Reaction time distribution analysis of neuropsychological performance in an ADHD sample
ADHD and Reaction Time Distribution
Aaron S Hervey , Jeffery N Epstein, John F Curry, Simon Tonev, L Eugene Arnold, C Keith Conners, Stephen P Hinshaw, James M Swanson, Lily Hechtman
Objectives
The study wanted to dive deeper into the link between ADHD and reaction time variability. One of the most significant cognitive deficits found in those with ADHD has been reaction time variability. This refers to the fact that those with ADHD often have a wider range of reaction times.
Differences in reaction time (RT) variability have been documented between children with and without Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Most previous research has utilized estimates of normal distributions to examine variability.
Methods
The study used a case-control method to compare children with ADHD and children without ADHD on reaction time tests. Researchers used a unique analytical approach that allowed them to gather more information about this effect.
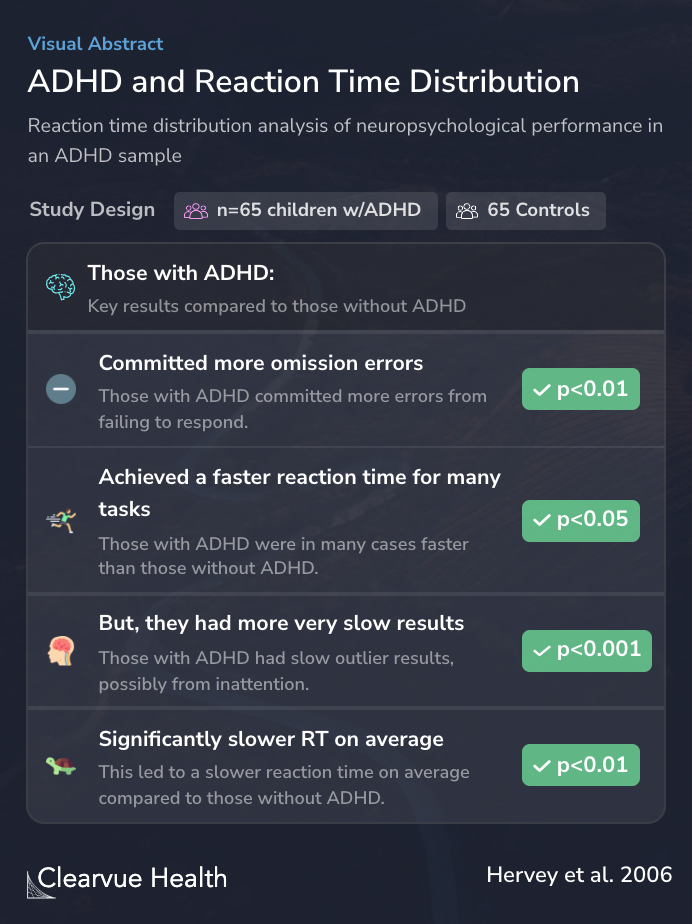
Using a nontraditional approach, the present study evaluated RT distributions on the Conners' Continuous Performance Test in children and adolescents from the Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD sample compared to a matched sample of normal controls (n = 65 pairs). The ex-Gaussian curve w...
Results
The results showed that those with ADHD weren’t necessarily slower. But, they often had a few prolonged responses that skewed the results.
One possible explanation is that those with ADHD can lose focus and take longer to respond to certain questions due to inattention.
In fact, in some cases, those with ADHD were even faster than those without ADHD. But, because of a few questions where they took longer to respond, those with ADHD generally had slower average response times. They also had more questions where they failed to respond.
Children with ADHD demonstrated faster RT associated with the normal portion of the curve and a greater proportion of abnormally slow responses associated with the exponential portion of the curve.
Conclusions
These findings show a key difference between those with ADHD and those without ADHD. It isn’t so much the response time but rather the pattern of response times that differentiates those with ADHD.
These are likely because children may lose focus on attention on some problems, causing them to fail to respond or take unusually long to respond.
These results are consistent with other studies that have linked ADHD with wider ranges of reaction times.
These results contradict previous interpretation that children with ADHD have slower than normal responding and demonstrate why slower RT is found when estimates of variability assume normal Gaussian distributions. Further, results of this study suggest that the greater number of abnorma...