time.
The results also showed that higher event rates tended to reduce response times for those with ADHD but did not reduce variability in response times.
Children with ADHD demonstrated greater RT variability than controls across all five tasks as measured by the ex-Gaussian indicator tau. There were minimal differences in RT variability across the ADHD subtypes. Children with ADHD also had poorer task accuracy than controls across all ta...
Conclusions
Researchers concluded that response time variability is vital to ADHD based on its effects across different tests and conditions.
High RT variability is a ubiquitous and robust phenomenon in children with ADHD.